Commissioning
7.1 Measures before commissioning
1LA5/6/7/9, 1LG4/6, 1MA6/7, 1MB..1/2/3/4/5 - SH 63 ... 355
Operating Instructions, 06/2018, A5E44455710A
91
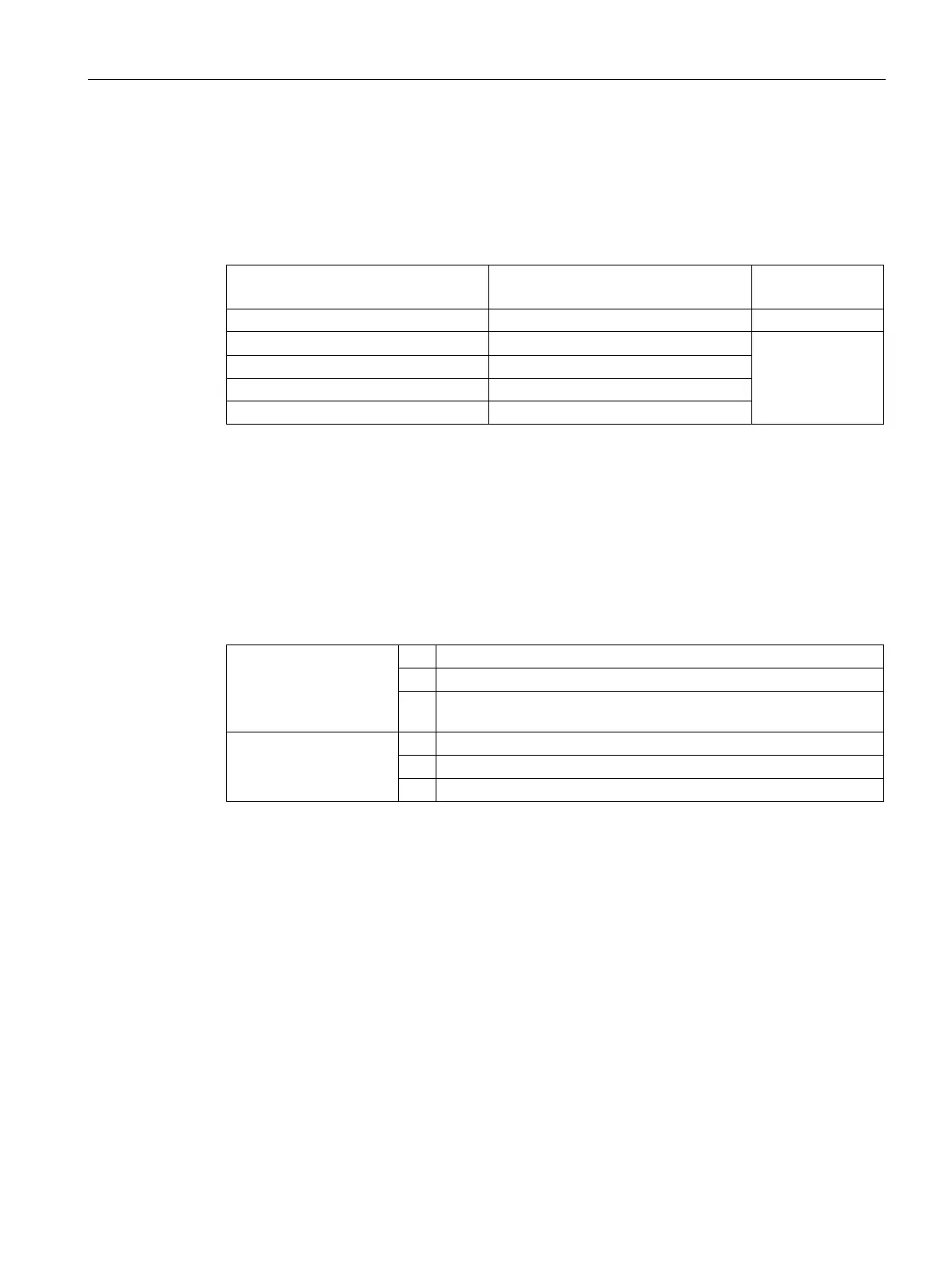
Limit values for the stator winding insulation resistance
The following table specifies the measuring voltage and limit values for the insulation
resistance. These values correspond to IEEE 43-2000 recommendations.
Table 7- 1 Stator winding insulation resistance at 40° C
1000 ≤ U ≤ 2500 500 (max. 1000) 100
5000 < U ≤ 12000 2500 (max. 5000)
rated
= rated voltage, see the rating plate
meas
= DC measuring voltage
R
C
= minimum insulation resistance at a reference temperature of 40 °C
Conversion to the reference temperature
When measuring with winding temperatures other than 40° C, convert the measuring value
to the reference temperature of 40° C according to the following equations from IEEE 43-
2000.
(1)
R
C
=
K
T
·
R
T
Insulation resistance converted to 40° C reference temperature
T
Temperature coefficient according to equation (2)
R
T
Measured insulation resistance for measuring/winding temperature
(2)
K
T
= (0.5)
(40-T)/10
Reference temperature in °C
Halving/doubling of the insulation resistance with 10 K
Measuring/winding temperature in °C
In this case, doubling or halving the insulation resistance at a temperature change of 10 K is
used as the basis.
● The insulation resistance halves every time the temperature rises by 10 K.
● The resistance doubles every time the temperature falls by 10 K.
For a winding temperature of approx. 25° C, the minimum insulation resistances are 20 MΩ
(U ≤ 1000 V) or 300 MΩ (U > 1000 V). The values apply for the complete winding to ground.
Twice the minimum values apply to the measurement of individual assemblies.
● Dry, new windings have an insulation resistance of between 100 and 2000 MΩ, or
possibly even higher values. An insulation resistance value close to the minimum value
could be due to moisture and/or dirt accumulation. The size of the winding, the rated
voltage and other characteristics affect the insulation resistance and may need to be
taken into account when determining measures.
● Over its operating lifetime, the motor winding insulation resistance can drop due to
ambient and operational influences. Calculate the critical insulation resistance value
depending on the rated voltage by multiplying the rated voltage (kV) by the specific

 Loading...
Loading...











