Final Drive / Propulsion
5.2
Ventilation / Cavitation Diagnostics
If a watercraft exhibits poor performance during accelerating, high engine RPM with little forward speed or power,
inconsistent RPM, or difficulty pulling skiers out of the water, pump ventilation or cavitation may be the cause.
Ventilation
Ventilation results when air enters the pump inlet tract and is compressed by the impeller, causing a reduction
in thrust and an increase in engine RPM. Small leaks are often difficult to diagnose. A hole or crack the size of
a pin in the sealed area around the pump intake tract is enough to cause ventilation.
Some possible sources of air are:
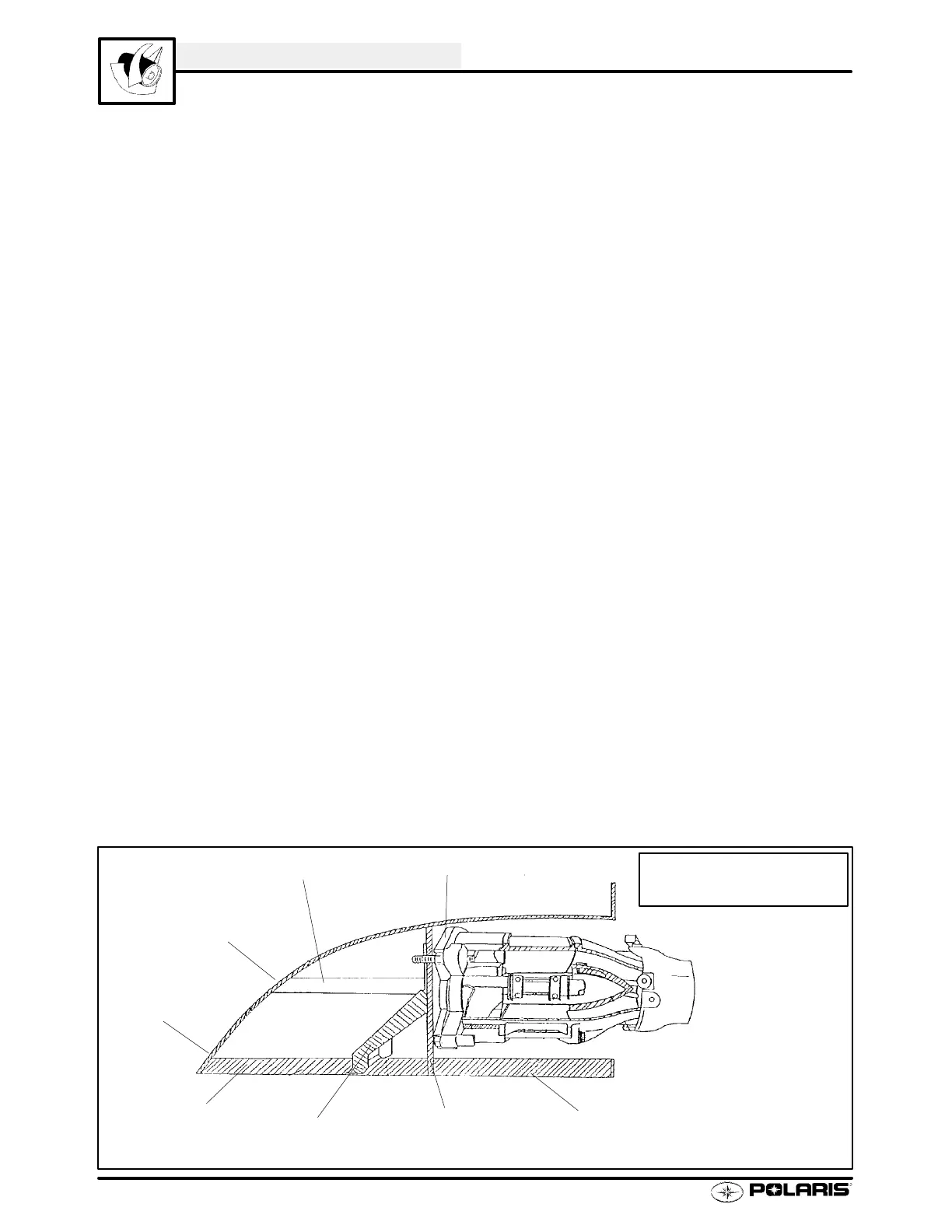
1. Intake scoop -- An improperly sealed intake scoop is the most common cause of ventilation. Make sure the
scoop has a complete bead of Marine Grade silicone sealer all the way around without any gaps or pin holes.
Sometimes, small leaks in the silicone sealer around the intake scoop are hard to detect with a visual inspection.
The following method may make it easier to see. See page 5.17 for scoop installation.
1. T urn high speed fuel screws out (counterclockwise) 1/2 turn, and operate the craft.
2. Remove intake grate, and look for exhaust trail (black smoke path) in the area around the scoop.
3. Remove intake scoop, clean and re-seal with a complete bead of Marine Grade silicone sealant. Refer to
illustration below for critical sealing points in the pump area.
4. Reinstall pump, ride plate, and intake grate and set high speed screws back to original position.
2. Ride plate -- The ride plate must be completely sealed in the area around the intake scoop, and also in the area
where the hull meets the pump cavity.
3. Drive shaft bearing housing or through hull fitting -- If the drive shaft bearing carrier seals are worn or damaged,
air may be drawn into the pump from the engine compartment. Also inspect the through-hull fitting. The entire
circumference of the fitting must be sealed to prevent water from entering the hull, and air from entering the pump.
Refer to Chapter 6 for through hull fitting repair .
4. Incorrectly mounted pump (pump sealing O-ring leakage). This can be caused by a damaged pump sealing
O-ring, an improperly installed intake scoop or a misaligned pump (there should be no detectable gap between
pump housing and hull).
Cavitation
Cavitation results when a low pressure area is created in the vicinity of the impeller blades, causing the surround-
ing water to boil or more accurately, the gas bubbles within the water implode with a destructive force. Cavitation
may be caused by cracked, damaged, bent or broken impeller blades, or an excessively worn impeller or housing
(check impeller clearance).
Ventilation or cavitation can drastically reduce the amount of output thrust produced by the pump. Evidence of
either problem may appear as burn marks on the impeller and stator vanes in the pump.
Drive Shaft
Intake Scoop
Hull
Pump Housing
Ride Plate
Intake Grate
Through-Hull
Fitting (Inside Hull)
Cutaway View Of Pump
Hull

 Loading...
Loading...