Publication 1734-UM014A-EN-P - November 2010
Configure the Adapter for Your EtherNet/IP Network 19
Gateway Address
This section applies to multi-network systems. If you have a single network
system, refer to the next section.
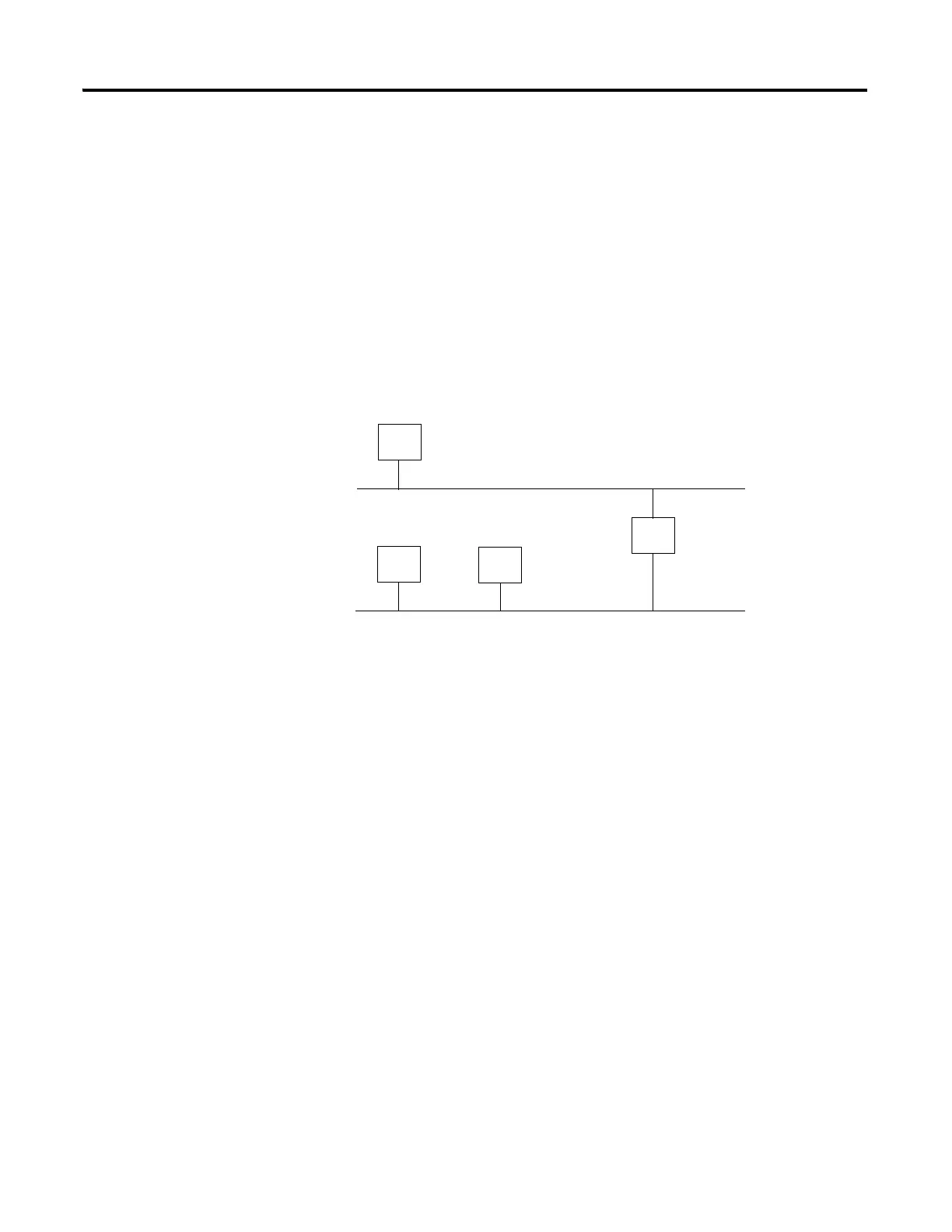
The Gateway Address is the default address of a network. It provides a single
domain name and point of entry to the site. Gateways connect individual
physical networks into a system of networks.
When a node needs to communicate with a node on another network, a
gateway transfers the data between the two networks. The figure shows
gateway G connecting Network 1 with Network 2.
When host B with IP address 128.2.0.1 communicates with host C, it knows
from C’s IP address that C is on the same network. in an Ethernet
environment, B can then resolve C’s IP address into a hardware address (MAC
address) and communicate with C directly.
When host B communicates with host A, it knows from A’s IP address that A
is on another network (the network IDs are different). In order to send data to
A, B must use the IP address of the gateway connecting the two networks. In
this example, the gateway’s IP address on Network 2 is 128.2.0.3.
The gateway has two IP addresses (128.1.0.2 and 128.2.0.3). The first must be
used by hosts on Network 1 and the second must be used by hosts on
Network 2. To be usable, a gateway of a host must be addressed using a
network ID matching its own.
Network 1
Network 2
128.1.0.1
128.2.0.1 128.2.0.2 128.2.0.3
128.1.0.2
A
B
G
C

 Loading...
Loading...











