59
• Designated port—Forwards data to the downstream network segment or device.
• Alternate port—The backup port for a root port or master port. When the root port or master
port is blocked, the alternate port takes over.
• Backup port—The backup port of a designated port. When the designated port is invalid, the
backup port becomes the new designated port. A loop occurs when two ports of the same
spanning tree device are interconnected, so the device blocks one of the ports. The blocked
port acts as the backup.
• Edge port—An edge port does not connect to any network device or network segment, but
directly connects to a user host.
• Master port—A port on the shortest path from the local MST region to the common root bridge.
The master port is not always located on the regional root. It is a root port on the IST or CIST
and still a master port on the other MSTIs.
• Boundary port—Connects an MST region to another MST region or to an STP/RSTP-running
device. In MSTP calculation, a boundary port’s role on an MSTI is consistent with its role on the
CIST. But that is not true with master ports. A master port on MSTIs is a root port on the CIST.
Port states
In MSTP, a port can be in one of the following states:
• Forwarding—The port receives and sends BPDUs, obtains MAC addresses, and forwards
user traffic.
• Learning—The port receives and sends BPDUs, obtains MAC addresses, but does not forward
user traffic. Learning is an intermediate port state.
• Discarding—The port receives and sends BPDUs, but does not obtain MAC addresses or
forward user traffic.
When in different MSTIs, a port can be in different states. A port state is not exclusively associated
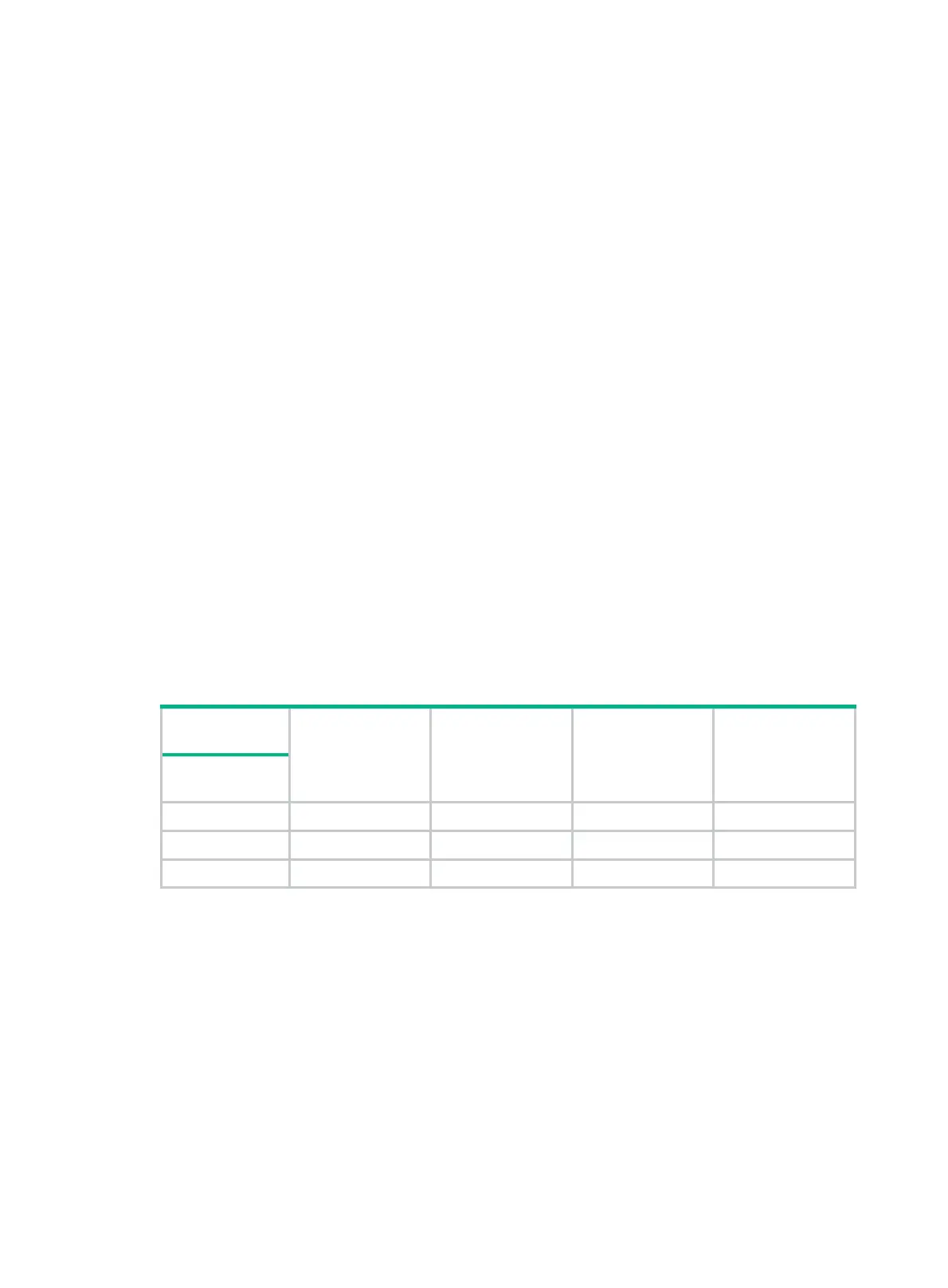
with a port role. Table 12 lists the port sta
tes that each port role supports. (A check mark [√] indicates
that the port supports this state, while a dash [—] indicates that the port does not support this state.)
Table 12 Port states that different port roles support
Port role
(right)
Root
port/master port
Designated port Alternate port Backup port
Port state
(below)
Forwarding √ √ — —
Learning √ √ — —
Discarding √ √ √ √

 Loading...
Loading...











