5 Categories and Use of Basic Application Instructions
DVP-PM Application Manual 5-9
Equation
()
127;.121 =××−
−
BM
BE
S
Therefore, the range of 32-bit floating point value is from ±2
-126
to
±2
+128
, i.e. from ±1.1755×10
-38
to
±3.4028×10
+38
Example 1:
Represent “23” in 32-bit floating point value
Step 1: Convert “23” into a binary value: 23.0 = 10111
Step 2: Normalize the binary value: 10111 = 1.0111 × 24, in which 0111 is mantissa and 4 is exponent.
Step 3: Obtain the exponent: ∵ E – B = 4 Æ E – 127 = 4 ∴ E = 131 = 10000011
2
Step 4: Combine the sign bit, exponent and mantissa into a floating point
0 10000011 01110000000000000000000
2
= 41B80000
16
Example 2:
Represent “-23.0” in 32-bit floating point value
The steps required are the same as those in Example 1 and only differs in modifying the sign bit into “1”.
1 10000011 01110000000000000000000
2
=C1B80000
16
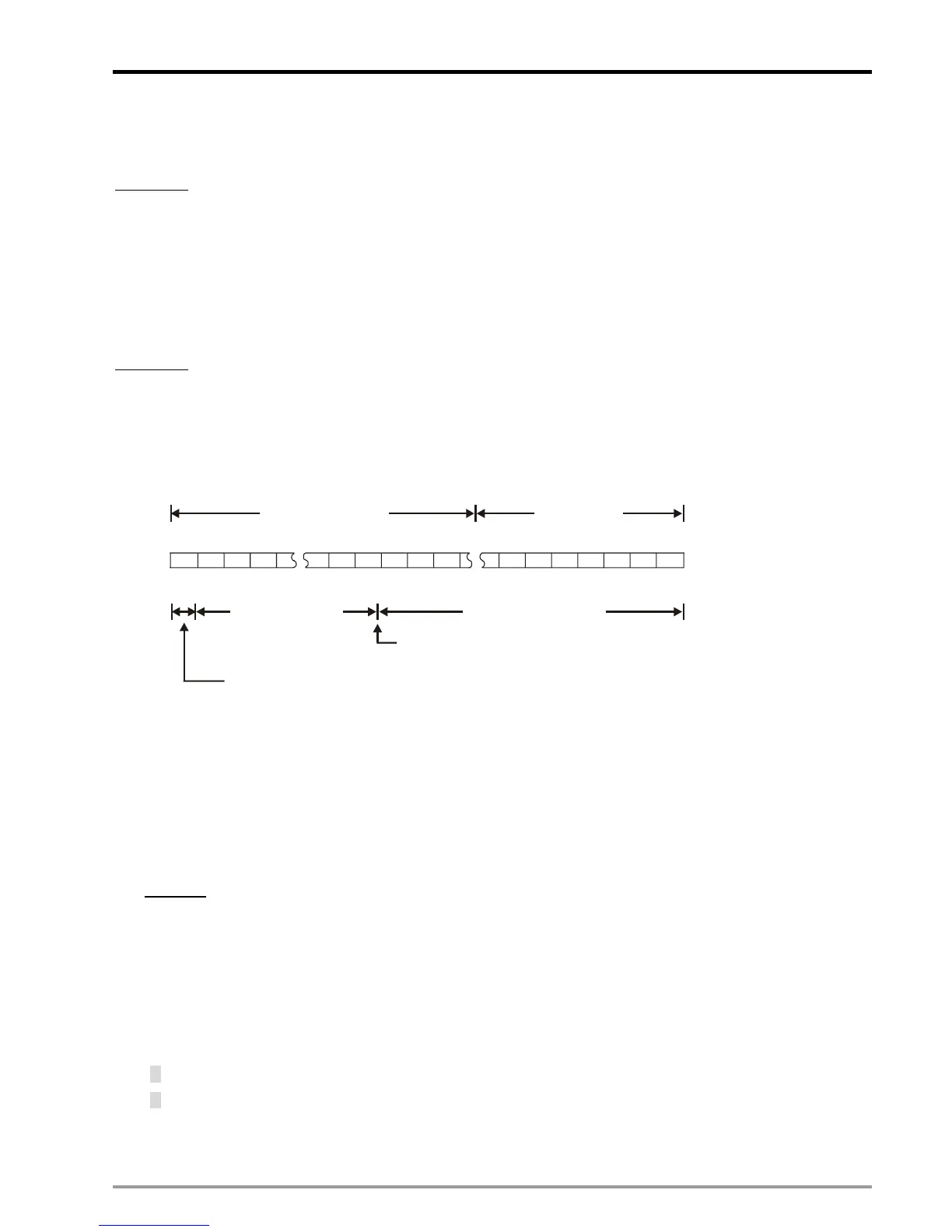
DVP-PM uses registers of 2 continuous No. to store a 32-bit floating point value. For example, we use registers
(D1, D0) for storing a binary floating point value as below:
S E7 E6 E5 E1 E0 A22 A21 A20 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
b0b1b2b3b4b5b6b20b21b22b23b24b28b29b30b31
2 22 222 22 2 222 222
7 6 5 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -17 -18 -19 -20 -21 -22 -23
D1(b15~b0) D0(b15~b0)
8 bits of exponent
23 bits of mantissa
Sign bit (0: positive 1: negative)
When b0~b31 is 0, the content is 0.
Hidden decimal point
Decimal Floating Point
Since the binary floating point value is not very user-friendly, we can convert it into a decimal floating point value
for use. However, the floating point operation in DVP-PM is still operated in binary floating point format..
The decimal floating point is represented by 2 continuous registers. The register of smaller number is for the
constant while the register of bigger number is for the exponent.
Example:
Store a decimal floating point in registers (D1, D0)
Decimal floating point = [constant D0] x 10
[exponent D1]
Constant D0 = ±1,000 ~ ±9,999
Exponent D1 = -41 ~ +35
Note: The constant 100 does not exist in D0 because 100 is represented as 1,000 × 10
-1
. The range of
decimal floating point is ±1175 × 10
-41
~ ±3402×10
+35
..
The decimal floating point value can be used in the following instructions:
DEBCD: Convert binary floating point into decimal floating point
DEBIN: Convert decimal floating point into binary floating point
In O100 ~ M102 main programs, the execution result will affect the status of M1968 ~ M1970 when using
ADD/SUB/MUL/DIV instructions. Zero flag (M1968), borrow flag (M1970) and carry flag (M1969) will also be

 Loading...
Loading...