Issue Number: 3 27
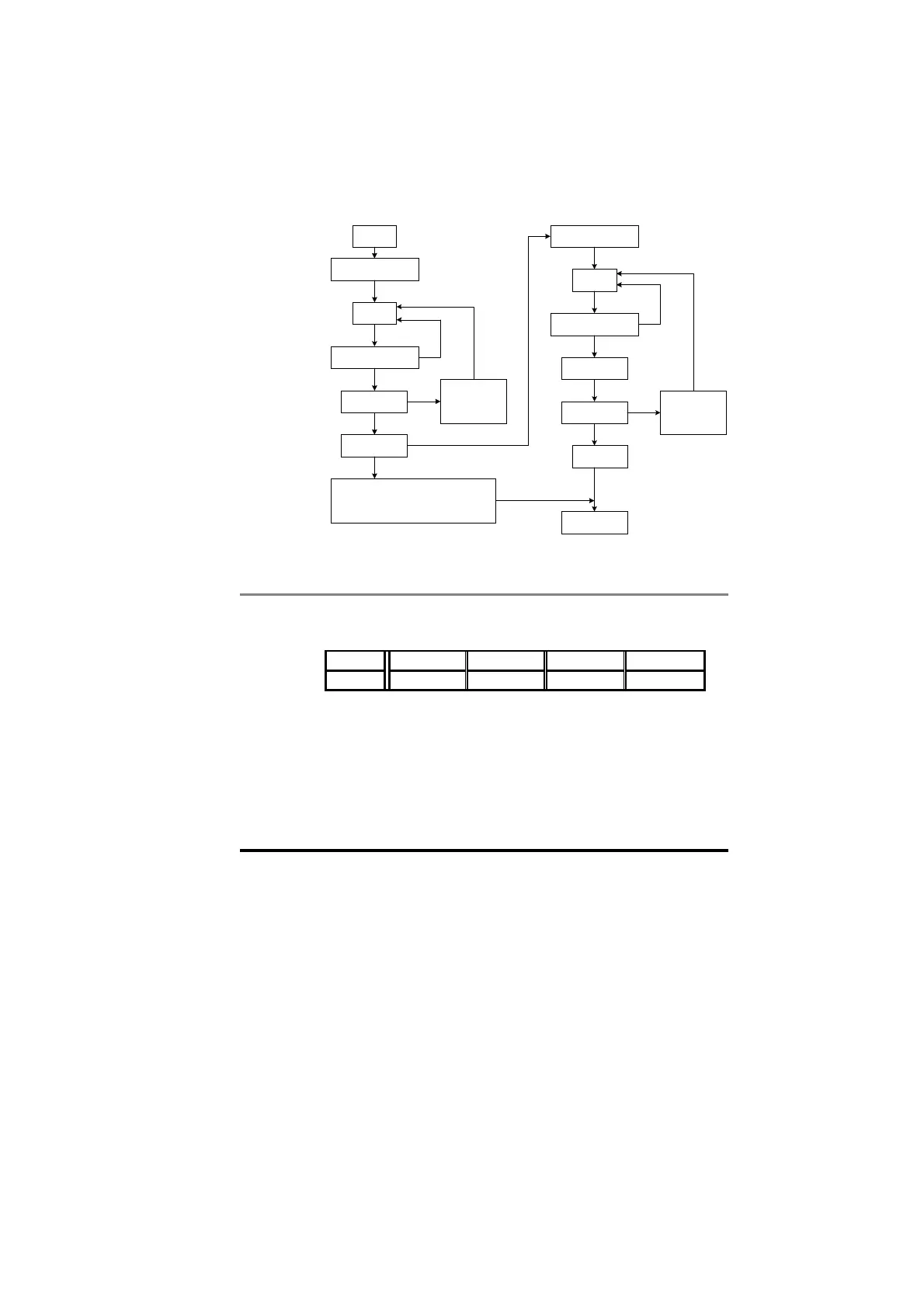
6.1.1 Reading parameters using Mode 1
To read parameters using the non-cyclic channel, the following
“telegrams” must be transmitted to construct the final message.
• Telegram 1 Define menu number.
• Telegram 2 Define parameter number.
• Telegram 3 Request high data byte.
• Telegram 4 Request low data byte.
READ
Start
Send first telegram
to OUT word 0
Read IN
word 0
Tx_Stamp_No =
Rx_Stamp_No?
Send next
telegram to
OUT word 0
Tx_Stamp_No
= 2?
No
Yes
Check status
of ERR bit
1
0
ERROR. Check paramter exists, data
is in correct range, and parameter is
Read/Write
Calculate
data value
END OF
SEQUENCE
Read IN
word 0
Tx_Stamp_No =
Rx_Stamp_No?
Send next
telegram to
OUT word 0
Tx_Stamp_No
= 4?
No
Yes
Send telegram 3 to
OUT word 0
Store data
byte
Yes
No
Yes
No
The following example telegrams show how to read the data value from
#3.02 in the Unidrive.
TELEGRAM 1
The first telegram from the master indicates a READ cycle, and the
stamp number is 1. The data byte would contain the menu number for
the parameter that is to be read.
Bit b15-b12 b11-b8 b7-b4 b3-b0
Value 1XXX 0001 0000 0011
Data word = 0x8103 Stamp number = 1 Menu = 3
When the first telegram has been received and processed in the slave
node, it is mirrored in the non-cyclic IN word back to the PLC. This is
the signal to the master controller program that the first telegram of the
message has been received and understood, and the second telegram
can be transmitted.
 Loading...
Loading...