0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6
transient bias - phaseA
Iadiff fundamental
Iop at max bias + transient bias - phaseA
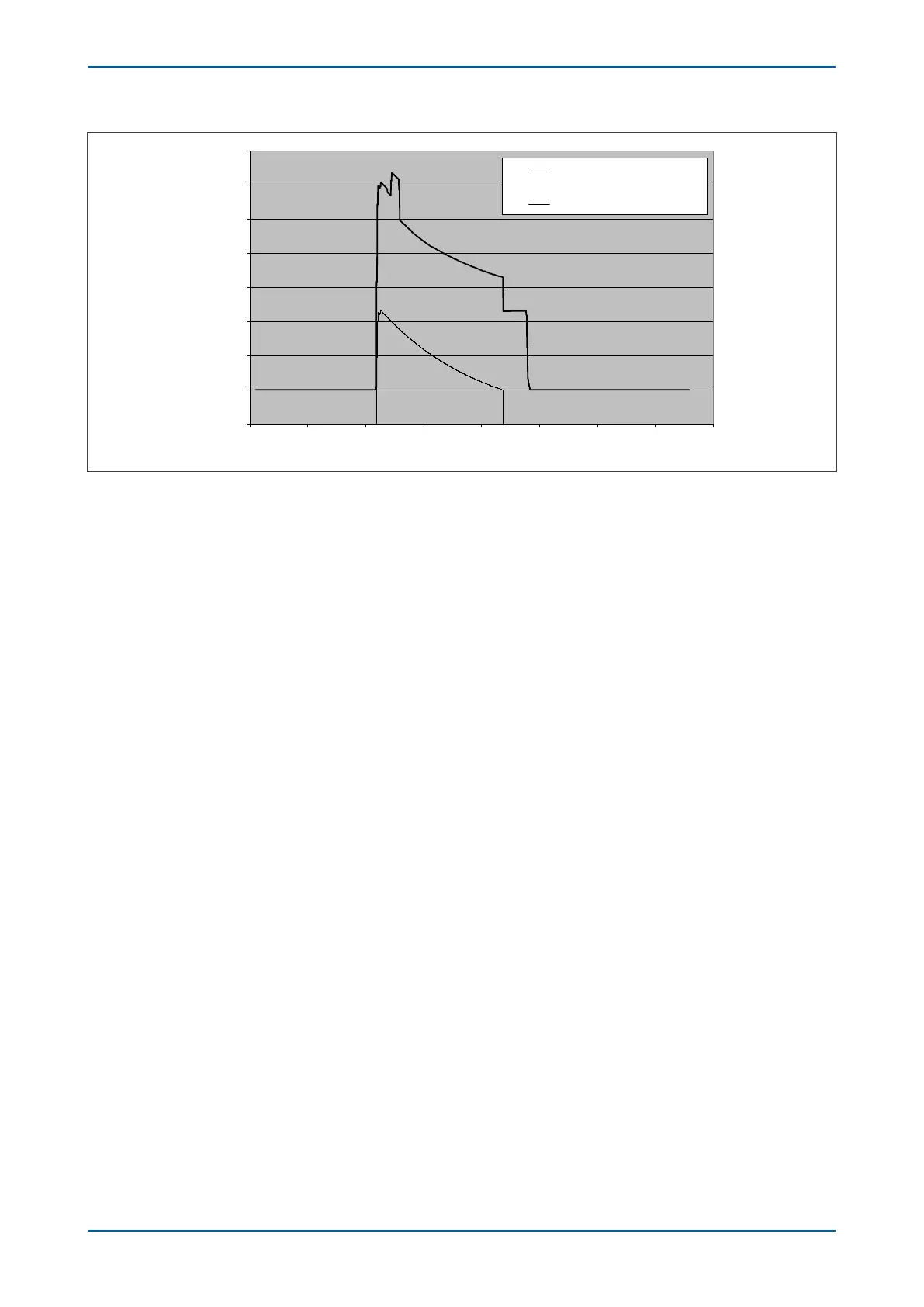
Figure 42: Transient bias characteristic
The transient bias f
unction enhances the stability of the differential element during external faults and allows for
the time delay in CT saturation caused by small external fault currents and high X/R ratios.
No transient bias is produced under load switching conditions, or when the CT comes out of saturation.
3.8.4 CT SATURATION TECHNIQUE
During CT saturation the second harmonic content may be high enough to block the low set differential element.
This w
ould result, in the operation of the low set differential element being delayed for some internal faults. The
device includes a CT Saturation Detection technique, which unblocks the low set differential element during
internal faults with heavy CT saturation. This CT saturation detection technique is capable of distinguishing
between magnetising inrush and CT saturation. Therefore the 2nd harmonic blocking will work properly for
magnetising inrush, but will not be asserted for internal faults where CT saturation is an issue. This function is
enabled or disabled with the CT Saturation setting in the DIFF PROTECTION column.
3.8.5 NO GAP DETECTION TECHNIQUE
The No Gap Detection technique detects light CT saturation on a per phase basis. The No Gap Detection technique
unblocks the low set differ
ential element during light CT saturation, allowing the low set differential element to trip
faster. Stability during inrush conditions is maintained, as this technique distinguishes between an inrush and a
saturated waveform. This function is enabled or disabled with the No Gap setting in the DIFF PROTECTION column.
3.8.6 EXTERNAL FAULT DETECTION TECHNIQUE
An External Fault Detection technique has been implemented so that the CT saturation and No gap detection
techniques do not affect the second harmonic block
ing during an external fault.
This technique considers the time to saturation, a delta bias start signal, a delta differential start signal and the
ratio of delta differential to delta bias at the time of start. As soon as an external fault occurs, the bias current
changes, but the differential current only increases after the time to saturation. The external fault detection DDBs
are asserted if the following conditions are fulfilled:
The delta bias start signal is asserted first. The delta bias start signal and the delta differential start signal are
asserted if the delta bias and delta differential currents are greater than 0.65 Is1 respectively.
The time difference between the assertion of the delta bias start signal and the assertion of the delta differential
signal is greater than the time to saturation. The minimum time to saturation is 2.5 ms for a 50 Hz system and 2.08
ms for a 60 Hz system.
P64x Chapter 6 - Transformer Differential Protection
P64x-TM-EN-1.3 113

 Loading...
Loading...