2. Amperometric measuring principles ABL800 FLEX Reference Manual
pO
2
electrode, Continued
Gas/liquid relationship:
Corrections -
blood samples
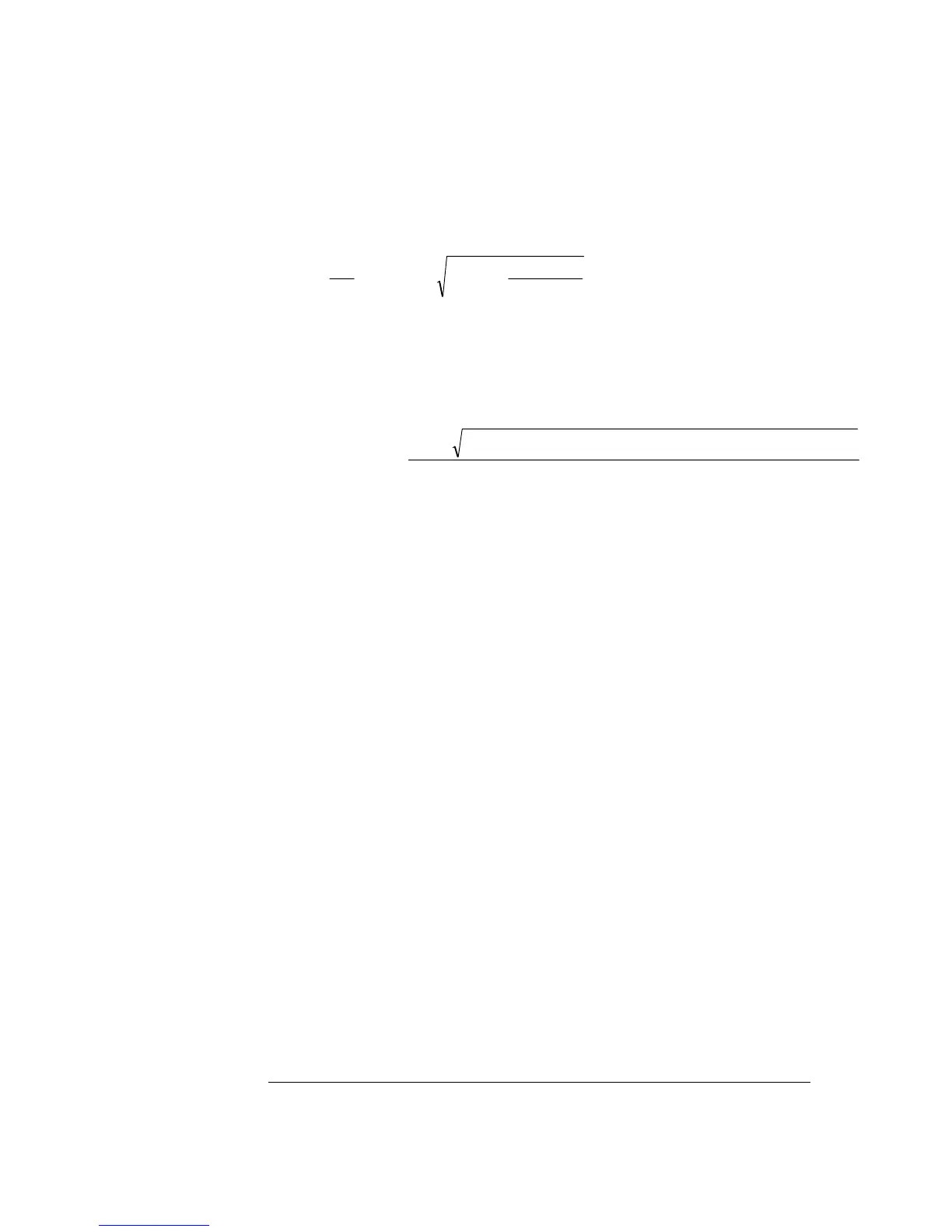
K
1
is a constant that describes the gas/liquid relationship for the electrode. The
constant is defined as follows:
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
++−+=
66294.3
)O(Sens
712.218370.5
100
1
1K
2
1
p
The pO
2
measured from the sample is then corrected for systematic deviations
from the reference method using the following equation:
Equation A:
)
p
dd ee e
O (sample,corr)
O (sample,v1) O (sample,v1)
2
2 2
=
−+ −× +× +×
11
2
23 4
2
4 pp
2
where:
• pO
2
value of the sample after the first part of correction is as follows:
)398.100()((sample)Ov1)(sample,O
4
2
(sample)O
2122
Bekkpp
pk
3
−××−+=
×
• and:
d
1
= e
0
× pO
2
(sample, v1) + e
1
k
1
= correction constant = 0.02614
k
2
= correction constant = 0.02107
k
3
= correction constant = −0.00281
e
0
, e
1
, e
2
, e
3
, e
4
= correction constants
B
= barometric pressure in kPa
Equation A+:
When an additional correction is needed, equation A is first used together with the
constants for the FLEXMODE (C195 and 165) – no message. Then the obtained
results are put back into equation A as pO
2
(sample) and then treated again, using
the constants for the specific mode.
Or
Equation B:
When an additional correction is needed, equation A is first used together with the
constants for the FLEXMODE (C195 and 165) – no message. Then the obtained
results are put back into equation B as pO
2
(sample) and then treated again, using
the constants for the specific mode.
cX(sample,corr) = A
0
× cX(sample) + A
1
Continued on next page
2-8
 Loading...
Loading...