| Functionality | 33
For example if the correction values for pixel (row,col)=(12;33) are (-1.1; 0.8): Final output data for the pixel is found
from (row,col)=(10.9; 33.8) by interpolating adjacent pixel data values.
Wavelength calibration, smile and keystone corrections are turned on and off with the same activation command at the
same time.
Offset correction
The offset correction subtracts a configurable positive or negative value from the live image and thus reduces the
fixed pattern noise of the CMOS sensor. In addition, hot pixels can be removed by interpolation. The gain correction
can be used to flatten uneven illumination or to compensate shading effects of a lens. Both offset and gain correction
work on a pixel-per-pixel basis, i.e. every pixel is corrected separately. For the correction, a black reference and a
grey reference image are required. Then, the correction values are determined automatically in the camera.
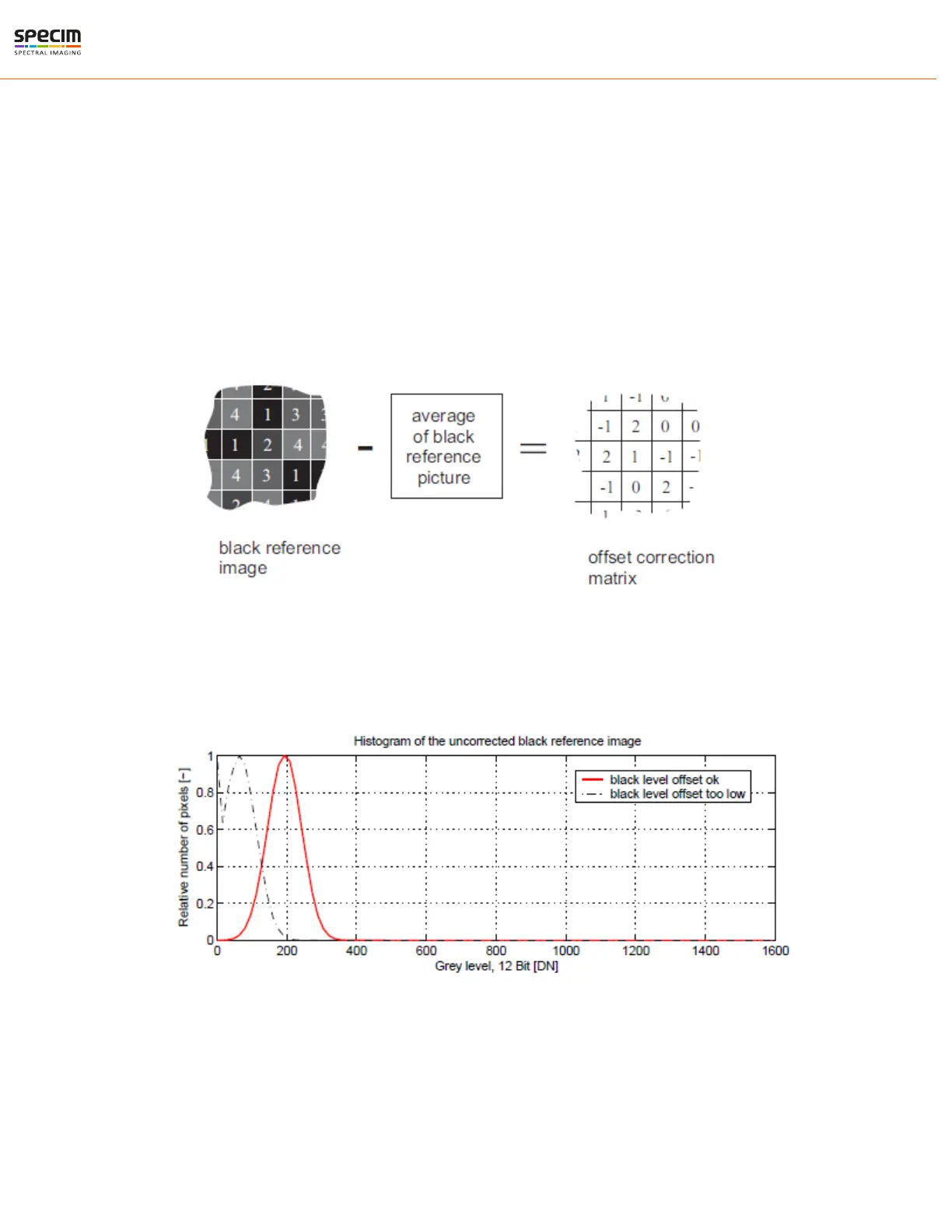
The offset correction is based on a black reference image, which is taken at no illumination (e.g. lens aperture
completely closed). The black reference image contains the fixed-pattern noise of the sensor, which can be subtracted
from the live images in order to minimise the static noise.
Offset correction algorithm
After configuring the camera with a black reference image, the camera is ready to apply the offset correction:
1.
Determine the average value of the black reference image.
2.
Subtract the black reference image from the average value.
3.
Mark pixels that have a grey level higher than 1008 DN (@ 12 bit) as hot pixels.
4.
Store the result in the camera as the offset correction matrix.
All rights reserved - Specim, Spectral Imaging Oy Ltd.
 Loading...
Loading...