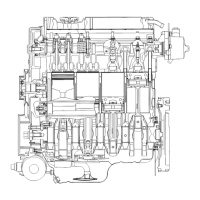
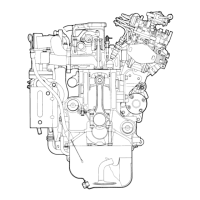
2-3 Valve clearances
Both lack and excess of valve clearances affect engine performance.
Especially-
excessive
valve
clearances
will
induce much strain. on
valve
mechanism, making the
engine subject
to
serious trouble.
Apart from regular checking required every 2S0Hr of run, check and adjust them
whenever
low-speed running
of
the
engine makes any unusual sounds. For new Engine,
adjust them when it has
run
for 60Hr. Proper clearances are, exhaust and inlet valves
alike, O.2Smm
as
measured
in
cold (or uniformly warm) engine.
Firing order
is:
1-3-4-2.
2-4 Compression pressure
1)
To
see whether or not intake air into cylinders undergoes there sufficient
compression with
no
blow-by
to
help the firing, measure compression pressure.
2)
The results
will
tell
if:
a)
Valve
seats are
in
tight enough contact.
b)
Cylinder liners and piston rings are not worn or sticking hard.
c)
There
is
any leak of
gas
ascribable
to
other cuases.
Regular measurement at intervals of about
SOOHr
of run
will
provide reliable data
to
decide when
to
overhaul
the
engine.
3) Prior
to
measuring it, check
and adjust
valve
clearances so
that
rockers
do
not press down
valves
in
compression stroke,
and make sure that Venturi
butterfly
valve
is
full
open.
4) Standard compression pressure
is
above 20kg/cm
2
at
an engine
speed
of
1S0-200
r.p.m., and
with
oil
and water tempera-
tures
in
a range of
20°-30°C.
Fig.3-10 Adjusting valve clearance
Please have it measured by your dealer or
at
a service shop.
3
OIL
SYSTEM
As can be seen
in
circulation diagram
(F
ig.
3-11), lubrication system
is
forced
lubrication by a trochoid
oil
pump.
At
option, a water-cooled
oil
cooler
is
equipped between
oil pump and oil filter
to
keep
oil
in
an optimum temperature range.
-
18-

 Loading...
Loading...