37-11
Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide
OL-10088-01
Chapter 37 Configuring WebVPN
Getting Started with WebVPN
An example POST request—with host HTTP header and body—follows:
POST
/emco/myemco/authc/forms/MCOlogin.fcc?TYPE=33554433&REALMOID=06-000430e1-7443-125c-ac05-83
846dc90034&GUID=&SMAUTHREASON=0&METHOD=GET&SMAGENTNAME=$SM$5FZmjnk3DRNwNjk2KcqVCFbIrNT9%2b
J0H0KPshFtg6rB1UV2PxkHqLw%3d%3d&TARGET=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com%2Femco%2Fmyemco%2F
HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.com
(BODY)
SMENC=ISO-8859-1&SMLOCALE=US-EN&USERID=Anyuser&USER_PASSWORD=XXXXXX&target=https%3A%2F%2Fw
ww.example.com%2Femco%2Fmyemco%2F&smauthreason=0
Step 4 Examine the POST request and copy the protocol, host, and the complete URL to configure the action-uri
parameter.
Step 5 Examine the POST request body and copy the following:
a. Username parameter. In the preceding example, this parameter is USERID, not the value anyuser.
b. Password parameter. In the preceding example, this parameter is USER_PASSWORD.
c. Hidden parameter. This parameter is everything in the POST body except the username and
password parameters. In the preceding example, the hidden parameter is:
SMENC=ISO-8859-1&SMLOCALE=US-EN&target=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com%2Fe
mco%2Fmyemco%2F&smauthreason=0
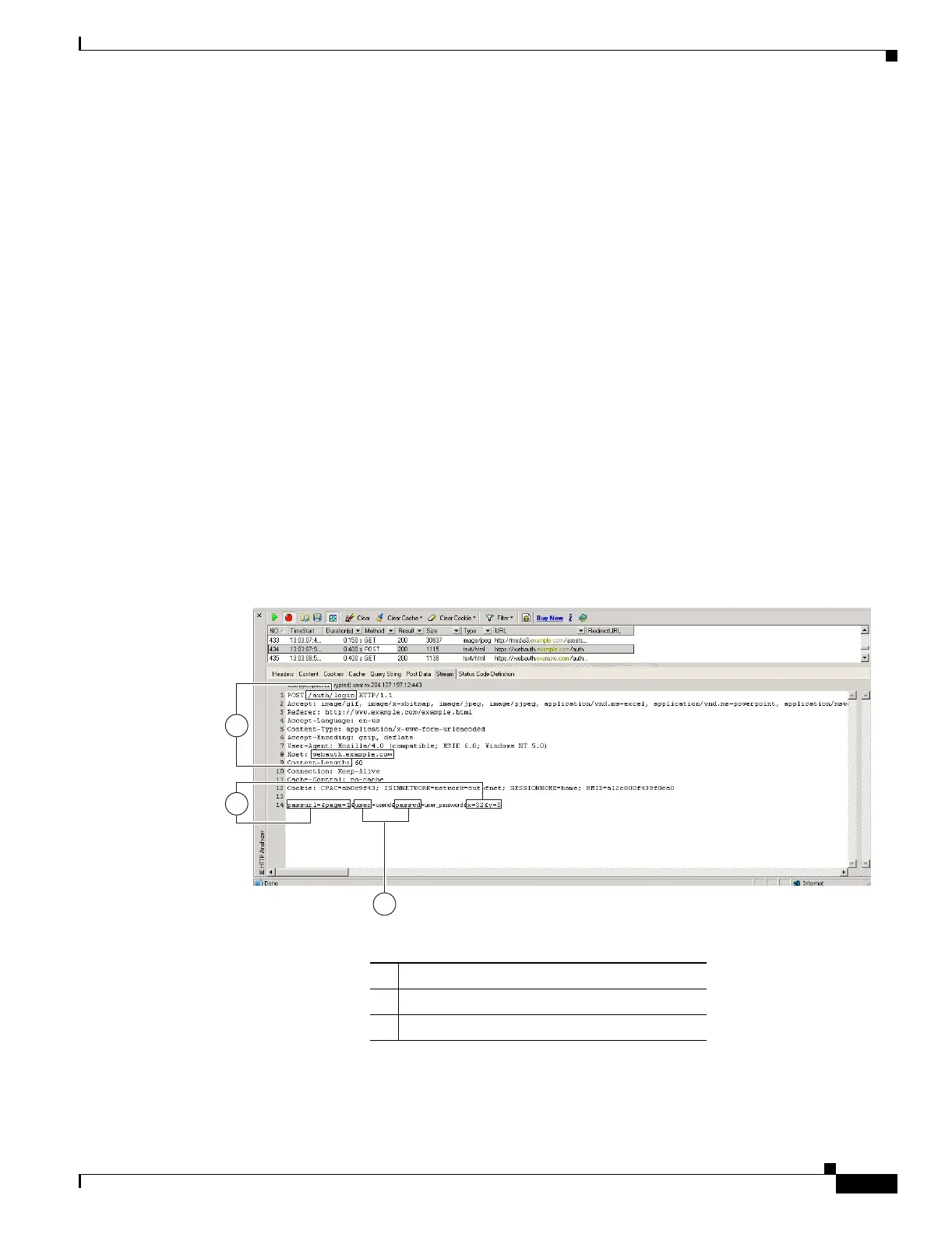
Figure 37-2 highlights the action URI, hidden, username and password parameters within sample output
from an HTTP analyzer. This is only an example; output varies widely across different websites.
Figure 37-2 Action-uri, hidden, username and password parameters
Step 6
If you successfully log in to the web server, examine the server response with the HTTP header analyzer
to locate the name of the session cookie set by the server in your browser. This is the auth-cookie-name
parameter.
148849
1
2
3
1 Action URI parameter
2 Hidden parameters
3 Username and password parameters

 Loading...
Loading...











