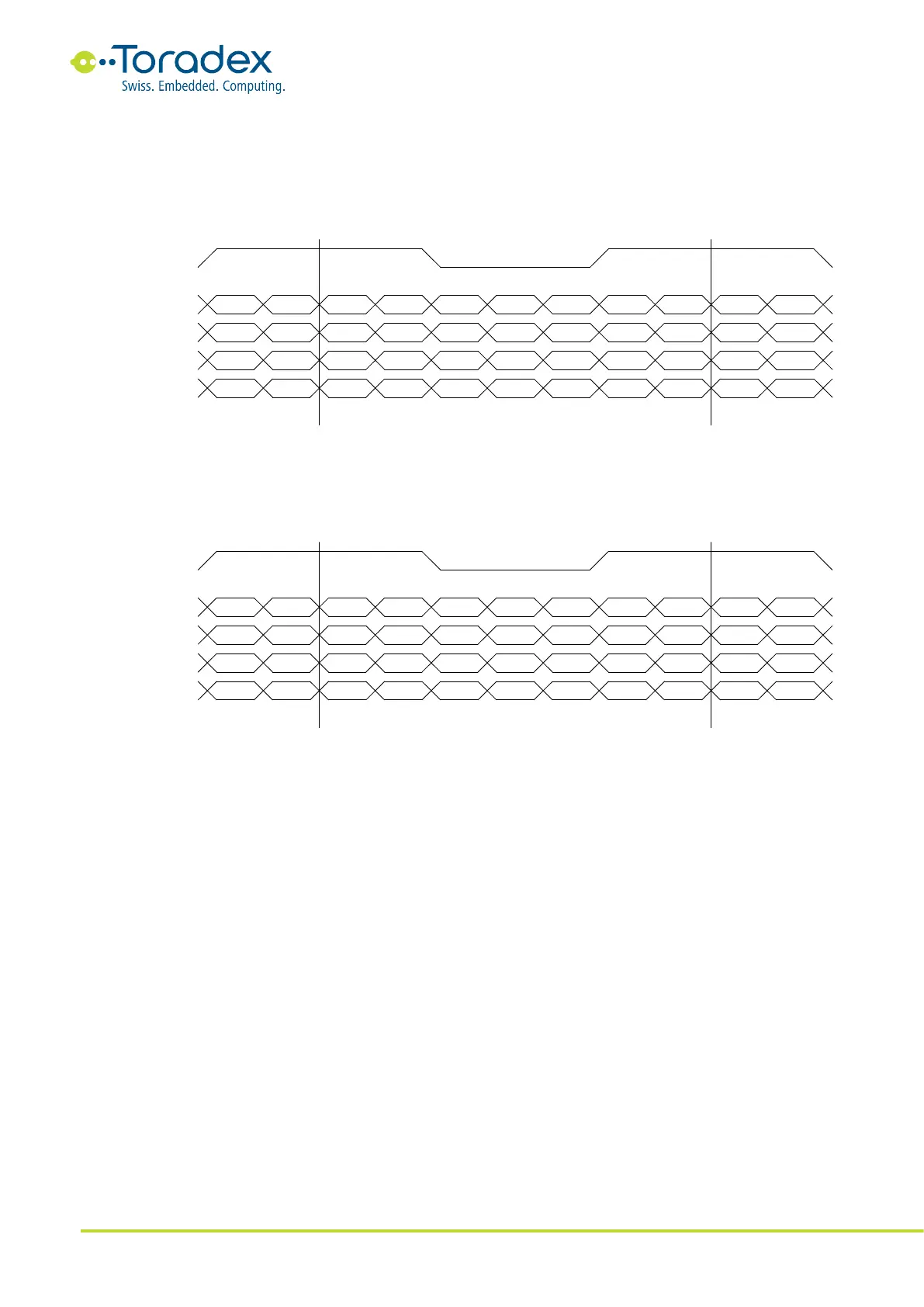
24-bit JEIDA Color Mapping
The JEIDA color mapping is compatible with the 18bit LVDS interface. Therefore, the mapping is
sometimes also called "24bit / 18bit Compatible Color Mapping". The signal names of the color
bits are renamed (e.g., the 18bit R5 is renamed to 24bit R7), but the MSB position is kept the
same. The additional least significant bits R0, R1, G0, G1, B0, and B1 are located at the additional
fourth LVDS data pair.
Figure 10: 24-bit JEIDA LVDS Color Mapping
24-bit VESA Color Mapping
Most of the 24bit LVDS displays follow the VESA Color mapping. The VESA color mapping does not
rename the signal bits. This means that the MSB position is changed since they are available at the
additional data pair. Therefore, the VESA color mapping is not compatible with the 18bit interface.
Figure 11: 24-bit VESA LVDS Color Mapping
2.4.3 Unused Parallel RGB Interface Signal Termination
All unused parallel RGB interface signals can be left unconnected.
2.5 HDMI/DVI
The HDMI and DVI interface uses a TMDS compatible physical link to transfer video and optional
audio data. While electrically, HDMI and DVI are similar, but there can be a few differences in
their protocols. HDMI is the DVI successor and specifies the additional transport for audio data and
content protection (HDCP). As HDMI is backward compatible, HDMI devices (monitor, television
set, and others) work with DVI signals. Forward compatibility is not guaranteed. Not all DVI
displays accept the HDMI protocol or are HDCP compatible. Please read the datasheet of the
Colibri modules for more information about the provided HDMI and DVI protocols.
The HDMI and DVI interface define different connectors. There are passive adapters available in
both types. Please be advised that HDMI and HDCP are required to be licensed. The HDMI/DVI
signals are available on a dedicated FFC connector. Check carefully to confirm which modules
provide the interface.
 Loading...
Loading...