JTAG Programming
UG0451 User Guide Revision 7.0 18
3.3 Programming Using an External Microprocessor
Programming using an on-board microprocessor can be accomplished by the following:
• The microprocessor's GPIO driving the JTAG or system controller's SPI port
• An algorithm written in C code known as DirectC
DirectC supports programming the FPGA fabric, eNVM, and security settings individually or at the same
time. For more information, see the DirectC User Guide.
Note: Programming through system controller's SPI port using DirectC-SPI is discussed in SPI Slave
Programming, page 19.
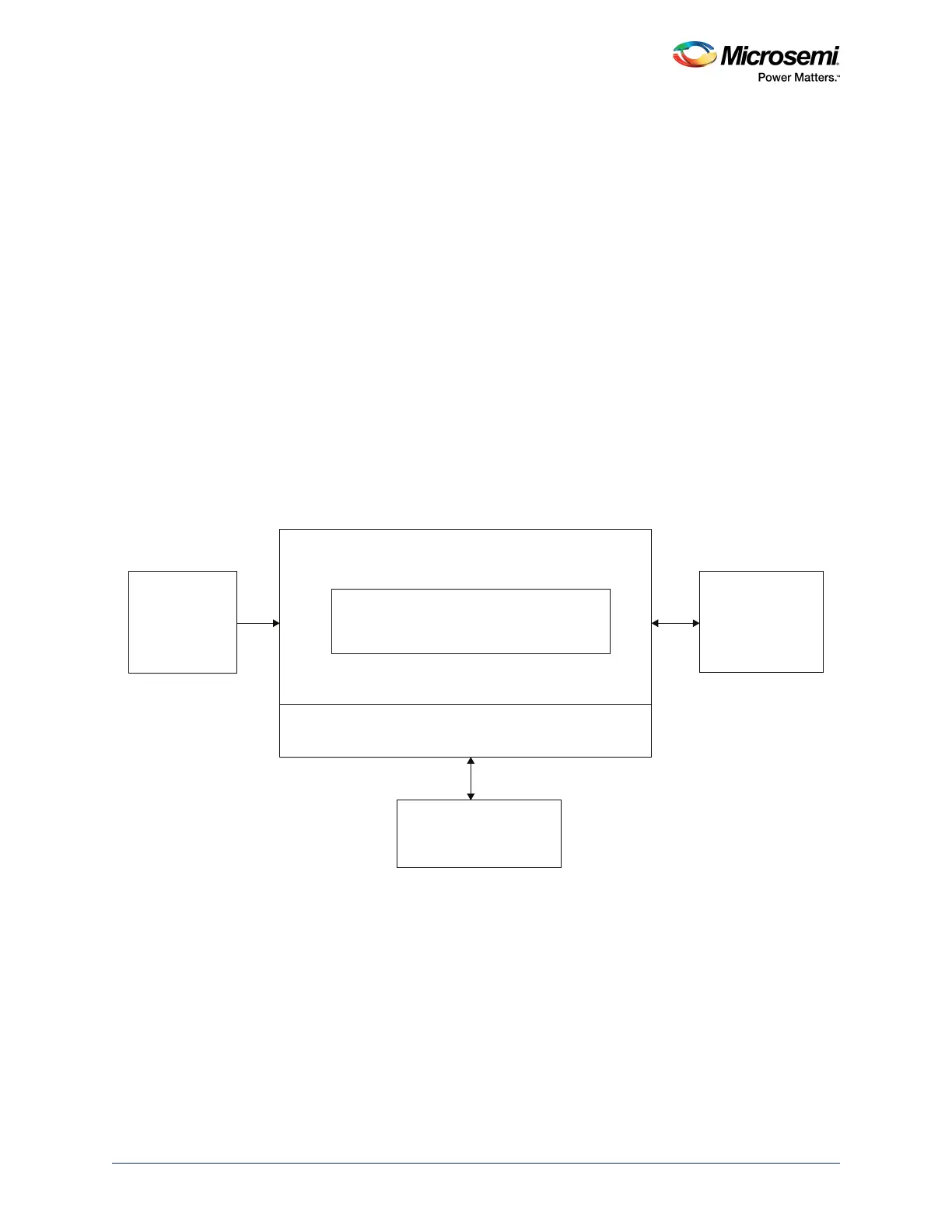
The following figure shows the programming implementation using:
• An external microprocessor with at least 256 bytes of RAM
• A memory device to store and run DirectC
• Access to the data file containing the programming bitstream
• A JTAG or SPI interface
3
to the target device
An API, I/O functions emulating JTAG or SPI protocols must be created to provide the required functions
that act as an interface between DirectC and the hardware. The API is then linked to DirectC and
compiled using the target microprocessor’s compiler. Once the API is compiled, the resulting binary must
be downloaded into the flash memory of microprocessor where it can be accessed to program the
device. While programming using the external microprocessor, the same board level considerations must
be followed as mentioned in the Programming Using an External Programmer, page 16.
Figure 7 • Programming Using an External Microprocessor
Internal or External
Memory Running
DirectC
On-Board Memory
Device Containing
Programming Data
SmartFusion2
Microprocessor
Internal RAM
I/O (JTAG or SPI) Function (API)

 Loading...
Loading...