while True:
try:
io.loop()
Second, you have a block of code that runs every 10 seconds. Inside, you obtain a
"random" value between 0-255 inclusive, print it to the serial console, and publish it
to an Adafruit IO feed. Finally, you reset timestamp so the block of code knows when
another 10 seconds has passed, and runs again.
[...]
if (time.monotonic() - timestamp) >= 10:
random_number = "{}".format(randint(0, 255))
print("Current 'random' number: {}".format(random_number))
io.publish("random", random_number)
timestamp = time.monotonic()
If at any time WiFi or Adafruit IO disconnects, the code will print the error to the serial
console, and the board will hard reset after 30 seconds.
[...]
except Exception as e:
print("Failed to get or send data, or connect. Error:", e,
"\nBoard will hard reset in 30 seconds.")
time.sleep(30)
microcontroller.reset()
That's all there is to using CircuitPython and Adafruit IO to send data to Adafruit IO,
and receive data from it!
I2C
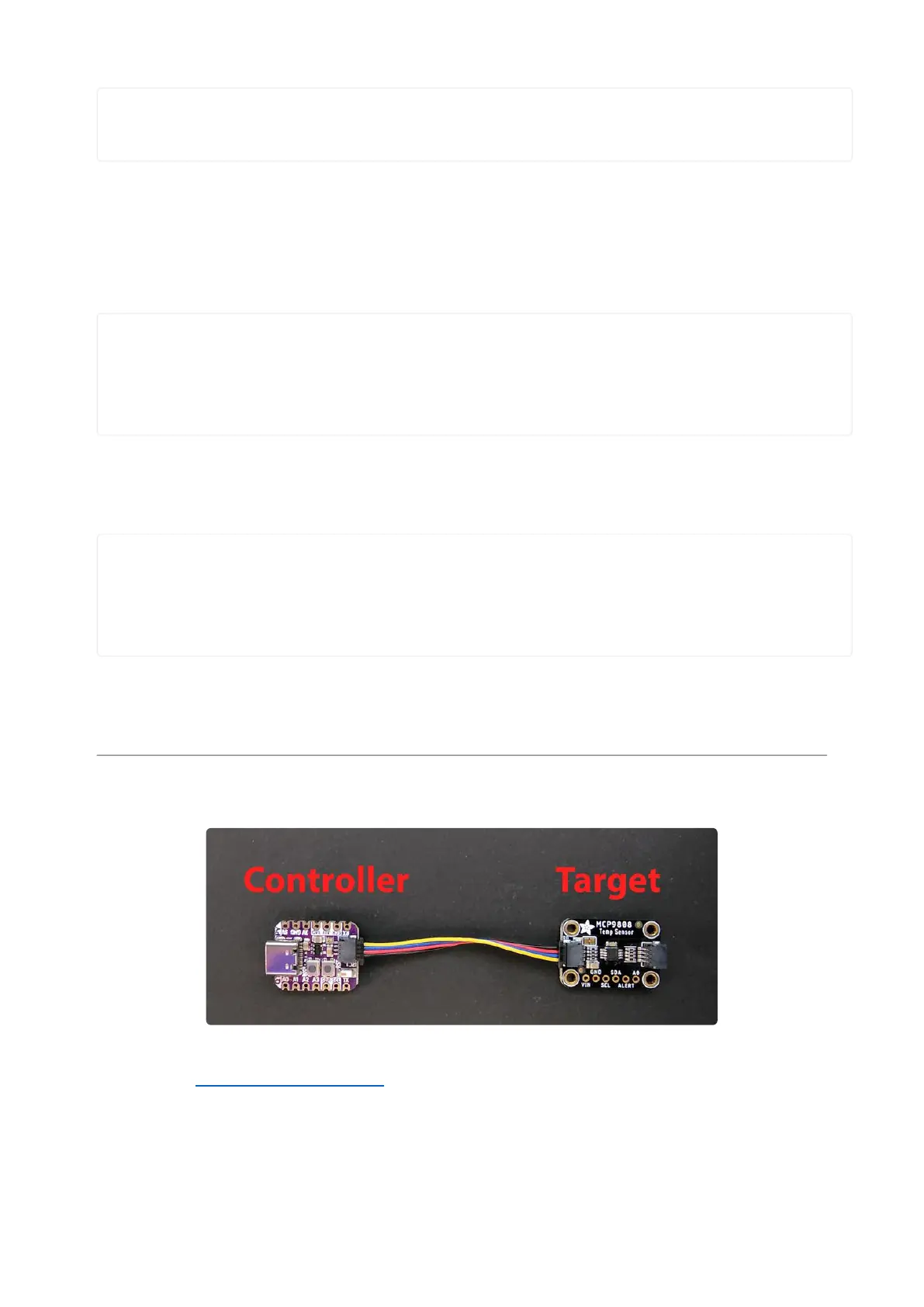
The I2C, or inter-integrated circuit(), is a 2-wire protocol for communicating with
simple sensors and devices, which means it uses two connections, or wires, for
transmitting and receiving data. One connection is a clock, called SCL. The other is
the data line, called SDA. Each pair of clock and data pins are referred to as a bus.
©Adafruit Industries Page 157 of 263

 Loading...
Loading...