SECTION 4 - INSTALLATION
QUANTECH
39
FORM QTC4-NM1
ISSUE DATE: 4/2/2018
4
water entering the process can be held at the desired
temperature. A tank can also be used to meet high leav-
ing water temperature requirements.
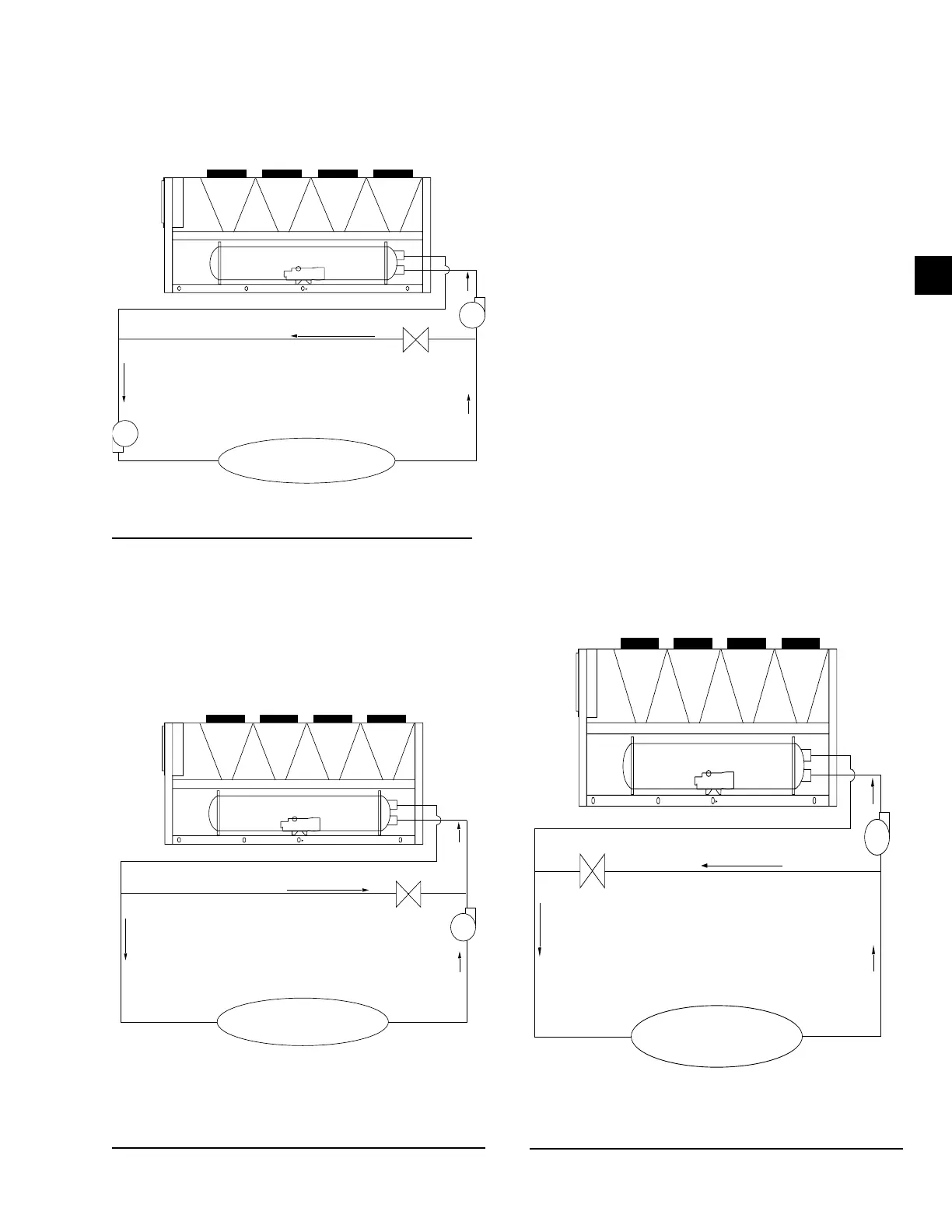
FIGURE 8 - LEAVING WATER TEMPERATURE OUT
OF RANGE SUGGESTED LAYOUT
LD15049
RECIRCULATION
SUPPLY TO LOAD
RETURN FROM LOAD
LOAD
FLOW RATE OUT OF RANGE
Each QTC4 evaporator has a minimum and maximum
flow rate. Some process applications require a flow
rate that is out of range for the evaporator. In those ap-
plications, a piping change can remove the problem.
LD15050
LOAD
SUPPLY TO LOAD
BYPASS
RETURN FROM LOAD
FIGURE 9 - SUGGESTED LAYOUT FOR
APPLICATIONS WITH FLOW RATES LESS THAN THE
EVAPORATOR MINIMUM ALLOWABLE FLOW RATE
In applications where the required flow rate is less than
the evaporator’s minimum allowable, the chilled water
can be recirculated to the chiller.
In applications where the required flow rate is greater
than the evaporator’s maximum allowable, the chilled
water can be recirculated to the load.
THERMAL STORAGE
Thermal storage is the practice of storing cooling ener-
gy during a period of little or no load and/or low energy
costs for use during periods of high load and/or energy
costs. Conventional cooling systems produce cooling
when it is needed which is commonly during times of
peak demand. Thermal storage allows generation of
cooling capacity to occur during off-peak periods and
store that capacity to meet future cooling requirements.
Using thermal storage can result in smaller equipment
sizes, thereby reducing capital cost, and also can result
in significant energy cost savings
The QTC4 has special control logic to be able to pro-
duce chilled leaving brine temperatures below 4.4°C
(40°F) so as to supply a storage tank with chilled liq-
uid during times of low demand. QTC4 chillers selected
for thermal storage operation can also be selected to
efficiently provide chilled fluid at nominal cooling loads.
LD15051
BYPASS
SUPPLY TO LOAD
LOAD
FIGURE 10 - SUGGESTED LAYOUT FOR
APPLICATIONS WITH A FLOW RATE GREATER
THAN THE EVAPORATOR MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE
FLOW RATE

 Loading...
Loading...