8 Rockwell Automation Publication 750-QS100B-EN-P - August 2020
Step 1: Gather the Required Information
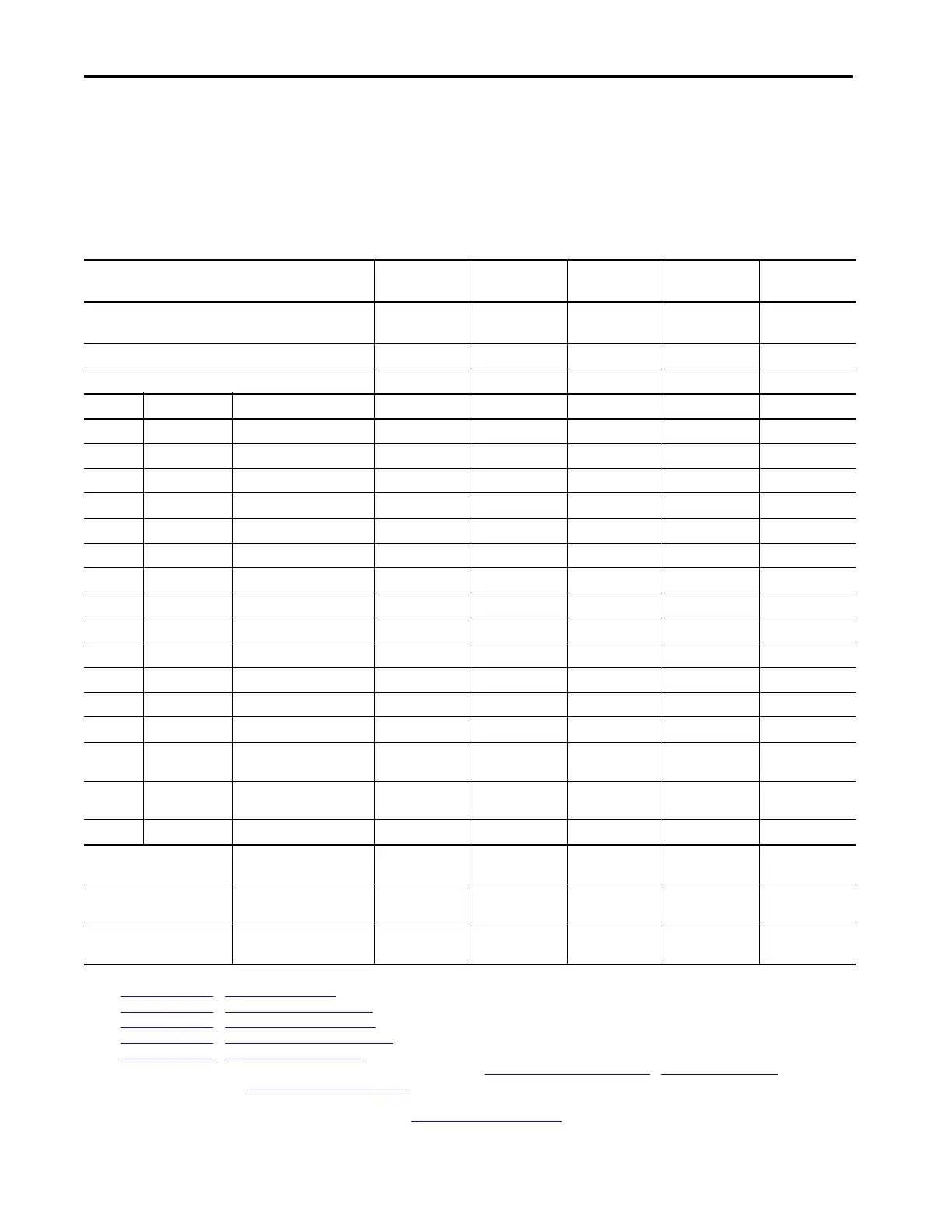
Record System Data
Record the data that will be used to configure system parameters. This includes motor nameplate data, AC power data,
and other motor data. Use this table to record a descriptive name, and parameter values for each drive/motor
combination. You can record data for up to five drive/motor combinations.
Table 1 - System Data
Drive/Motor Identifier (example, Main Exhaust Fan) Drive/Motor 1: Drive/Motor 2: Drive/Motor 3: Drive/Motor 4: Drive/Motor 5:
Drive Type
❑
755TL
❑
755TR
❑
755TL
❑
755TR
❑
755TL
❑
755TR
❑
755TL
❑
755TR
❑
755TL
❑
755TR
Drive Catalog Number 20G1 20G1 20G1 20G1 20G1
Transformer Identifier
Port No. Parameter No. Description
(1)
Drive/Motor 1: Drive/Motor 2: Drive/Motor 3: Drive/Motor 4: Drive/Motor 5:
10 400 Motor Nameplate Volts
10 401 Motor Nameplate Amps
10 402 Motor Nameplate Hertz
10 403 Motor Nameplate RPM
10 405 Motor Nameplate Power Units
❑
kW
❑
Hp
❑
kW
❑
Hp
❑
kW
❑
Hp
❑
kW
❑
Hp
❑
kW
❑
Hp
10 406 Motor Nameplate Power
10 407 Motor Poles
(2)
10 204 Motor Overload Hertz
(3)
10 209 Motor Protection Class
(4)
10 210 Motor Hot Start Coefficient
(5)
10 210 Motor Cooling Time
(6)
10 900 Motor Inertia
(7)
(kg•m2)
0 33 AC Line Voltage nom (V AC)
13 30 AC Line Frequency nom
(50 Hz or 60 Hz)
❑
50 Hz
❑
60 Hz
❑
50 Hz
❑
60 Hz
❑
50 Hz
❑
60 Hz
❑
50 Hz
❑
60 Hz
❑
50 Hz
❑
60 Hz
13 32 AC Line Transformer Rating
(kVA)
13 34 AC Line Impedance (%)
(8)
Power jumpers configuration. AC Power Source Grounding
Method
(9)
Braking Chopper (only if used) External Brake Chopper and
DB Resistor Data
❑
—
❑
—
❑
—
❑
—
❑
—
Motor Encoder, also known as a
Feedback Device (only if used)
Motor Encoder Data
(10)
❑
—
PPR: _____
❑
—
PPR: _____
❑
—
PPR: _____
❑
—
PPR: _____
❑
—
PPR: _____
(1) Motor parameters with descriptions that do not include “Motor Nameplate” are typically not present on the motor nameplate.
(2) See Step 5: Enter Motor Data
> Enter Motor Poles on page 30.
(3) See Step 5: Enter Motor Data
> Enter Motor Overload Hertz on page 31.
(4) See Step 5: Enter Motor Data
> Enter Motor Protection Class on page 31.
(5) See Step 5: Enter Motor Data
> Enter Motor Hot Start Coefficient on page 32.
(6) See Step 5: Enter Motor Data
> Enter Motor Cooling Time on page 32.
(7) Only needed for Flux Vector motor control mode. Methods to determine motor inertia are covered in Step 7: Tune the Motor Side Inverter Control
> Enter Motor Inertia on page 39.
(8) If your system uses a line reactor, see Calculating AC Line Impedance on page 60
.
(9) For example, solid (low res), non-solid (high res).
(10) Only needed if a motor encoder is used. For more information, see Appendix A > Line Side Converter Settings on page 57
.

 Loading...
Loading...
















