29
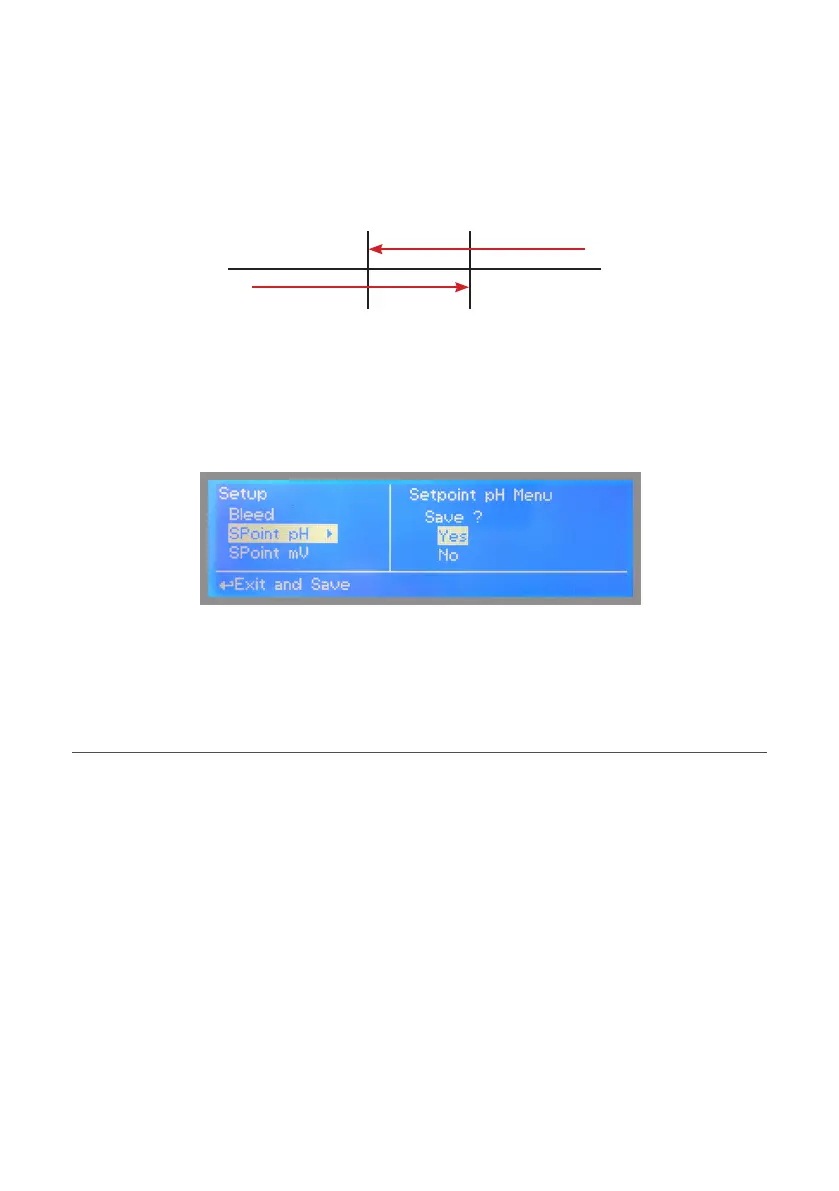
“Set-Point pH” (on/off) mode ACID
This mode is valid for “Digital D1” output. ON/OFF mode while dosing ACID
Set pH value at 7.00 OFF and 7.10 ON. Set Pulse Speed per minute (strokes per minute) based on dosing device capabilities.
Instrument will leave the pH pump active until reading value will decrease up to 7.00pH
At 7.00pH the pH pump will be disabled until reading value will increase up to 7.10pH.
To end procedure move cursor on “OK” and press wheel to proceed to “Save” request screen. Move wheel on “YES” to
save or “NO” to discard changes.
Did you know ?
In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal element. Alkalis are best known for
being bases (compounds with pH greater than 7) that dissolve in water. The adjective alkaline is commonly used in English
as a synonym for base, especially for soluble bases. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because
alkalis were the rst bases known to obey the Arrhenius denition of a base and are still among the more common bases.
Since Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory, the term alkali in chemistry is normally restricted to those salts containing alkali
and alkaline earth metal elements.
An acid (often represented by the generic formula HA [H+A−]) is traditionally considered any chemical compound that,
when dissolved in water, gives a solution with a hydrogen ion activity greater than in pure water, i.e. a pH less than 7.0.
That approximates the modern denition of Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Martin Lowry, who independently dened an
acid as a compound which donates a hydrogen ion (H+) to another compound (called a base). Common examples include
acetic acid (in vinegar) and sulfuric acid (used in car batteries). Acid/base systems are different from redox reactions in
that there is no change in oxidation state.
7.00 7.10
ON
OFF

 Loading...
Loading...