Vertiv
™
|Liebert
®
MBSM
™
User Manual | 14
2.8.1 Liebert MBSM Activation on Bus A
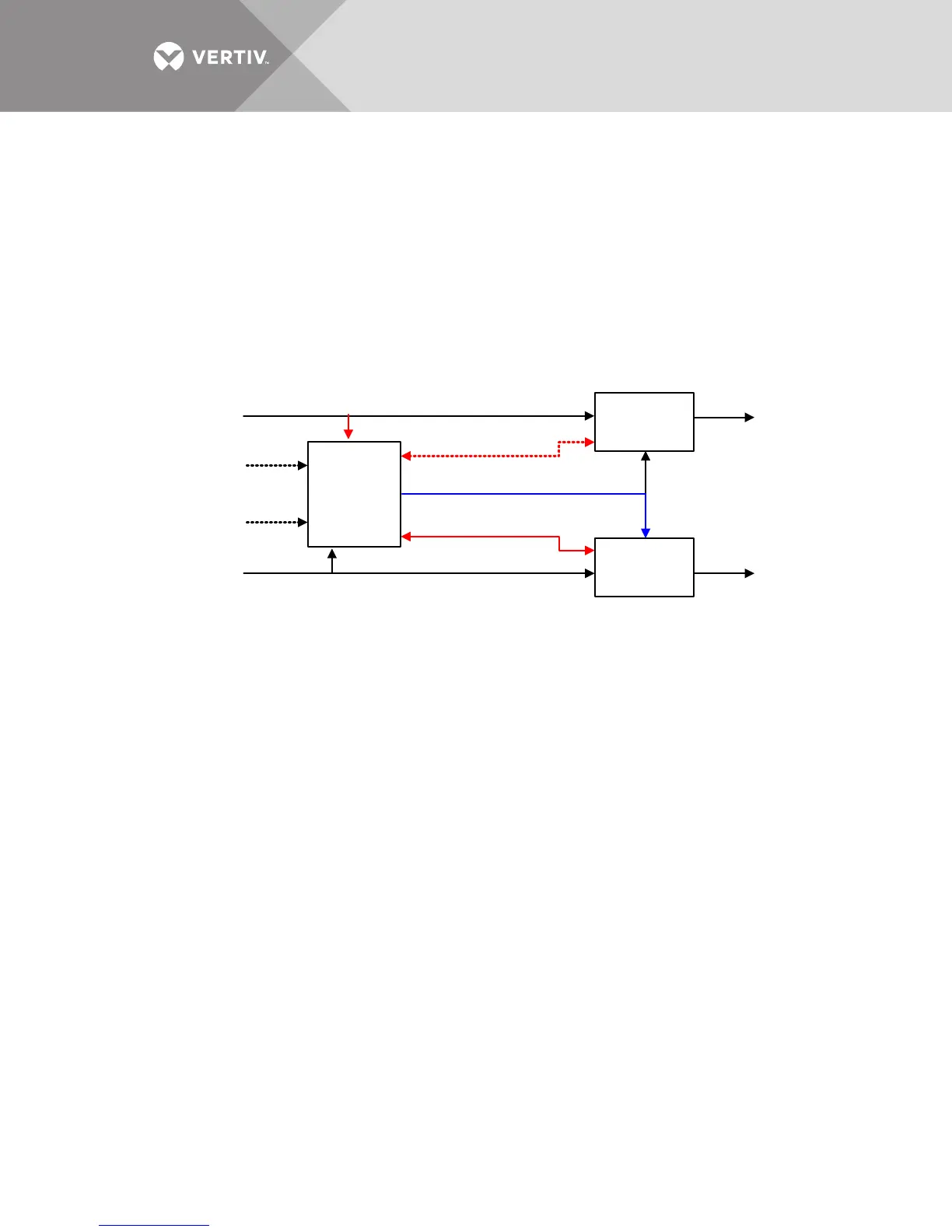
Both the power buses are inside limits and the Liebert MBSM is set on the Bus A; this means that
the frequency reference generated by the Liebert MBSM is actually phase referred to the Bus A. If
the phase difference between the two buses is detected over the set limit, the Liebert MBSM will
send a signal to the UPS system B forcing it to synchronize to the generated frequency reference
(see Figure 8).
The UPS A is naturally synchronized with its incoming Bus A, while UPS B is forced by the Liebert
MBSM to sync the frequency reference generated on the Bus A phase reference. The UPS B is
actually out of sync with its own input power bus. UPS B can transfer the critical Bus B on static
bypass input (input power Bus B) but this will cause a critical bus interruption of 20ms.
Figure 8 Synchronizing to Bus A for Dual Bus System
Should the phase error between the two power buses return to the required condition, the Liebert
MBSM will release the CNTRL command, letting System B return to natural operation (Liebert
MBSM returns to passive operation).
2.8.2 Liebert MBSM activation on Bus B
Both the power buses are inside limits and the Liebert MBSM is set on the Bus B; this means that
the frequency reference generated by the Liebert MBSM is actually phase referred to the Bus B. If
the phase difference between the two buses is detected over the set limit, the Liebert MBSM will
send a signal to the UPS system A forcing it to synchronize the generated frequency reference
(Figure 9). The UPS B is naturally synchronized with its incoming Bus B, while UPS A is forced by
the Liebert MBSM to sync the frequency reference generated on the Bus B phase reference. The
UPS A is actually out of sync with its own input power bus. Should the UPS A be in need to
transfer the critical Bus A on static bypass input (input power Bus A), this will be possible with
limited critical bus interruption (20ms).
UPS
System A
UPS
System B
MSBM
Power Bus A
Power Bus B
Secure
Bus B
Secure
Bus A
System A CNTRL
System B CNTRL
Bus B
Remote
CNTRL
Bus A
Remote
CNTRL
Frequency Reference

 Loading...
Loading...











