38
Pseudobinary Formats
Pseudobinary formats produce ASCII reports of 6-bit pseudo-binary formatted data
values. The formats are “pseudo”-binary, because each sensor value is expressed in the
range of ASCII characters, but not in such a way that is readily human-readable.
Pseudobinary B (Interleaved and Non-Interleaved)
The Pseudobinary-B Interleaved format is identical to the 8210 binary transmission
format. “Interleaved” means the most recent values of all sensors come first, followed by
the next most recent, and so on. “Non-interleaved” means all the data for sensor 1 is
followed by all the data for sensor 2, and so on, i.e., the data is not “interleaved”
according to time.
This pseudobinary format cannot be easily read by a person. Here’s is an example
message:
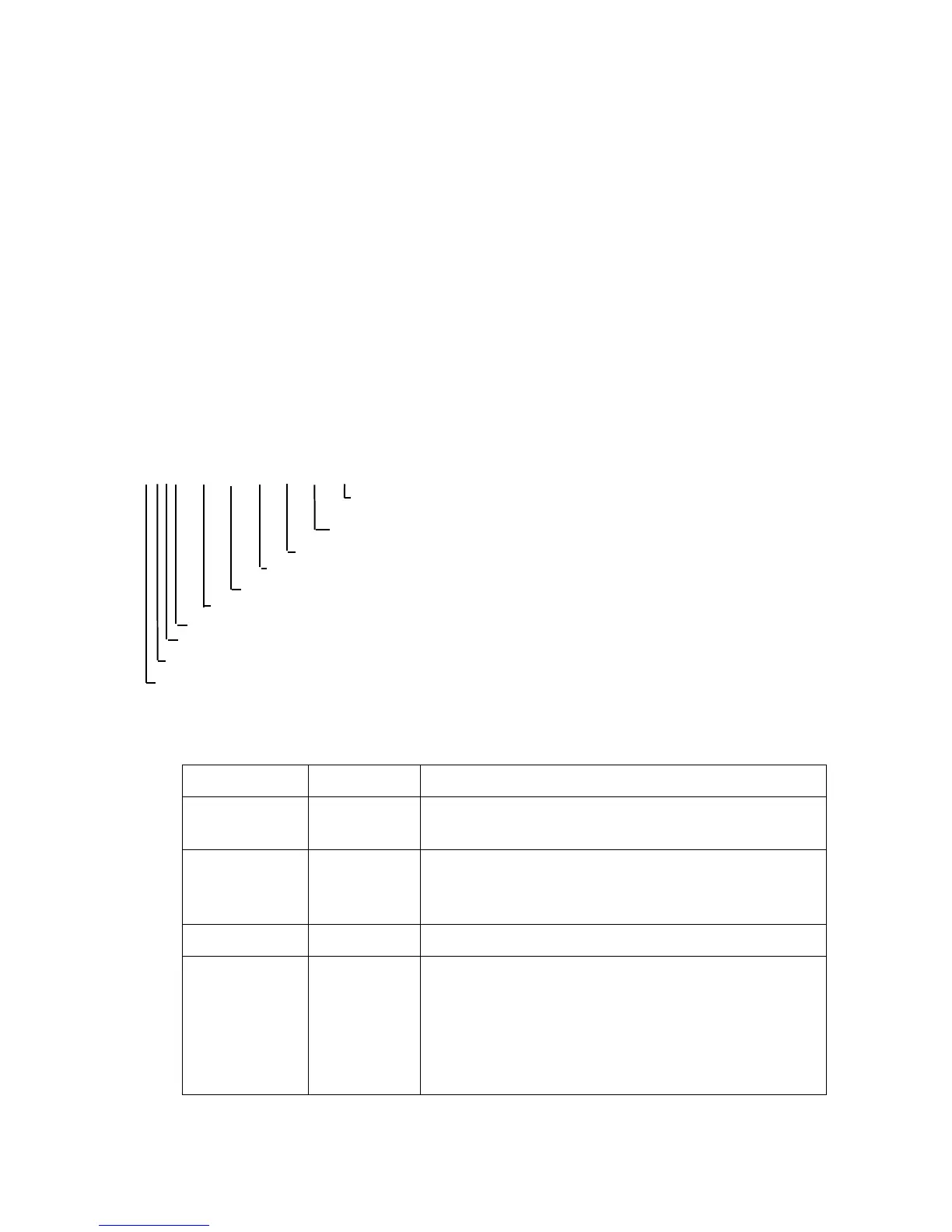
1@@Gt@Sx@@i@Gs@Sr@@iI
Battery Voltage
Temp #2
Precip #2
Stage #2
Temp #1
Precip #1
Stage #1
Delta Time
Group ID
B
Block ID
Pseudobinary-B Format
BLOCK-IDENTIFIER is always sent as "B" to
indicate that this is the pseudobinary B format.
GROUP-ID can be "1" to indicate a scheduled
transmission, “2” meaning an alarm transmission,
and “3” indicating a forced transmission.
Age in minutes of the most recent data
Data in either interleaved, or non-interleaved
format. The example above shows the data
interleaved (most recent of all sensors followed by
next oldest, and so on). See the section below,
“Six-Bit Binary Encoded Format” for details on
how these values are encoded.
 Loading...
Loading...