Series 2600 System SourceMeters Reference Manual Status Model D-33
Return to Appendix D topics 2600S-901-01 Rev. A / May 2006
Queue when it is read. The Error Queue is considered cleared when it is empty.
An empty Error Queue clears the EAV bit in the Status Byte Register.
The commands to control the Error Queue are listed in Table D-10. When you
read a single message in the Error Queue, the “oldest” message is read and then
removed from the queue. On power-up, the Error Queue is initially empty. If there
are problems detected during power-on, entries will be placed in the queue. When
empty, the error number 0 and “No Error” is placed in the queue.
Messages in the Error Queue include a code number, message text, severity, and
TSP-Link node number. The messages are listed in
Table B-2.
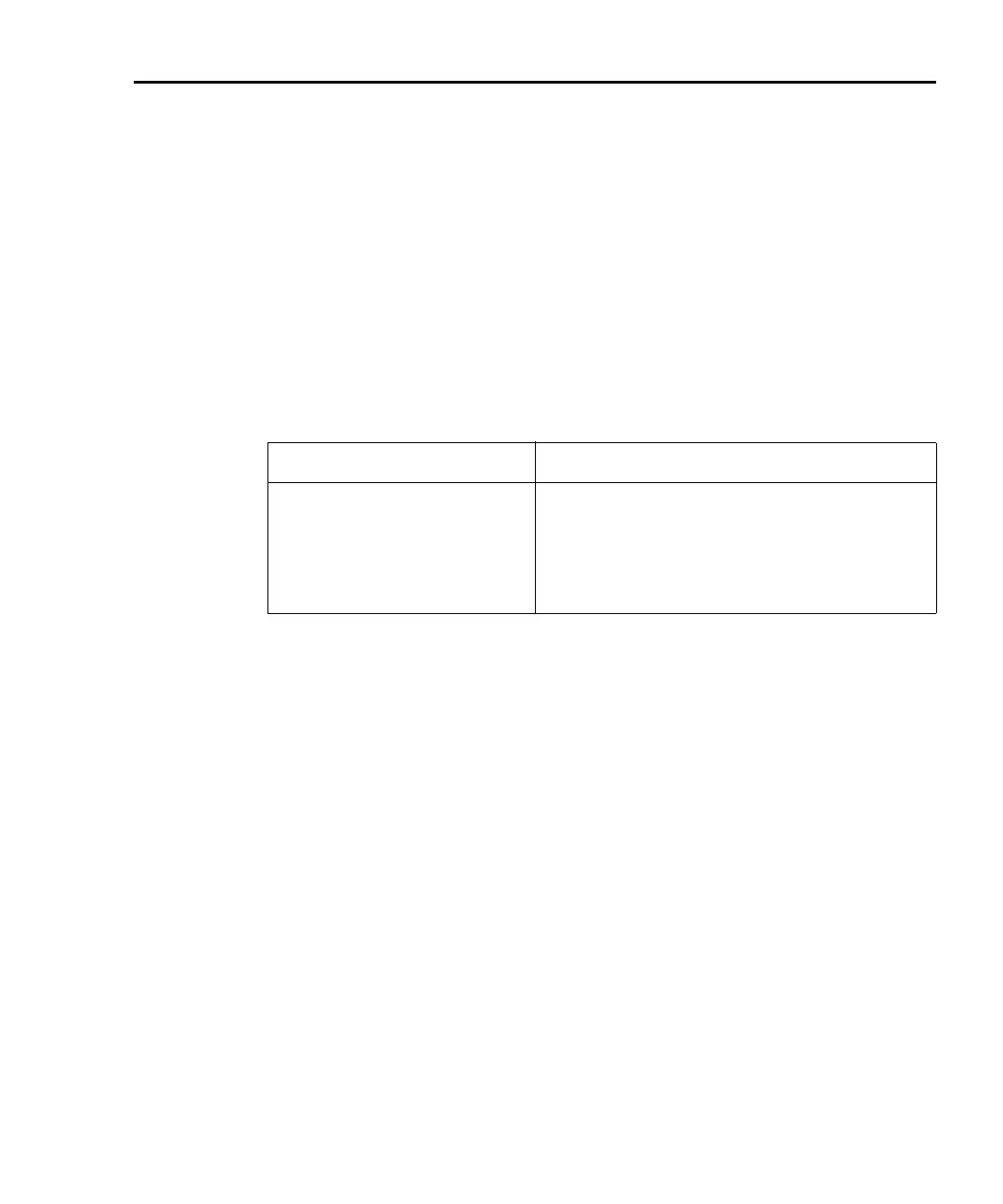
Table D-10
Error queue commands
Error queue command Description
errorqueue.clear() Clear error queue of all errors.
errorqueue.count Number of messages in the error/event queue.
errorcode, message, severity,
node = errorqueue.next()
Request error code, text message, severity, and
TSP-Link node number.
TSP-Link system status
The TSP-Link is an expansion interface that allows the instruments to
communicate with each other. The test system can be expanded to include up to
64 TSP-Link-enabled instruments. In a TSP-Link system, one node (instrument) is
the Master and the other nodes are the Slaves. The Master can control the other
nodes (Slaves) in the system. See
Section 9 for details on the TSP-Link.
The system summary registers (shown in Figure D-1 and Figure D-2) are shared
by all nodes in the TSP-Link system. A status event that occurs at a Slave node
can generate an SRQ (service request) in the Master node. After detecting the
service request, your program can then branch to an appropriate subroutine that
will service the request. See “
Status byte and service request (SRQ)” in this
appendix for details.
Status model configuration example
Figure D-9 shows an example status model configuration for a TSP-Link system.
In this example, a current limit (compliance) event in SMU A or SMU B of Node 15
will set the RQS bit of the Status Byte of the Master Node. The commands to con
-
figure the status model for this example are provided in “Status configuration
(enable) commands” in this appendix.

 Loading...
Loading...











