166 Rockwell Automation Publication 1769-UM021I-EN-P - May 2018
Chapter 7 Use I/O Modules with CompactLogix 5370 L1 Controllers
Module Faults Related to RPI Estimates
When following the guidelines described on page 165, most
CompactLogix 5370 L1 control systems operate as expected.
Some systems that follow the guidelines can experience minor faults that are
described in the following table.
Calculate System Power Consumption
An embedded 24V DC nominal, non-isolated power supply with an input
range of 10…28.8V DC powers the CompactLogix 5370 L1 control system.
The embedded power supply provides 1 A @ 5V DC to the POINTBus
backplane to power all system components, including local expansion modules,
in most system configurations. Local expansion modules include 1734 POINT
I/O modules.
In some circumstances, you can configure a system that requires more current
than the embedded power supply of the system provides. This type of
configuration results from using a combination of local expansion modules
that, when combined with current consumption of the rest of the system,
exceeds 1 A @ 5V DC.
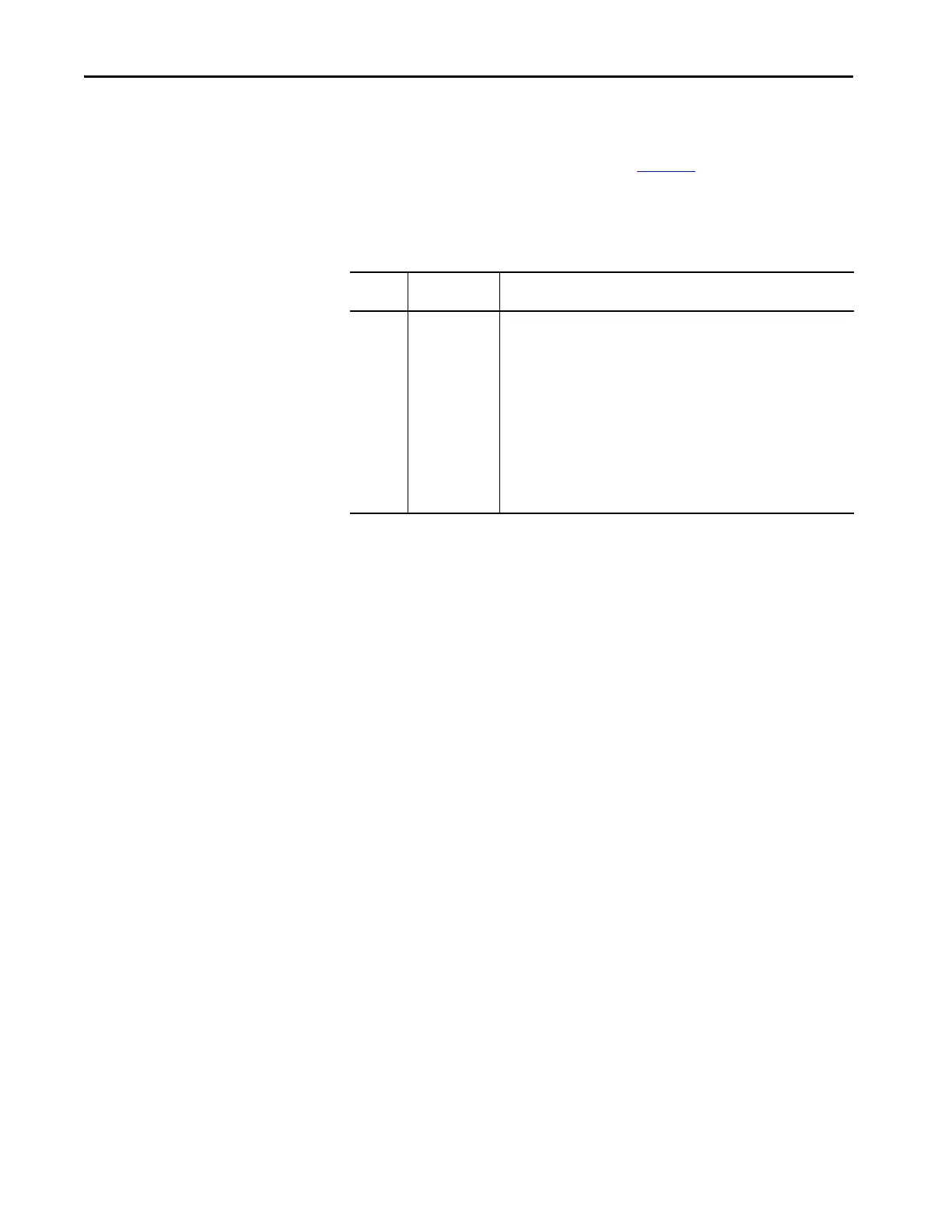
Name Fault
Information
Condition In Which Fault Occurs
Module
RPI
Overlap
(Type 03) I/O fault
(Code 94) Module
RPI overlap
detected
Module Slot = x,
where x is the slot
number of the I/O
module in the I/O
Configuration
section
This fault is logged when the current RPI update of an I/O module overlaps with
its previous RPI update. The Minor Faults tab in the Controller Properties dialog
box indicates which module the RPI overlaps.
If multiple I/O modules experience the fault, the application indicates that the
fault occurred on the first such I/O module. Typically, it is an I/O module with a
lower RPI rate and/or an I/O module with large input/output data sizes. For
example, the 1734-232ASC and 1734-485ASC modules use large input/output
data sizes.
Once the fault is cleared from the first I/O module, the application indicates the
next module that experiences the fault. This pattern continues until the fault is
cleared from all affected I/O modules.
To avoid this fault, set the RPI rate of the I/O modules to a higher numerical
value.

 Loading...
Loading...











