Chapter 9
Routed IPoA
E-DOC-CTC-20051017-0167 v1.0
75
9 Routed IPoA
Introduction Routed IP over ATM, also referred to as RFC2684 Routed relies on standard IP
Routing for its forwarding.
Features Routed IPoA:
Provides Always-On type of connections.
Is auto-configurable if DHCP is enabled on IPoA interfaces.
Allows multiple users to simultaneously share a single IP address in case
NAPT is enabled on the IPoA interface.
Allows your network to be shielded from the Internet via the SpeedTouch™
programmable firewall.
Routed IPoA vs. connection
service
The Routed IPoA Packet Service relies on the AAL5/RFC2684/Routed IP Connection
Service to achieve end-to-end connectivity.
For the SpeedTouch™ this boils down in using the IPoA (IP over ATM) Connection
Service type, which implies the encapsulation of IP packets in AAL5/ATM.
The SpeedTouch™ products are compliant with RFC2684 “Multiprotocol
Encapsulation over ATM Adaptation Layer 5” and support the LLC/SNAP and VC-
MUX method for Routed non-ISO PDUs.
Routed Ethernet vs TCP/IP
Configuration
As the Routed IPoA Packet service completely relies on the TCP/IP Protocol stack, all
that is required on the local LAN is the TCP/IP protocol.
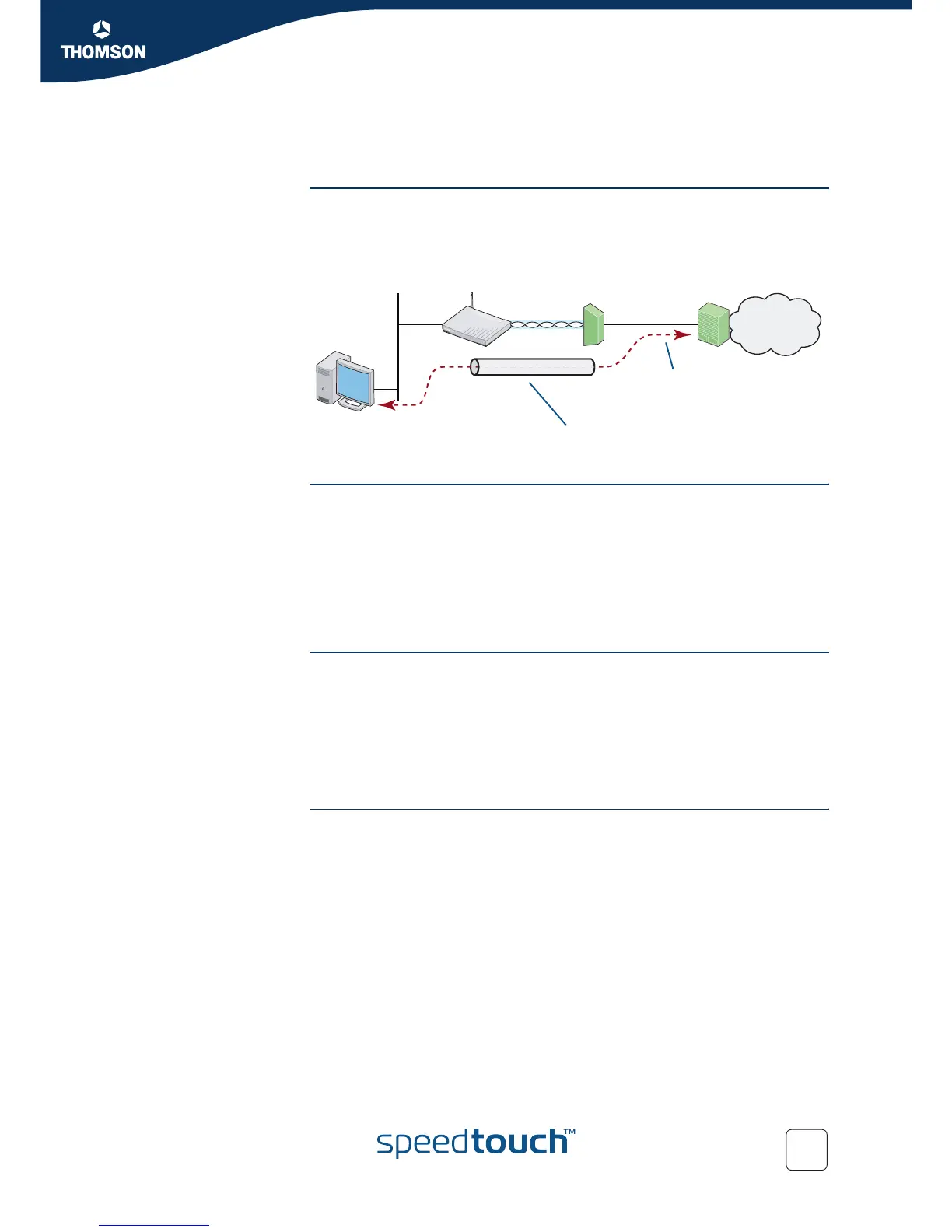
DSLAM
SpeedTouch™ operating as
DHCP server and
Internet IP Gateway router
PC configured
as DHCP client
Virtual Channel with:
ATM Encapsulation Type: VC-MUX
Connection Service Name: Routed IPoA
Connection Service Type: IPoA
BRAS
Internet

 Loading...
Loading...











