5 Categories and Use of Basic Application Instructions
DVP-PM Application Manual 5-29
API Mnemonic Operands Function
14
D CML P
Compliment
Controllers
20PM 10PM
Bit Devices Word devices Program Steps
Type
OP
X Y M S K H KnX KnY KnM KnS T C D E F
S
** * * * * * * ***
D
* * * * * ***
CML, CMLP: 5 steps
DCML, DCMLP: 9 steps
Operands:
S: Source of data D: Destination device
Explanations:
1. The instruction reverses the bit pattern (0→1, 1→0) of all the contents in S and sends the contents to D.
2. When CML is used as 16-bit instruction, Z device cannot be adopted; when CML is used as 32-bit instruction,
V device cannot be adopted.
3. When specifying the bit device of KnX(Y/M/S), the starting No. should be a multiple of 16 in octal or decimal
format. For example, K1X0, K4Y20 (octal); K1M0, K4S16 (decimal).
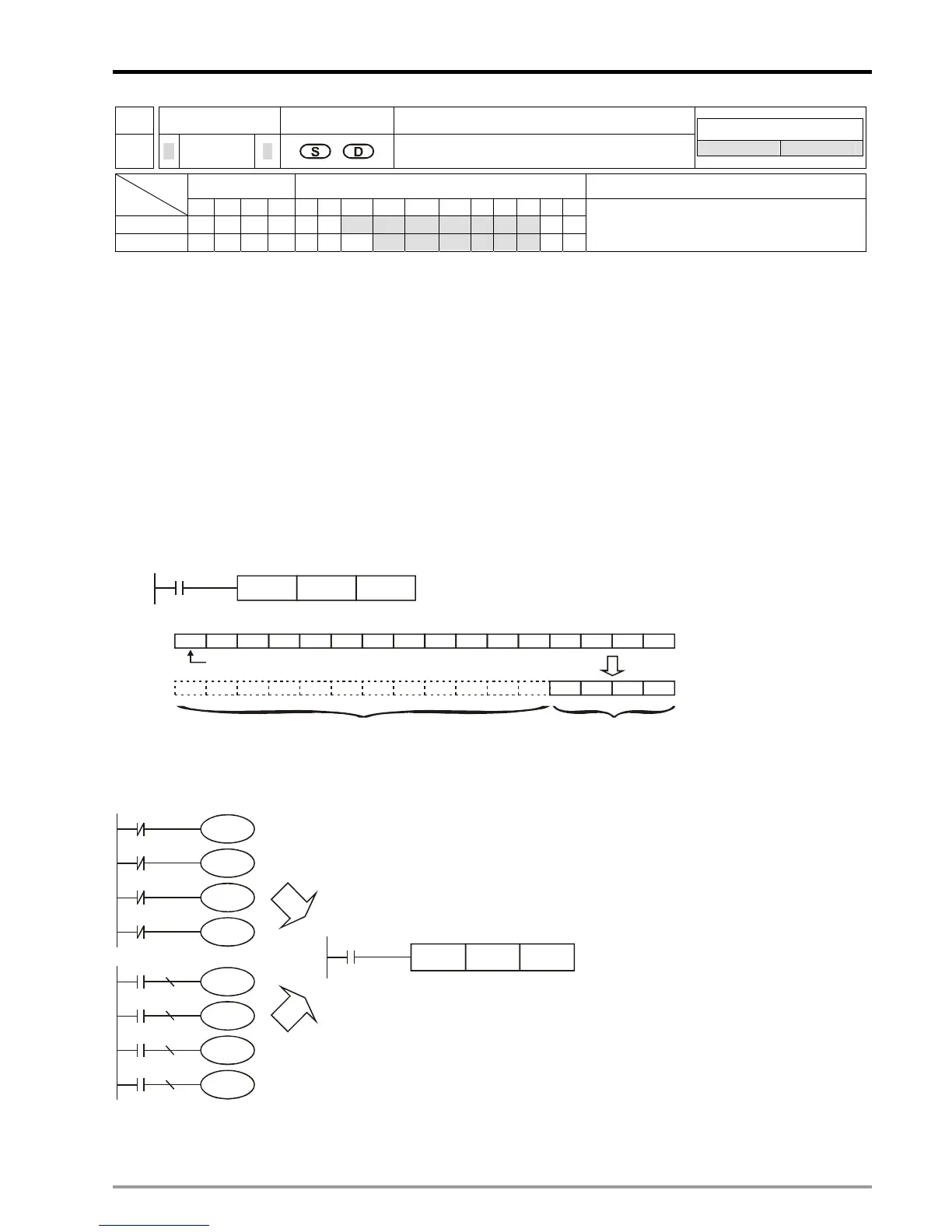
Program example 1:
When X10 = ON, b0 ~ b3 in D1 will be inverted and sent to Y0 ~ Y3
X20
CML K1Y0D1
b0b1b2b3b15
D1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Symbol bit 0=positive, 1=negative) (
0
1
0
1
No variation Transfer data
Program example 2:
The diagram below can be substituted by the instruction on the right.
X000
M0
M1
M2
M3
X001
X002
X003
X000
M0
M1
M2
M3
X001
X002
X003
M1000
CML K1X0 K1M0
Normally ON contact

 Loading...
Loading...