Configuring the FortiGate unit Planning the FortiGate configuration
FortiGate-200, FortiGate-300, FortiGate-400, FortiGate-500 and FortiGate-1000 FortiOS 3.0 MR4 Install Guide
01-30004-0267-20070215 33
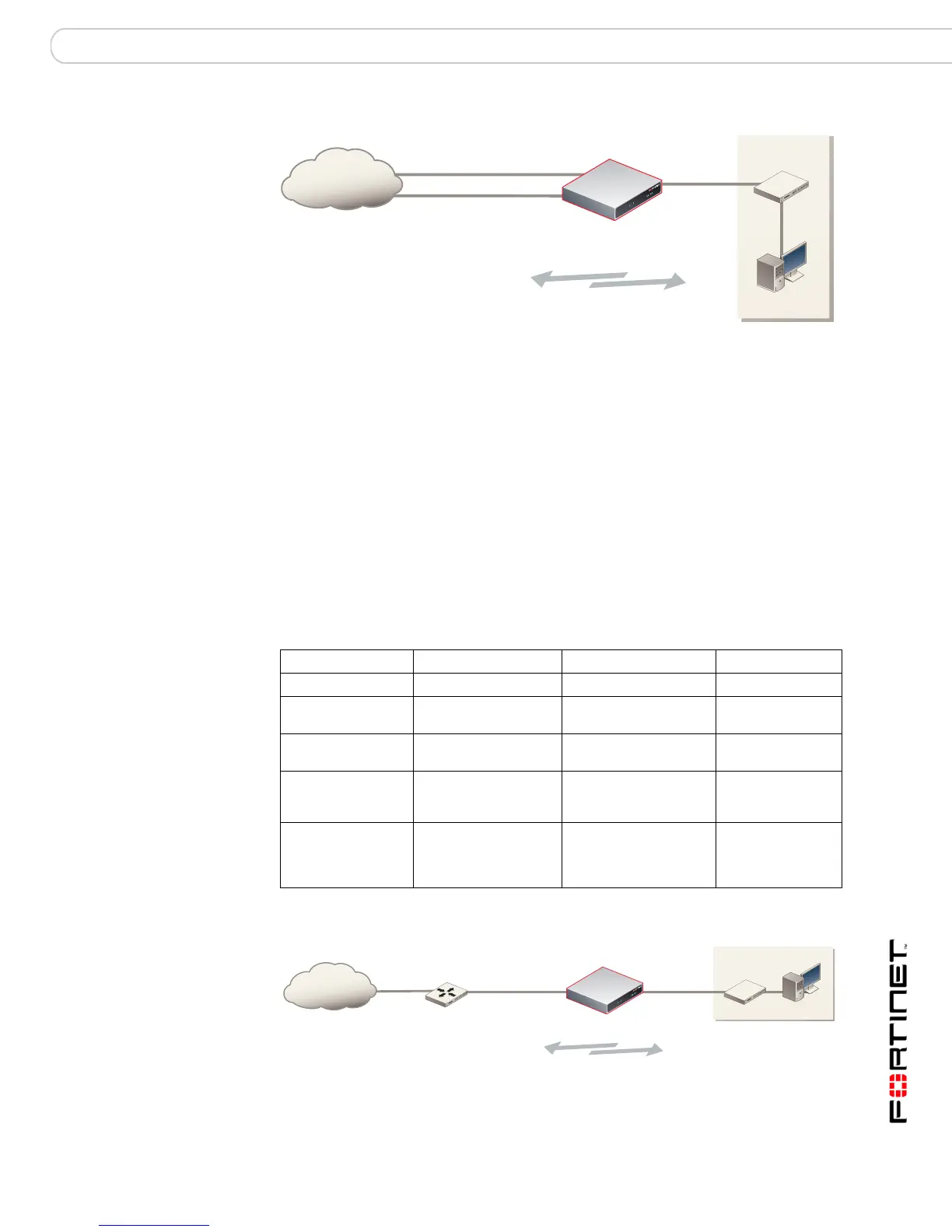
Figure 10: NAT/Route multiple internet connection for a FortiGate-300.
Transparent mode
In Transparent mode, the FortiGate unit is invisible to the network. Similar to a
network bridge, all FortiGate interfaces must be on the same subnet. You only
have to configure a management IP address so that you can make configuration
changes. The management IP address is also used for antivirus and attack
definition updates.
You typically use the FortiGate unit in Transparent mode on a private network
behind an existing firewall or behind a router. The FortiGate unit performs firewall
functions, IPSec VPN, virus scanning, IPS web filtering, and Spam filtering.
You can connect several network segments to the FortiGate unit to control traffic
between these network segments. Depending on the FortiGate unit, you can
connect up to twelve network segments.
Table 13: Transparent mode network segments
Figure 11: Example Transparent mode configuration for a FortiGate-500.
FortiGate-300 unit
in NAT/Route mode
Internet
Internal
network
192.168.1.3
NAT policies controlling
traffic between internal
and external networks.
External
204.23.1.5
DMZ
64.83.32.45
Internal
FortiGate Unit Internal Interface External Interface Other
FortiGate-200 Internal External DMZ
FortiGate-300 Internal External DMZ
HA
FortiGate-400 Port 1 Port 2 Port 3
Port 4/HA
FortiGate-500 Internal External DMZ
HA
Ports 1 to 8
FortiGate-1000 Internal External Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4/HA
FortiGate-500 unit
in Transparent mode
Internet
Router
10.10.10.1
Management IP
Internal
Internal Network
10.10.10.3
External
Gateway to public network
204.23.1.5 10.10.10.2
Policies controlling traffic between
internal and external networks.

 Loading...
Loading...











