IP Series Installation Manual Function 3: Extension programming
F.1
Function 3: Extension programming
This section provides programming for extensions and department groups.
Important: Where any gray shading (■) appears in an example, it represents values either
unavailable to the function or unused in the particular example.
Function 31: Extension definition and routing
Extensions can be either of the following:
• IP Feature Phone extensions (IP PHONE in the chart below and succeeding charts) — These are
numbered with extensions between 100 and 195, inclusive, and may be either local phones or
remote phones.
• Analog ports (ANALOG in the same charts) — These are numbered with extensions between 200
and 229, inclusive, and are dependent on the port card to which they are attached — i.e., the
first 303 port card will host extensions 200, 201 and 202, while the second 303 hosts exten-
sions 203, 204 and 205 — and so on.
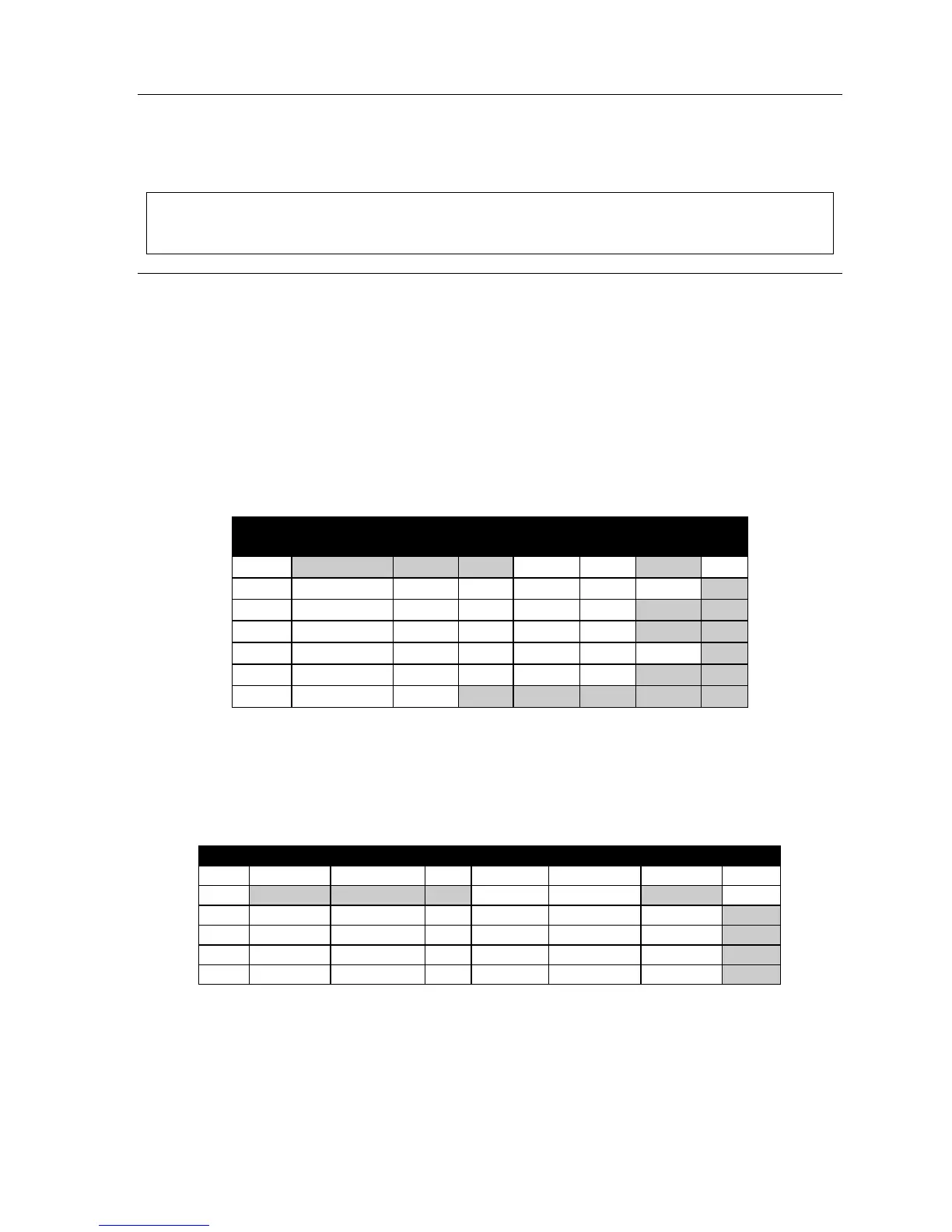
Below is an example of the portion of a completed programming worksheet (Appendix II).
Ext Type Name Line
groups
CF day CF
night
Pg zone Ext
0
Operator
X100 X100
X100
100 Local IP Jane 9 MB100 X105 0,1,2
101 Remote IP Roger 9 MB101 MB101
102 Remote IP Sally 9,8 MB102 MB102
109 Local IP Dean 9,8 MB109 MB109 0, 2
200 Analog Roger 2 9 MB110 MB106
201 Fax Fax
Note:
Extension 100 defaults as OPR (when a user dials 0) and is an example of system default.
Local IP Feature Phones
Below is an example of the portion of a completed programming worksheet (Appendix II) for local
IP Feature Phones.
1.
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Ext Type Name CO CF day CF night Pg zone Ext
0 Operator X100 X100 X100
100 Local IP Jane 9 MB100 X105 0, 1, 2
105 Local IP Carl 9 MB105 MB105 0, 2
113 Local IP Maria 9,8 MB113 MB100 0, 1
109 Local IP Dean 9,8 MB109 MB109 0, 2
Note:
Extension 100 defaults as OPR (when a user dials 0) and is an example of system default.

 Loading...
Loading...