Planning wireless systems
105542_en_05 PHOENIX CONTACT 141 / 198
8.11 Propagation of radio waves
In addition to free space attenuation, there are other factors which influence the wireless
path. Dispersion, diffraction, and reflection represent types of interference that occur when
the wireless signal encounters obstacles. They result in multipath propagation.
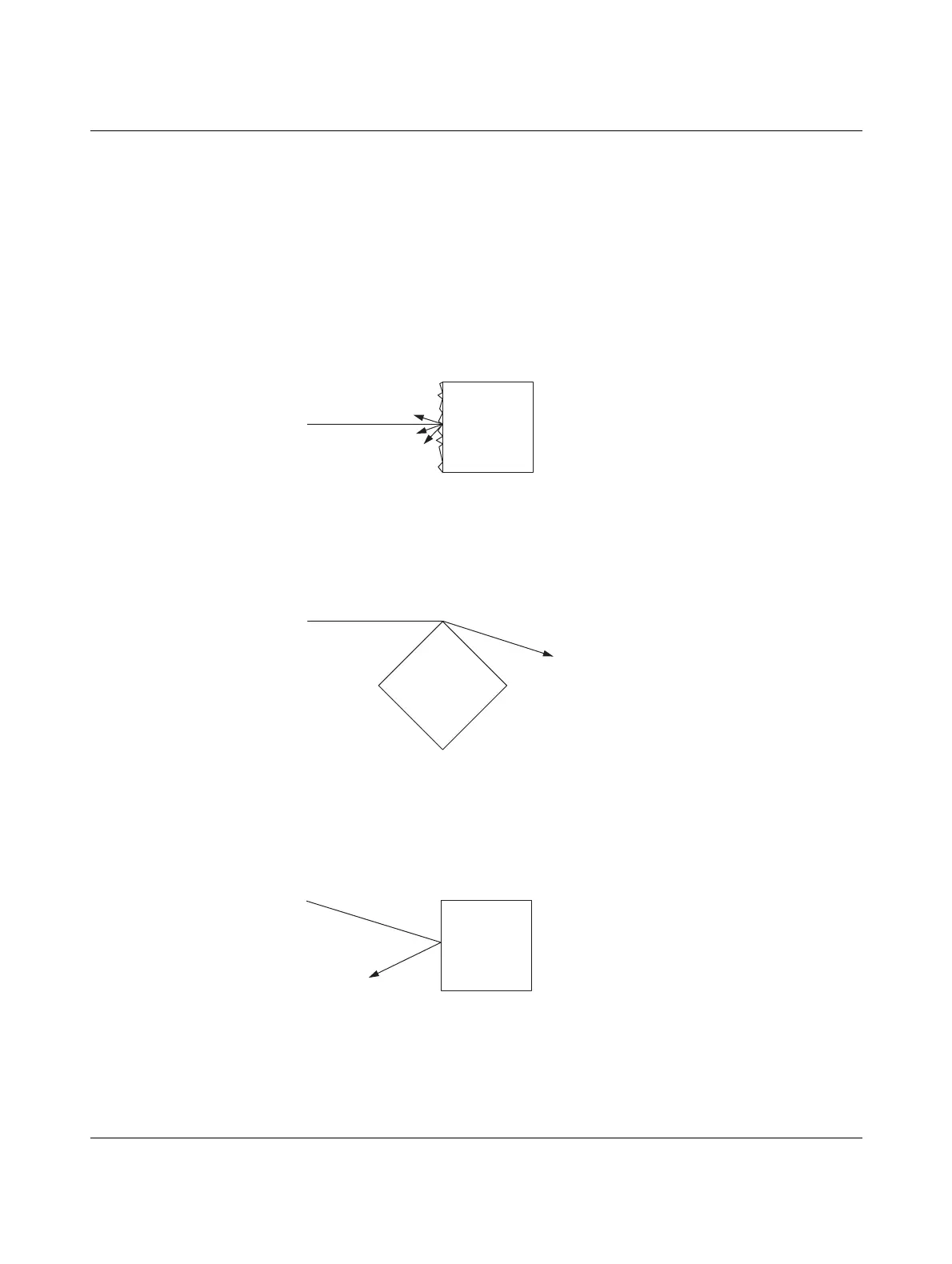
Dispersion
Dispersion of the wireless signal, e.g., at a tree, means that the wireless signal is dispersed
in several directions. A bare tree will let signals through almost completely. However, a tree
with leaves will scatter the signals considerably. The leaf surfaces disperse the wireless sig-
nal in many different directions.
Figure 8-9 Dispersion on a rough surface
Diffraction
Diffraction of the wireless signal, e.g., on edges and obstacles, involves the signal being re-
fracted around the edge. The signal then changes its direction. This is similar to the refrac-
tion of light in a crystal.
Figure 8-10 Diffraction on an edge
Reflection
Reflection on a smooth metal surface involves virtually the entire wireless signal being re-
flected at the same angle. In certain applications, the reflection may have a positive effect,
e.g., if there is no line of sight. Reflections mainly occur in buildings.
Figure 8-11 Reflection on a metal surface

 Loading...
Loading...