CHAPTER 4: Advanced Hardware Setup
38
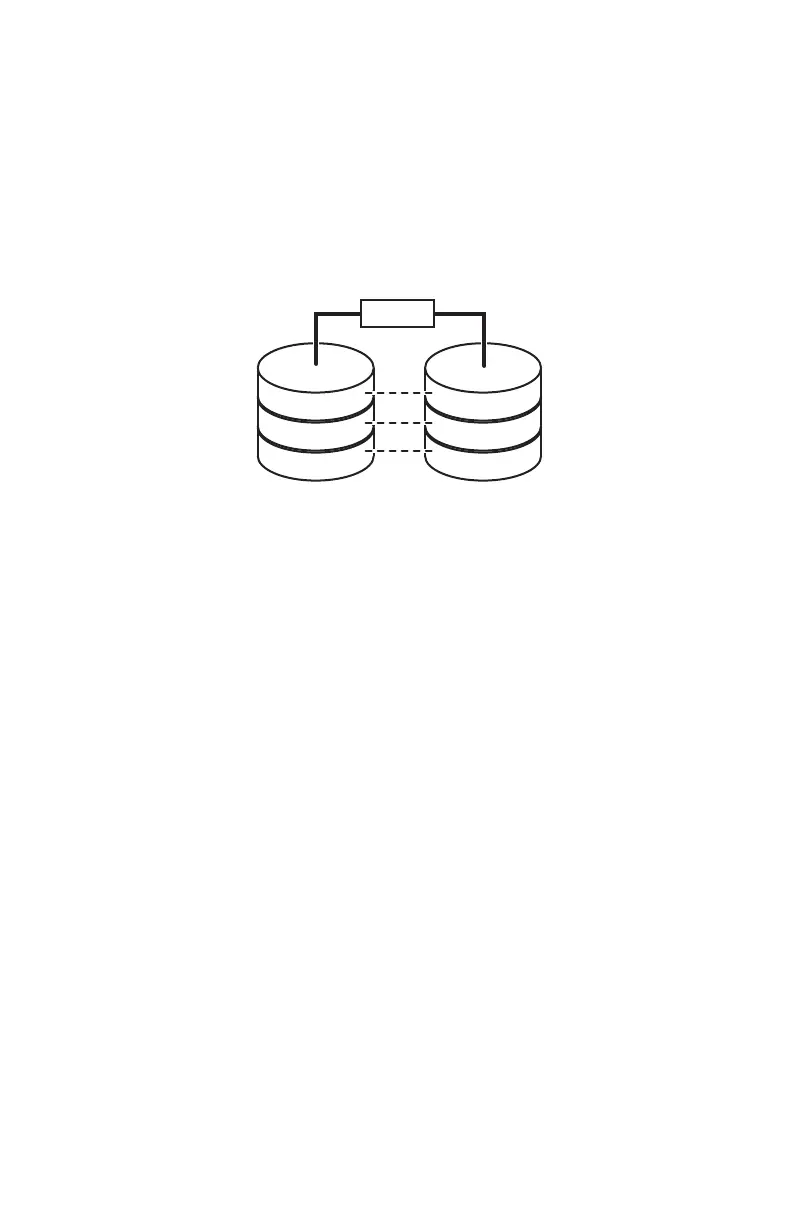
RAID 1 for security
RAID 1 maintains a complete copy of all files on each physical
hard drive in the array. Maintaining simultaneous, complete
copies of files across multiple hard drives is called mirroring.
If a drive fails, the mirrored drive takes over and acts as the
primary drive.
In the following graphic, each letter represents a unique block
of data, and each column represents a separate hard drive.
File reading performance (seek time) is increased using the
same methods that RAID 0 uses, although writing speed is the
same as if writing to a single hard drive.
Drawback
RAID 1 treats the entire array as a single drive with the storage
capacity of the smallest physical drive in the array. So if you
have two drives (300 GB and 250 GB) in a RAID 1 array, your
computer only recognizes a single drive with 250 GB total
capacity.
RAID 5 and 10 for both performance and
security
Understanding RAID 5
RAID 5 uses striping (at the file level) with on-the-fly error
correction across all drives. Because of this error correction,
small file read/write errors can be quickly and automatically
fixed without a significant drop in system performance. RAID 5
offers good performance and data redundancy. This array
preserves your files if a drive fails.
RAID 5 stripes both data and parity information (error-checking
information) across multiple drives. Striping across drives
improves overall performance, and the parity information
provides data protection. Because of the error-correction
capabilities, if a drive fails, the data can be quickly and
automatically fixed.
A
B
C
A
B
C
RAID 1
8513217.book Page 38 Wednesday, August 27, 2008 3:30 PM

 Loading...
Loading...