4 Memory of measurement result data
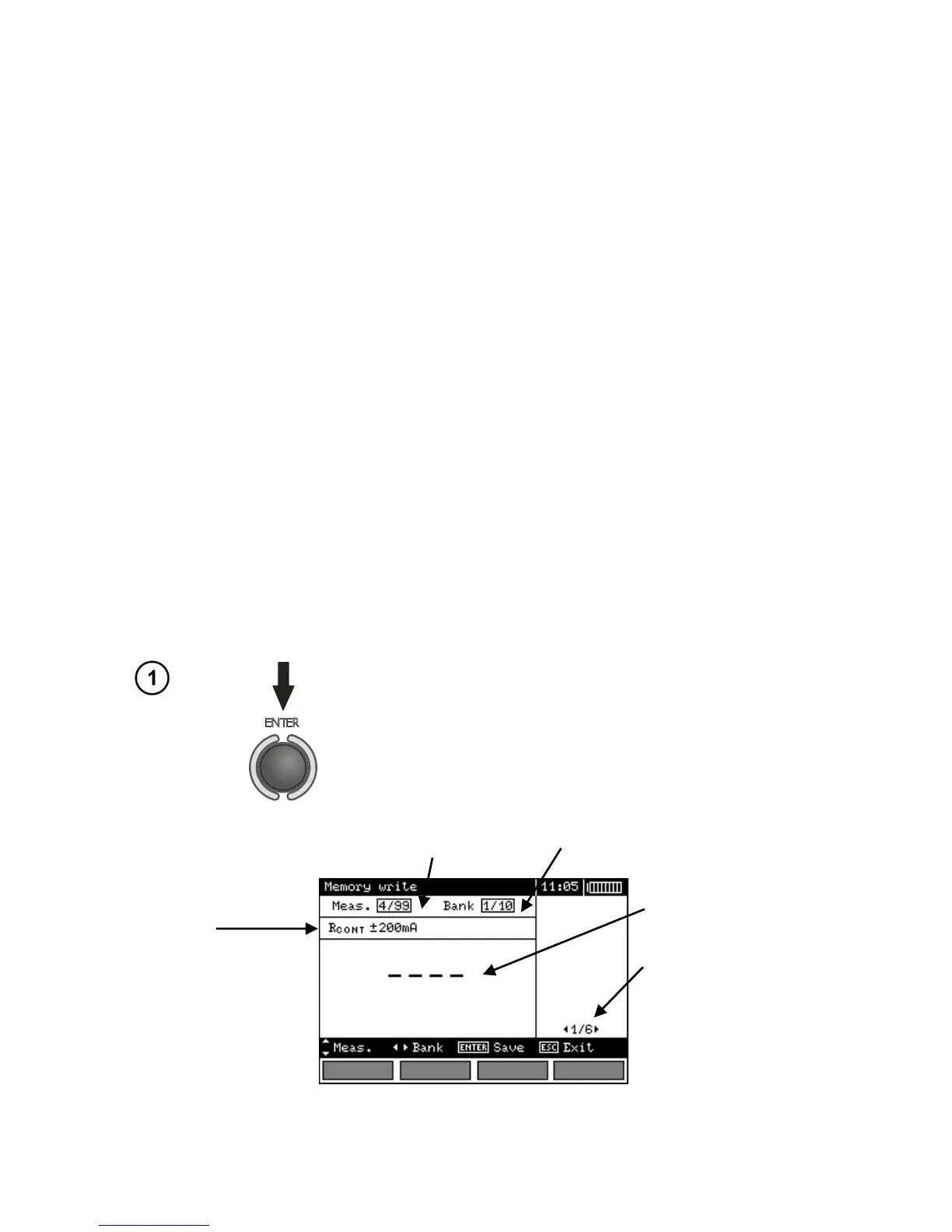
MPI-520 meters are equipped with the memory that can store 50,000 single measurement results.
The whole memory is divided into 10 memory banks each of them containing 99 memory cells.
Thanks to dynamic memory allocation, each of the memory cells can contain different quantity of sin-
gle measurement results, depending on the needs. Optimal use of the memory can be ensured in this
way. Each measurement result can be stored in a memory cell marked with a selected number and in
a selected memory bank. Thanks to this, the user of the meter can, at his/her option, assign memory
cell numbers to individual measurement points and the memory bank numbers to individual objects as
well as the user can perform measurements in any sequence and repeat them without losing other
data.
Memory of measurement result data is not deleted when the meter is switched off. Thanks to
this, the data can be later read or sent to a computer. Also, the number of a current memory cell or
memory bank is not changed.
Remarks:
- Results of measurements performed for all measuring functions can be stored in one memory cell.
- When autoincrementing of memory cell number is deactivated, a single result (group of results)
stored into the memory does not increase automatically the number of the current memory cell in or-
der to enable storing in this memory cell successive measurement results concerning a given meas-
urement point (object). If series of measurements are made for one function, autoincrementing of
memory cell number can be set in MENU. Such autoincrementing takes place after each case of data
storing in the memory (activation of autoincrementing – point 2.1.5).
- Only the results of the measurements started by pressing START key button can be stored in the
memory (except autozeroing in low-voltage measurement of resistance).
- Deletion of the memory is recommended after reading the data or before performing a new series of
measurements that may be stored into the same memory cells as the previous ones.
4.1 Recording measurement result data in the memory
 Loading...
Loading...