DC Inverter Air
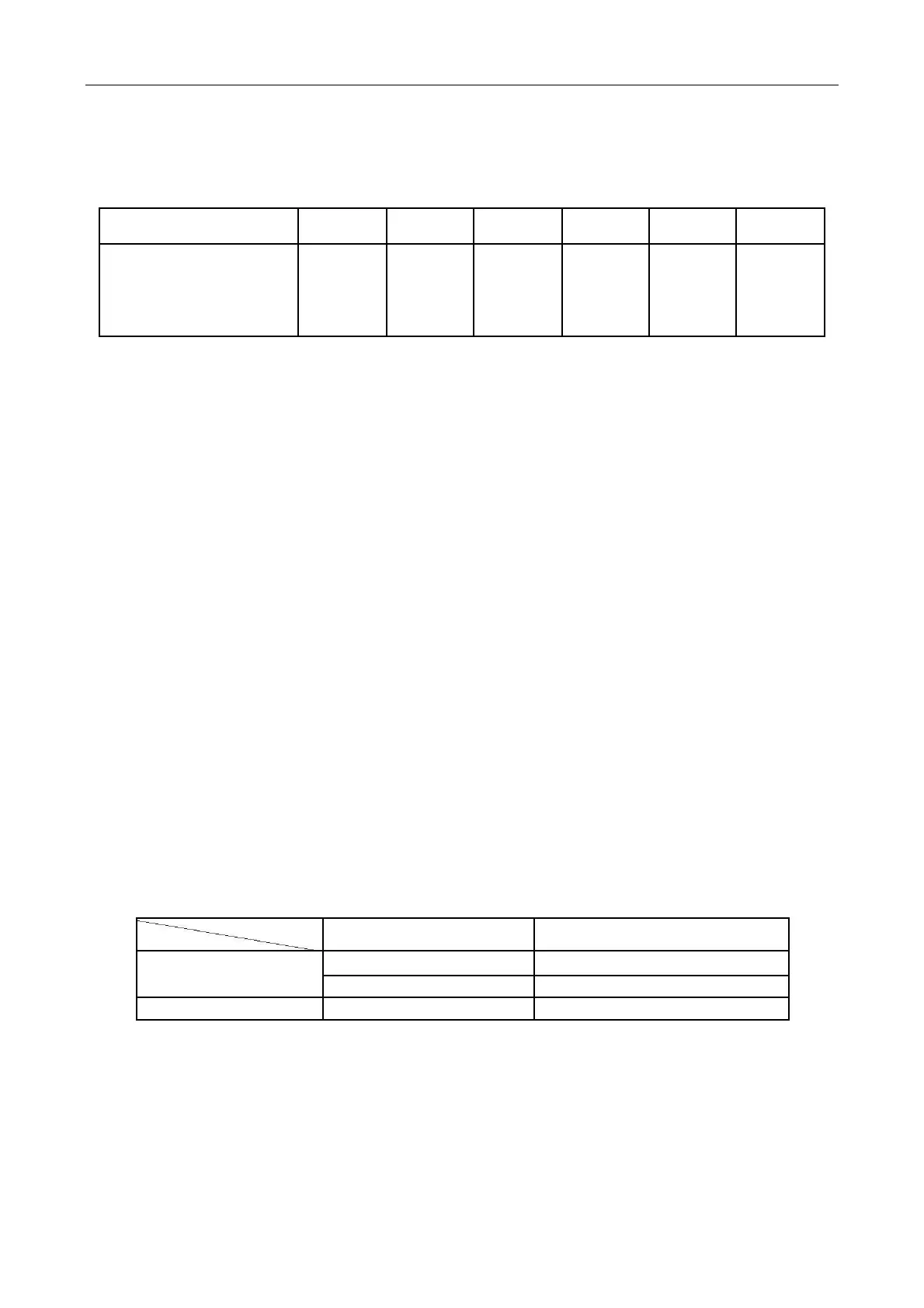
Recharging Amount: R (Kg) = (L1‐L2)×A/m)
Where, L1— actual length of liquid pipe (m);
L2— actual standard length for delivery (m) (see the Recharging label of the
outdoor unit)
A—The refrigerant to be added for pipe m, see the following table.
Add R410A for an increase
C. Correctly measure the refrigerant using the scale and filler tank;
D. Connect the filler tank, instrument manifolds and maintenance valve of liquid pipe of outdoor unit (at
high‐pressure side) and charge the refrigerant in its liquid state. The air in the hose and manifold
must be removed by the refrigerant before the recharging operation.
E. After completing the recharging operation, check whether there is refrigerant leakage at the flare
positions of indoor/outdoor units;
F. Record the adding amount of refrigerant onto the refrigerant indicator nameplate of outdoor
unit; G. The recharged amount shall be measured by the electronic scale.
9. Heat Insulation Works
9.1. Insulation Materials and Thickness
1) Insulation Materials
The insulation materials shall use the materials that can withstand the temperature of pipes: the
withstand pressure at high‐pressure side shall not be less than 70℃ and at low‐pressure side shall
not be less than 120℃.(no such a requirement at the low‐pressure side for single‐cold unit) For
example: heat‐pump type – heat‐resisting polyethylene foam (over 120℃)
Single‐cold type – foaming polyethylene (over 100℃).
2)Thickness selection of insulation materials:
Thickness of Insulation Materials
9.2. Heat Insulation of Refrigerant Pipes
1) Operation Sequence
A. The non‐welded or non‐connected positions shall be subject to the heat‐insulation treatment prior
to the laying of pipes;
74/ 113

 Loading...
Loading...