Part number 550-142-950/0122
39
FreeStyle
®
series
2
wall mount gas-fired water boiler – boiler manual
18 Primary/Secondary System Piping
Figure 49 Maximum and minimum ow rates through
boiler heat exchanger
System water piping methods
Primary/secondary piping to boiler
Using primary/secondary piping will provide the most ecient
and reliable operation of the boiler and the heating system.
1. Use information beginning on this page to size pump for
proper ow through the boiler.
2. Reference suggested piping layouts on pages 40-45.
System water piping methods
Near boiler piping
1. Connect boiler to system only as shown in Figure51,page40.
e primary/secondary piping shown ensures the boiler loop
will have sucient ow.
2. Install a system circulator or zone circulators as shown in the
piping diagrams in the Primary/Secondary System Piping
section in this manual. ese circulators must be supplied
by the installer.
System or zone circulators ow rates
1. Size circulators based on the ow rate required to achieve the
temperature drop required. You can closely estimate temper-
ature rise (or drop) through a circuit by using the following
formula, where TD is temperature rise (or drop), FLOW is
ow rate (in gpm), and BTUH is the heat load for the circuit:
FLOW =
BTUH
—–—–—–—–
TD x 500
Examples:
1. Consider a system loop for a system with total heating load
equal to 143,000 Btuh. e desired temperature drop through
the system piping is 20°F. en the required ow rate is:
FLOW =
143,000
—–—–—–—–
20 x 500
= 14 gpm
SIMPLIFIED:
For 20° temperature drop, FLOW = MBH / 10.
System or zone circulator head requirement
1. e circulator must be capable of delivering the required
ow against the head loss that will occur in the piping.
2. Determine the pipe size needed and the resultant head
loss using accepted engineering methods.
Boiler
Model
MAX
Flow Rate
20° F
temperature
rise
GPM
MIN
Flow Rate
50° F
temperature
rise
GPM
Flow Rate
Delta T1
protection
67° F
temperature
rise
GPM
FS-80 7.9 2.9 2.3
FS-120 12.0 4.3 3.4
FS-155 15.2 6.1 4.5
Expansion Tank Location
Figure51,page40show typical installation of the system expansion
tank. It is highly recommended that you locate the air separator
and expansion tank as shown in the suggested piping drawings
on pages 39 - 41.
Ensure that the expansion tank size will handle boiler and system
water volume and temperature. See tank manufacturer’s instruc-
tions and ratings for details. Additional tanks may be added to
the system if needed to handle the expansion. ese tanks may be
installed by connecting to tees in the system piping.
Undersized expansion tanks cause system water to
be lost from the relief valve and makeup water to be
added through the ll valve. Eventual boiler failure
can result due to excessive make-up water addition.
Always locate the cold-water ll connection at the
expansion tank. Never locate this elsewhere.
Diaphragm- or bladder-type tank:
Refer to Figure 51, page40 for suggested piping when using a
diaphragm- or bladder-type expansion tank.
Diaphragm- or bladder-type expansion tank—
Always check pressure and charge tank with tank
removed from system to be sure reading is accu-
rate. Boiler relief valve is set for 30 PSIG. Operat-
ing pressure of system, aer temperature expansion
above cold ll pressure, should not exceed 24 PSIG
to avoid weeping of relief valve.
Install an automatic air vent on top of the air separator, per separa-
tor manufacturer’s instructions.
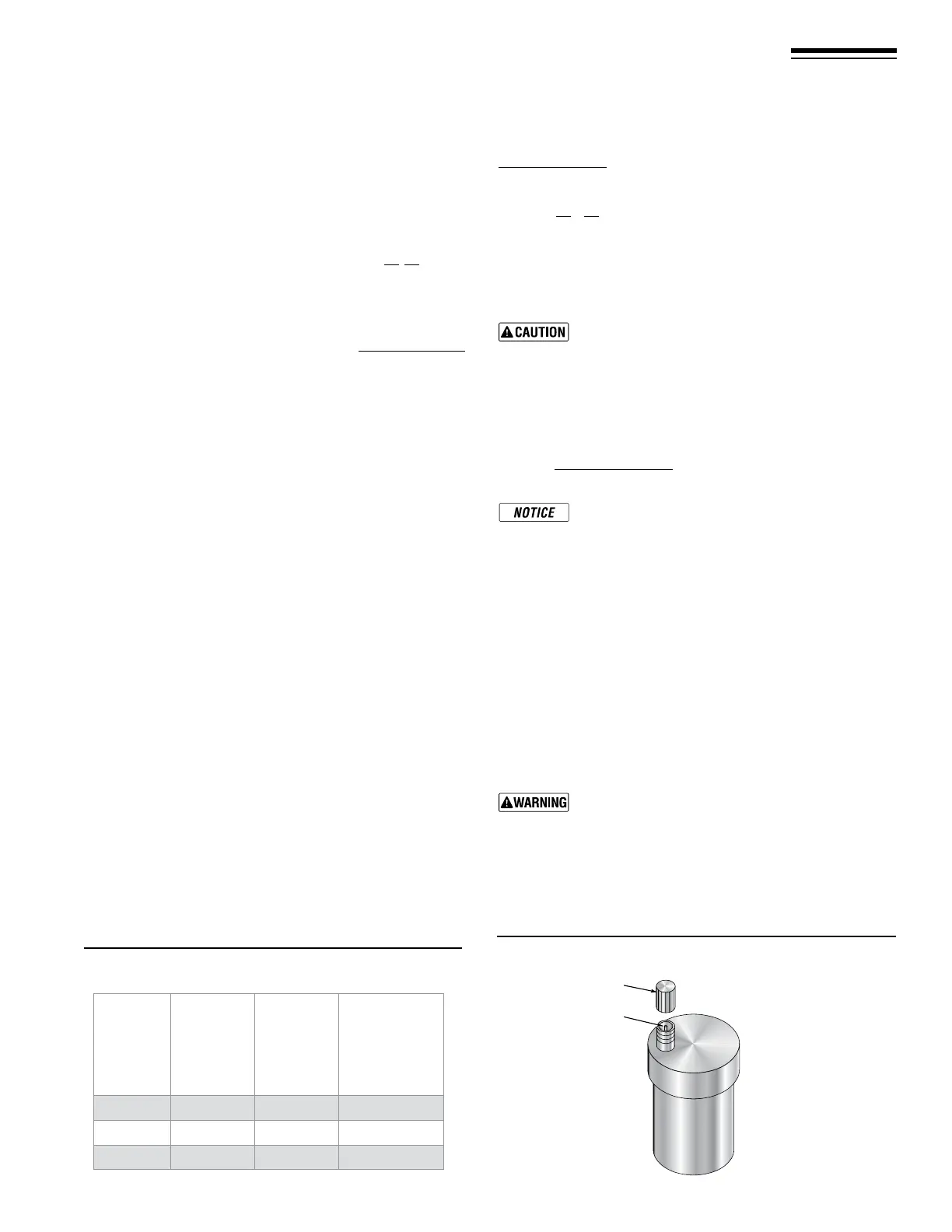
Automatic air vents (if used — automatic air
vents must be used with diaghragm-type expansion
tanks only)
1. Remove the cap from any automatic air vent in the system
and check operation by depressing valve “B” slightly with the
tip of a screwdriver.
Scald hazard — Water from air vent may be very
hot. Avoid contact to prevent possible severe per-
sonal injury.
2. If the air vent valve appears to be working freely and not leak-
ing, replace cap “A”, twisting all the way on.
3. Loosen cap “A” one turn to allow vent to operate.
4. Have vent replaced if it does not operate correctly.
Figure 50 Automatic air vent

 Loading...
Loading...