Mechanical properties of the motors
3.2 Liquid cooling
1FT7 Synchronous Motors
Configuration Manual, (PFT7S) 01/2009, 6SN1197-0AD13-0BP2
53
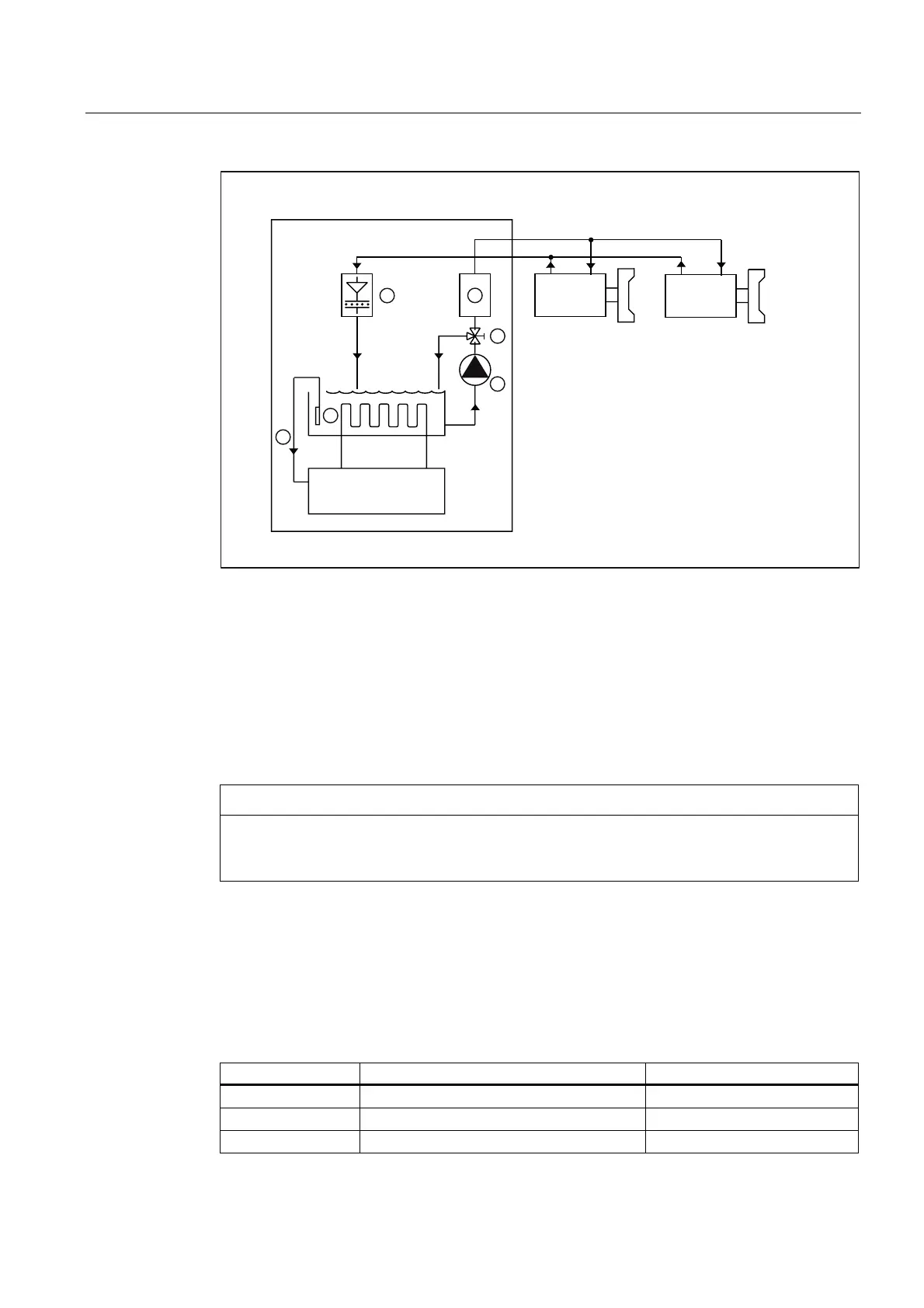
&RPSUHVVRUF
RROLQJXQLW
0RWRU
)LOWHU
)ORZPHWHU
3UHVVXUHUHOLHIYDOYHVHWWLQJYDOYHIORZTXDQWLW\
3XPS
&RROLQJZDWHUWDQN
7HPSHUDWXUHVHQVLQJFRROLQJZDWHU
7KHVHFRPSRQHQWVDUHQRWDEVROXWHO\QHFHVVDU\
&RROLQJXQLW
0RWRU
Figure 3-1 Example of a semi-open cooling circuit
Equipotential bonding
All components in the cooling system (motor, heat exchanger, piping system, pump,
pressure equalization tank, etc.) must be connected to an equipotential bonding system. This
is implemented using a copper bar or finely stranded copper cable with the appropriate cable
cross-sections.
NOTICE
Under no circumstances may the coolant pipes come into contact with live components.
There must always be an isolating clearance of > 13 mm! The pipes must be securely
mounted and checked for leaks.
Materials used in the motor cooling circuit
The materials used in the cooling circuit must be coordinated with the materials in the motor.
Table 3- 2 Materials used in the motor cooling circuit
Shaft height Bearing shield Pipes in the stator
1FT706x Cast iron (EN-GJL-200) Stainless steel
1FT708x Cast iron (EN-GJL-200) Stainless steel
1FT710x Cast iron (EN-GJL-200) Stainless steel

 Loading...
Loading...