Delem
V0208, 2.3
2.b
The following adjustment procedure can be followed to set the parameters to correct values.
Changes in the settings should be checked by moving the axis from one position to another.
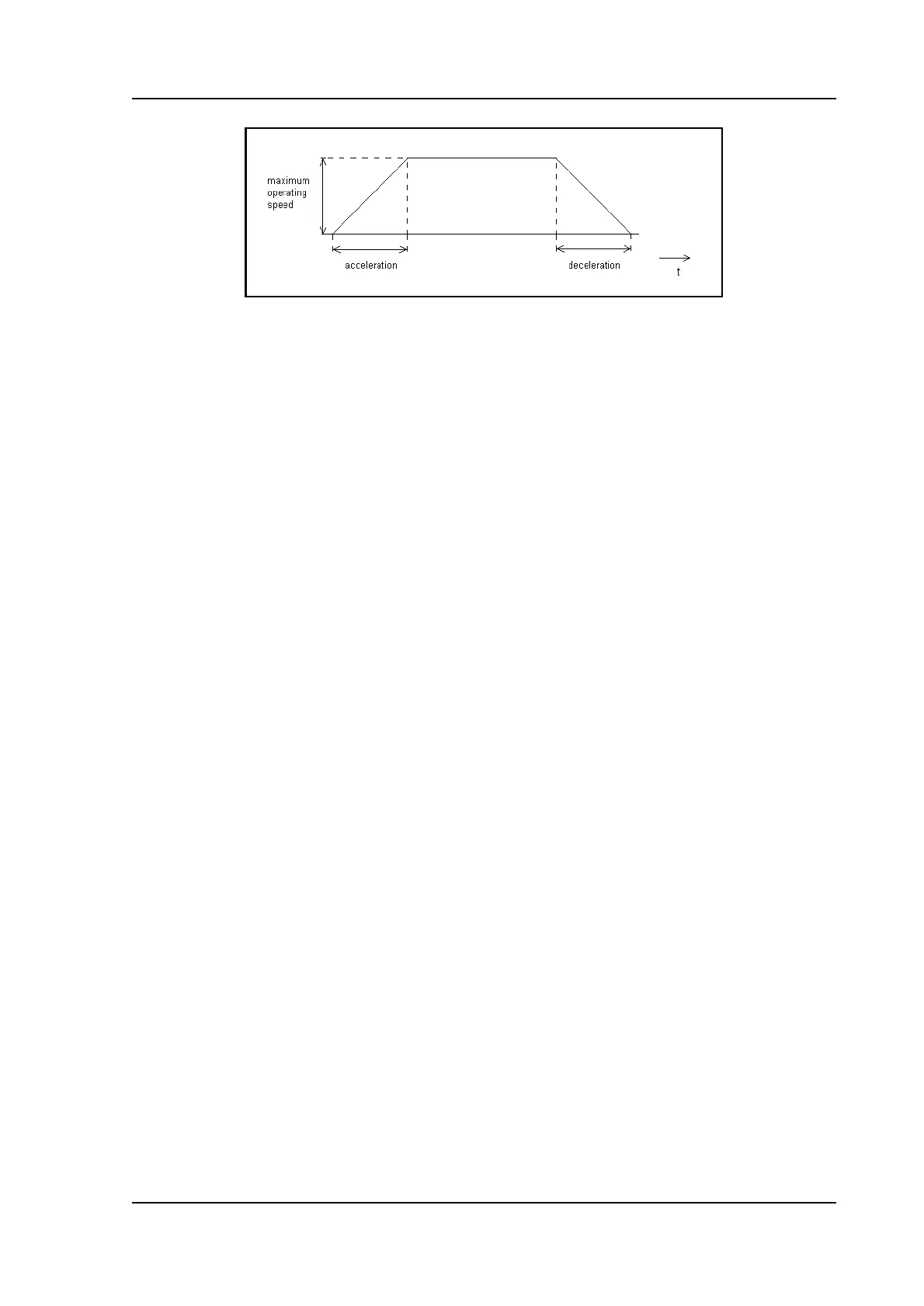
This stroke should be large enough, so that the axis will reach its maximum speed.
• Set the standard machine parameters, like minimum value, maximum value, scale
factor etc., to the correct values.
• Set the maximum operating speed to the correct value. This is the speed of the axis, in
mm/s, when the output of the module to the motor amplifier is 10V. If required the speed
can be set to a lower value.
• Set the acceleration and deceleration ramp parameters to safe values, for example
500ms or more. Of course these values depend on the actual combination of motor,
motordrive and load.
• Set the gain parameters to safe default values, for example:
• P-gain = 2.50
•I-gain = 1
• Increase the P-gain until you notice oscillation during the movement and especially at
the end position. Reduce the P-gain again to the point where there was no oscillation.
• Increase the I-gain until you notice oscillation at the end position. Reduce the I-gain
again to the point where there was no oscillation.
• Optimise the acceleration and deceleration times. Reduce these times until you find an
optimal compromise between a fast and smooth movement. If one of these values is set
too small, it will lead to irregular behaviour of the axis during acceleration or
deceleration.
1.2.2. AC drive
In this paragraph, the parameters for axes with AC drives are discussed.
When using AC drives, it is possible to program 1-side positioning or 2-side positioning.
Beside this, it must be indicated whether a one-speed or 2-speed motor drive is used.
With these parameters you can optimize the positioning accuracy of the AC-axis:
• Brake point high speed (BHS)
• Brake point low speed (BLS)
• Overrun (OR)
• Overrun wait time
• Stop time (T)
• DC low speed
• DC high speed
• AC-brake enable
For the movement control of the axis there are two possibilities:
• two, three or four digital outputs of the module;
 Loading...
Loading...