Fuel Injection (Fuel System)
SENSORS AND SWITCHES
FU-17
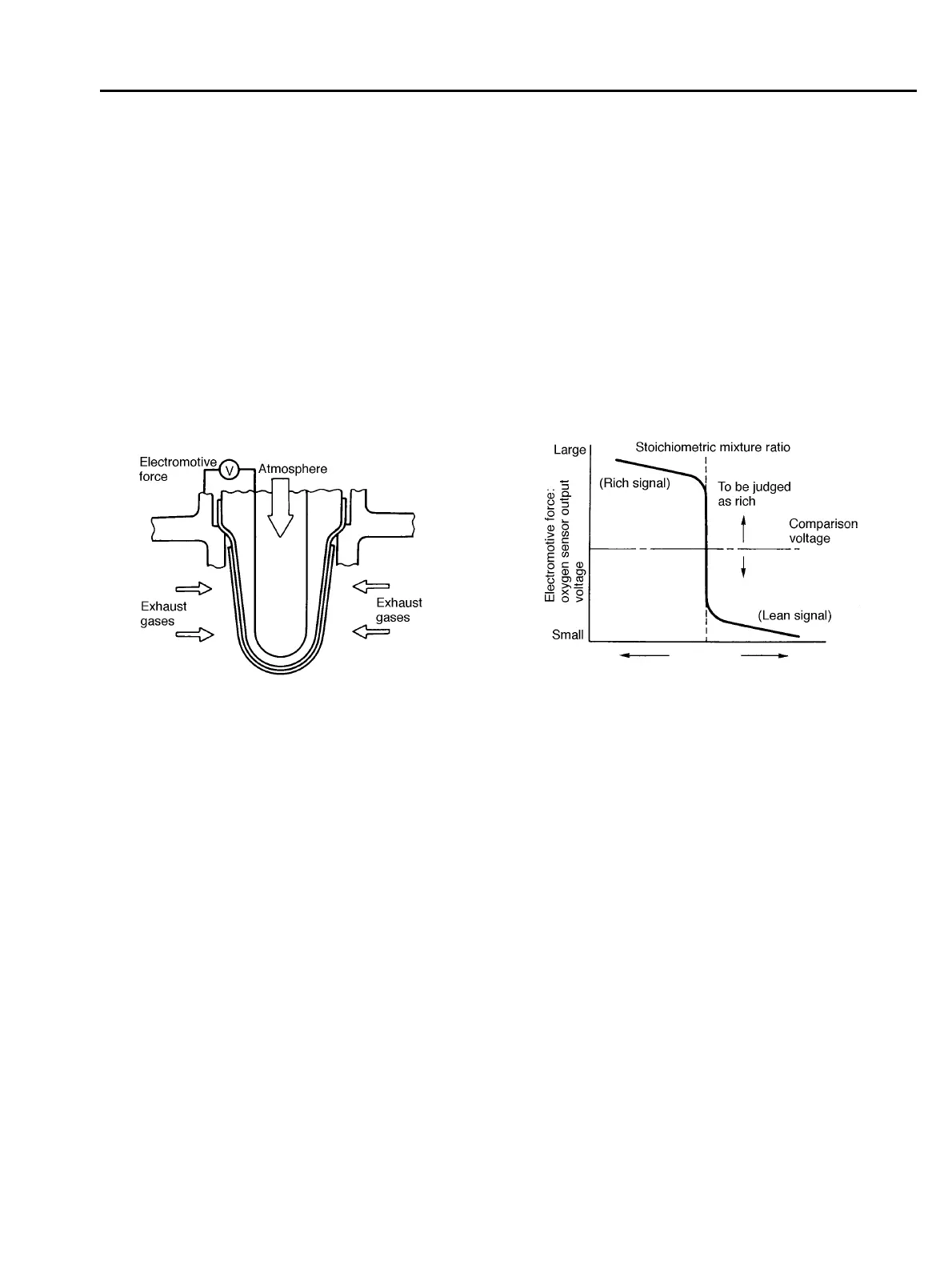
! When rich air-fuel mixture is burnt in the cylinder, the oxygen in the exhaust gases is almost
completely used in the catalytic reaction by the platinum coating on the external surface of the zir-
conia tube. This results in a very large difference in the oxygen ion concentration between the in-
side and outside of the tube, and the electromotive force generated is large.
! When a lean air-fuel mixture is burnt in the cylinder, relatively large amount of oxygen remains
in the exhaust gases even after the catalytic action, and this results in a small difference in the
oxygen ion concentration between the tube’s internal and external surfaces. The electromotive
force in this case is very small.
! The difference in oxygen concentration changes drastically in the vicinity of the stoichiometric
air-fuel ratio, and hence the change in the electromotive force is also large. By using this informa-
tion, the ECM can determine the air-fuel ratio of the supplied mixture easily. The rear oxygen sen-
sor does not generate much electromotive force when the temperature is low. The output
characteristics of the sensor stabilize at a temperature of approximately 300 to 400°C (572 to
752°F).
Lean Air-fuel ratio
To be judged
as lean
Rich
G2H0038B
W2290GE_03_FU-.fm 17 ページ 2001年4月11日 水曜日 午前9時36分
 Loading...
Loading...











