7.2 Troubleshooting
Alarm severities are dened as follows:
● Major: The inverter is faulty. As a result, the output power decreases or the
grid-tied power generation is stopped.
● Minor: Some components are faulty without
aecting the grid-tied power
generation.
● Warning: The inverter works properly. The output power decreases or some
authorization functions fail due to external factors.
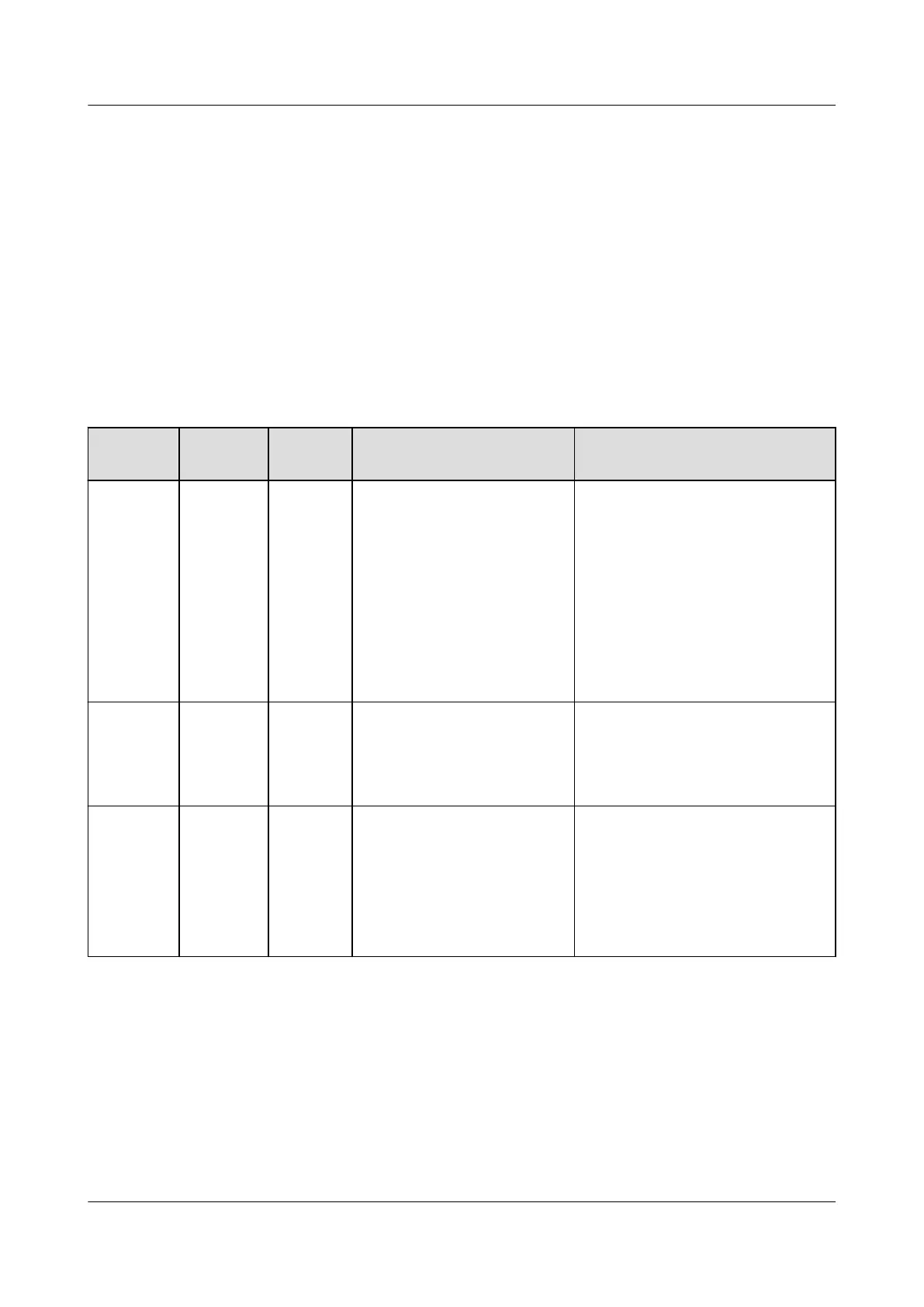
Table 7-2 Common alarms and troubleshooting measures
Alarm ID Alarm
Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause Troubleshooting Suggestion
2001 High
String
Input
Voltage
Major The PV array is not
properly congured.
Excessive PV modules are
connected in series to the
PV string, and therefore the
open-circuit voltage
exceeds the maximum
inverter operating voltage.
● Cause ID 1 = PV1
● Cause ID 2 = PV2
Reduce the number of PV
modules connected in series to
the PV string until the PV string
open-circuit voltage is less than
or equal to the maximum
inverter operating voltage. After
the PV array is correctly
congured, the inverter alarm
disappears.
2002 DC Arc
Fault
Major The PV string power cable
arcs or is in poor contact.
● Cause ID 1 = PV1
● Cause ID 2 = PV2
Check that the PV string power
cable does not arc and is in
good contact.
2011 String
Reverse
Connecti
on
Major The PV string polarity is
reversed.
● Cause ID 1 = PV1
● Cause ID 2 = PV2
Check whether the PV string is
reversely connected to the
SUN2000. If yes, wait until the
PV string current decreases
below 0.5 A, set DC SWITCH to
OFF, and adjust the PV string
polarity.
SUN2000-(3KTL-10KTL)-M0
User Manual 7 Maintenance
Issue 06 (2020-10-23) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 69

 Loading...
Loading...











