Motion control is easy
10.5 Motion control instructions
Easy Book
226 Manual, 03/2014, A5E02486774-AF
The MC_Halt task can be aborted by the
following motion control tasks:
MC_Home Mode = 3
MC_Halt
MC_MoveAbsolute
MC_MoveRelative
MC_MoveVelocity
MC_MoveJog
The new MC_Halt task aborts the following
active motion control tasks:
MC_Home Mode = 3
MC_Halt
MC_MoveAbsolute
MC_MoveRelative
MC_MoveVelocity
MC_MoveJog
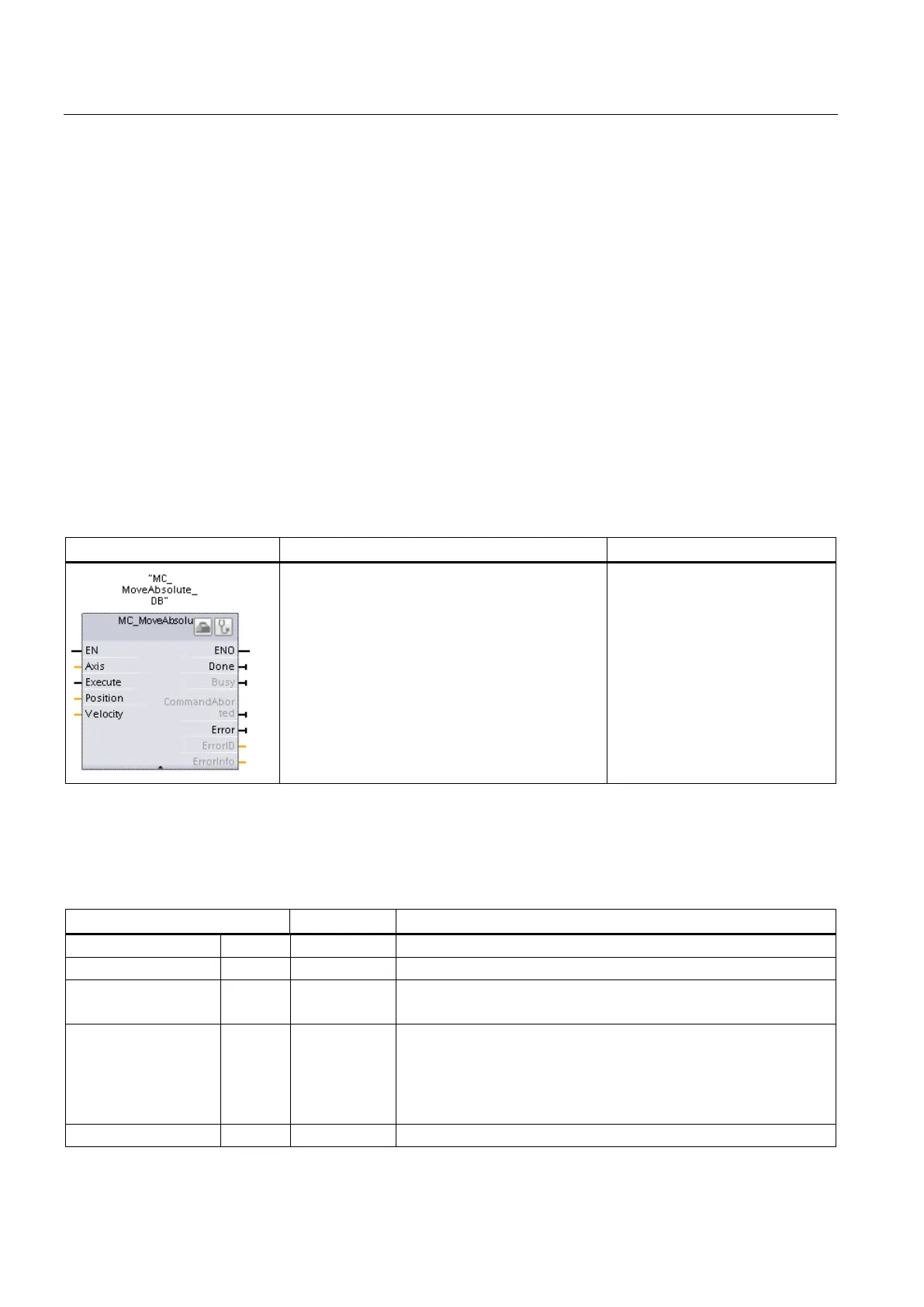
MC_MoveAbsolute (Position axis absolutely) instruction
Table 10- 16 MC_MoveAbsolute instruction
Axis:=_multi_fb_in_,
Execute:=_bool_in_,
Position:=_real_in_,
Velocity:=_real_in_,
Done=>_bool_out_,
Busy=>_bool_out_,
CommandAborted=>_bool_out_,
Error=>_bool_out_,
ErrorID=>_word_out_,
ErrorInfo=>_word_out_);
Use the MC_MoveAbsolute
instruction to start a positioning
motion of the axis to an absolute
position.
In order to use the
MC_MoveAbsolute instruction, the
axis must first be enabled and also
must be homed.
STEP 7 automatically creates the DB when you insert the instruction.
2
In the SCL example, "MC_MoveAbsolute_DB" is the name of the instance DB.
Table 10- 17 Parameters for the MC_MoveAbsolute instruction
Start of the task with a positive edge (Default value: False)
Position IN Real Absolute target position (Default value: 0.0)
12
12
Velocity IN Real Velocity of axis (Default value: 10.0)
This velocity is not always reached because of the configured
acceleration and deceleration and the target position to be
approached.
Limit values: Start/stop velocity ≤ Velocity ≤ maximum velocity
TRUE = Absolute target position reached

 Loading...
Loading...


















