39
mode is also consistent.
7.3 Cartesian Coordinate Representation
Obtain the vertical angle “Vertical Angle”, the horizontal angle “Point Azimuth”
and the distance parameter “Distance” of the corresponding point of the lidar
and convert the angle and distance information in polar coordinates into x, y, and
z coordinates in the right-hand Cartesian coordinate system. There are two
conversion methods, as follows:
1) When the y direction is 0:
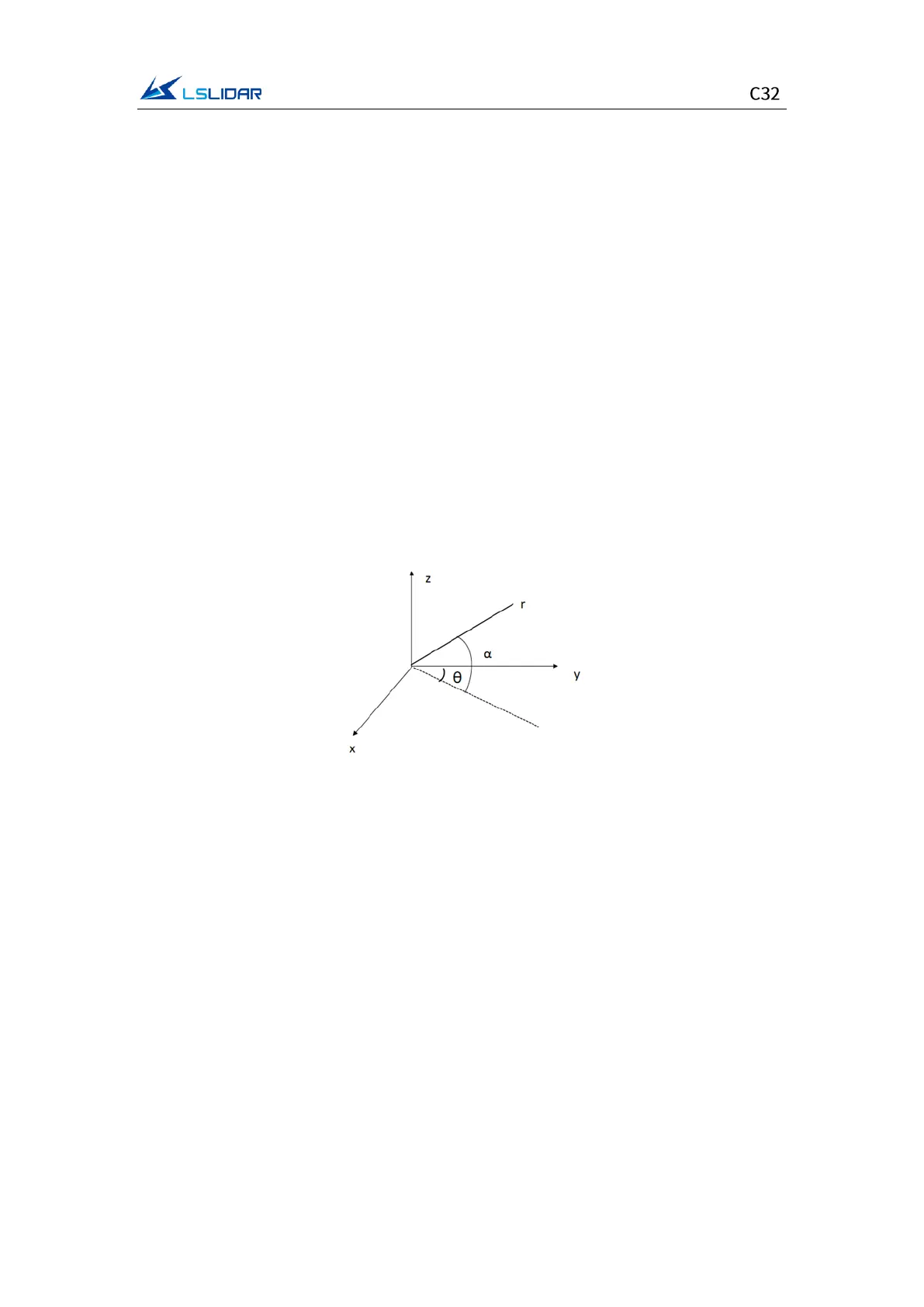
where r is the distance, α is the vertical angle, and θ is the horizontal rotation
angle. x, y, z are polar coordinates projected onto the x, y, z axes.
𝑥=𝑟cos𝛼sin𝜃;
𝑦=𝑟cos𝛼 cos𝜃;
𝑧=𝑟sin𝛼
Figure 7.3 Coordinate Mapping (1)
2) When the x direction is 0:
where r is the distance, α is the vertical angle, θ is the horizontal rotation angle
(the horizontal correction angle needs to be considered in the calculation), and
x, y, and z are the polar coordinates projected onto the x, y, and z axes.
{
𝑥=𝑟 cos𝛼cos𝜃;
𝑦=−𝑟cos𝛼sin𝜃;
𝑧=𝑟sin𝛼
 Loading...
Loading...