Application Examples ASDA Series Application Note
3-66 March, 2015
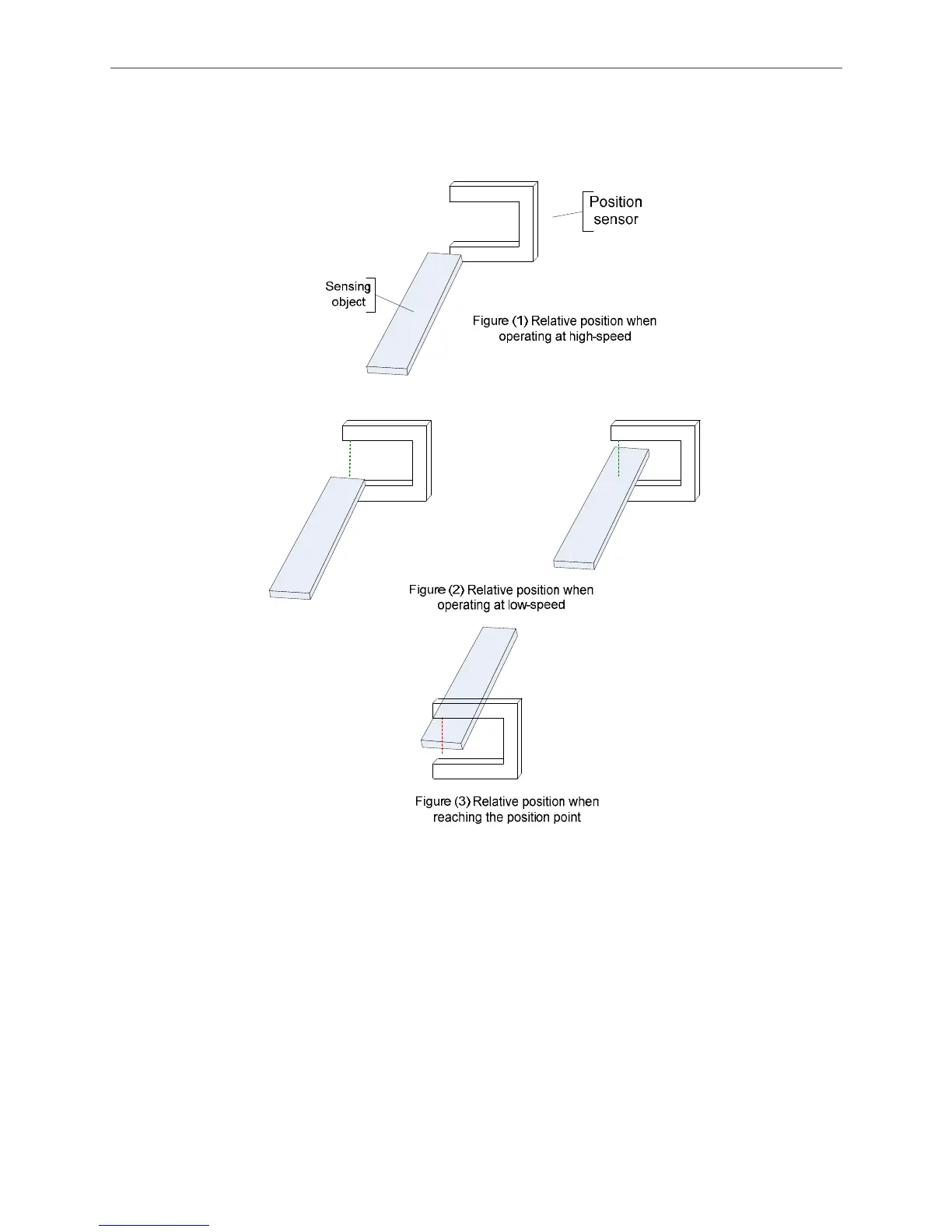
Figure 3.5.3 demonstrates the relative position between the sensing object and the position
sensor. This is an example of a grooved-type photoelectric sensor.
Figure 3.5.3 The Relative Position of the Position Sensor and Sensing Object
Figure 3.5.4 demonstrates the status before positioning. If position deviation between two axes
has been existed, one of the axes will arrive at the low-speed zone earlier than the other. When
any of the axes reaches the low-speed zone, the entire system will operate at low speed. Due to
the deviation, the axis entering the low-speed zone first will reach the positioning point earlier.
See the example shown in figure 3.5.4, Axis 1 that reaches the positioning point first will stop and
waits for Axis 2 to arrive. After both two axes reach the positioning point, both axes can then
move forward (or backward) at the same time and look for Z pulse as the homing origin.
Positioning point can also be regarded as homing origin. It is determined by different applications
and demands.

 Loading...
Loading...











