RS485 Transmission
General Topology of RS 485 Network
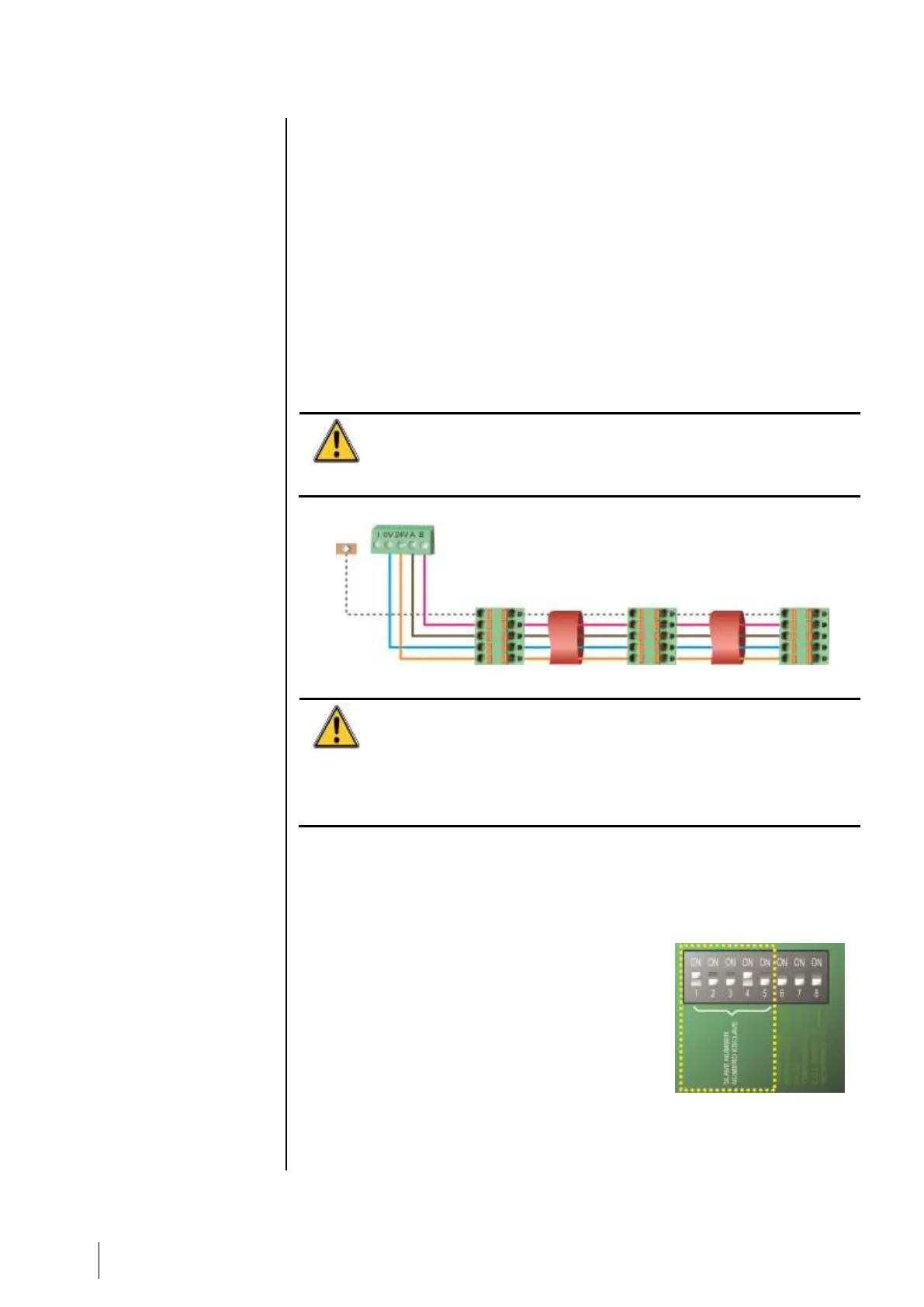
The digital modules are linked by 2 twisted cable pairs of 4 x 0.22 m²
minimum, type MPI-22A, nominal resistance of 120 Ohms. This cable carries
the RS485 (A and B) signal on one pair and the power supply of the modules
(0–24 VDC) connected to the line on the other pair. Shielding necessarily links
all the modules to the terminal block of MX 43.
The + 24 VDC, 0V, A, B terminals are respectively connected to +24VDC, 0V,
A, B terminals of the other modules on the line and then to the connector of
the corresponding line on the controller. The cable shielding must be
connected to the grounding rod of the MX 43.
At the end of the busbar, the 120-Ohm end of line resistor (EOL
RESISTOR/RESISTANCE F.D.L) must be activated (whatever the last module).
No portion of the bare end of the terminal wires should be visible.
For protection against any electromagnetic disturbances, the data
as well as screen wires (or braids) must be cut as short as
possible.
Figure 16: Principle of connecting modules to a MX 43 line.
The incorrect installation of the cables or cable glands can cause
measurement errors or a malfunctioning of the system.
Do not lay the cables close to equipment such as engines,
transformers, or lines generating important magnetic fields.
It is recommended to always ensure a distinct separation between
these cables and the cables of other circuits.
Configuration of Communication
Module Address
All the digital modules on a line must be
identified by a unique address.
Switches 1 to 5 of the configuration block of
each module make it possible to establish an
address number (1 to 32) in binary mode.
In the illustration to the right, the address 9
(10010) has been defined.
The Addressing Table below lists the possible
combinations.
Figure 17: Switches of
address configuration.
Terminal (detector,
module)

 Loading...
Loading...