Chapter 2 Designing an RQ Experiment
Selecting the Chemistry
Applied Biosystems 7300/7500/7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System Relative Quantification Getting Started Guide 11
Notes
2
Selecting the Chemistry
About
Chemistries
Applied Biosystems offers two types of chemistries that you can use to detect PCR
products on real-time instruments, as explained in the following table. Both TaqMan
®
probe-based and SYBR
®
Green I dye chemistries can be used for either one- or two-step
RT-PCR. For more information about these chemistries, refer to the Real-Time PCR
Systems Chemistry Guide.
Chemistry Process
Taq M an
®
reagents or kits
Description
TaqMan reagent-based chemistry uses a
fluorogenic probe to enable detection of a specific
PCR product as it accumulates during PCR cycles.
Advantages
• Increases specificity with a probe. Specific
hybridization between probe and target
generates fluorescence signal.
• Provides multiplex capability.
• Optimized assays available.
• Allows 5′ -nuclease assay to be carried out
during PCR.
SYBR
®
Green I reagents
Description
Uses SYBR Green I dye, a double-stranded DNA
binding dye, to detect PCR products as they
accumulate during PCR cycles.
Advantages
• Reduces cost (no probe needed)
• Amplifies all double-stranded DNA
• Yields a melting profile of distinct PCR runs
• Increases signal fluorescence as amplification
product length increases.
Limitations
Binds nonspecifically to all double-stranded DNA
sequences. To avoid false positive signals, check
for nonspecific product formation using dissociation
curve or gel analysis.
3′
5′
5′
5′ 3′
3′
5′
FORWARD
PRIMER
PROBE
R = REPORTER
Q = QUENCHER
REVERSE
PRIMER
Polymerization
QR
3′
5′
5′
5′ 3′
3′
5′
Strand Displacement
Q
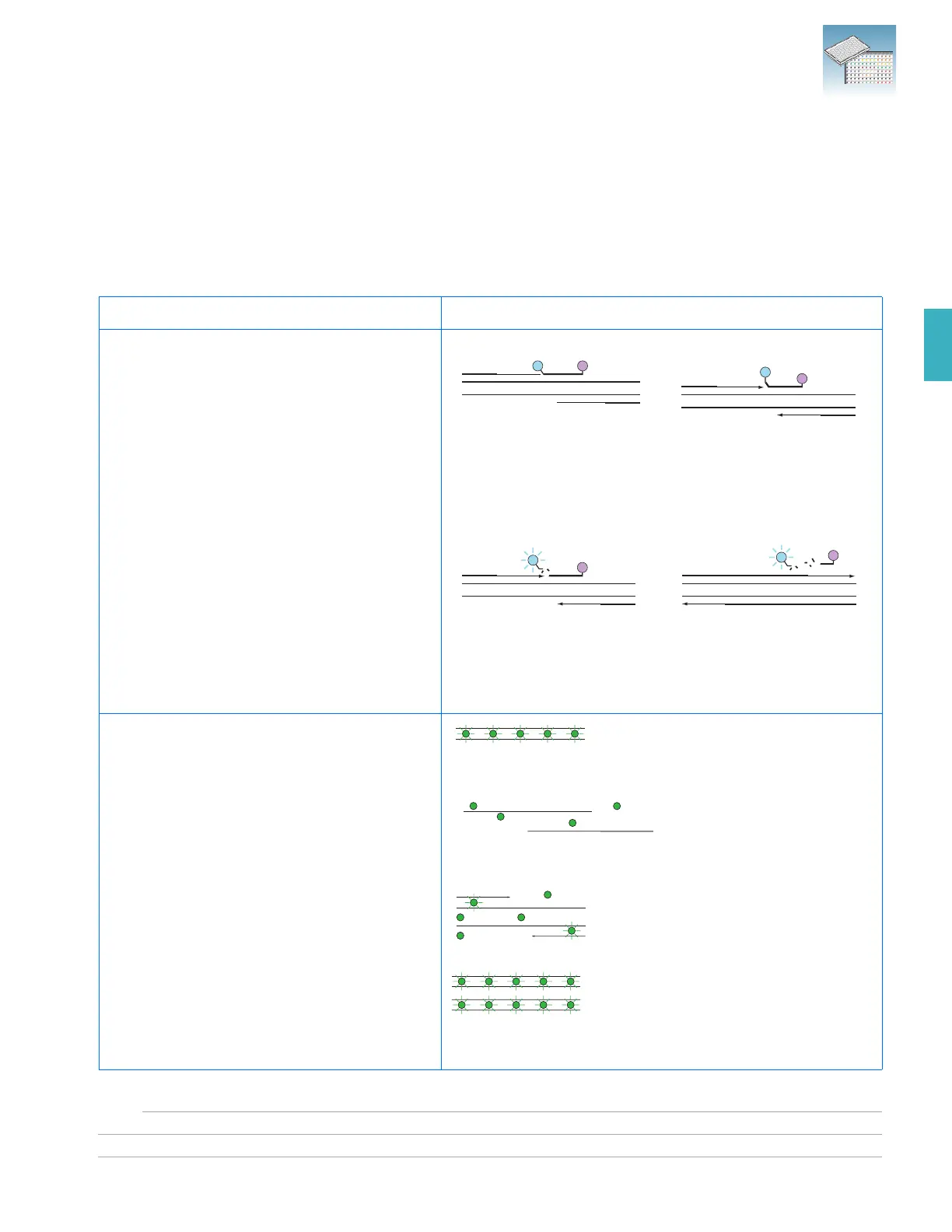
R
Step 1: A reporter (R) and a
quencher (Q) are attached to the
5' and 3' ends of a TaqMan
probe.
Step 1 (continued): When both dyes
are attached to the probe, reporter
dye emission is quenched.
3′
5′
5′
5′ 3′
3′
5′
Cleavage
Q
R
3′
5′
5′
5′ 3′
3′
5′
Polymerization Completed
Q
R
Step 2: During each extension
cycle, the AmpliTaq Gold
®
DNA
polymerase cleaves the reporter
dye from the probe.
Step 3: After being separated from
the quencher, the reporter dye
emits its characteristic
fluorescence.
FORWARD
PRIMER
REVERSE
PRIMER
Step 1: Reaction setup
The SYBR
®
Green I dye
fluoresces when bound to
double-stranded DNA.
Step 2: Denaturation
When the DNA is denatured,
the SYBR
®
Green I dye is
released and the fluorescence
is drastically reduced.
Step 3: Polymerization
During extension, primers
anneal and PCR product
is generated.
Step 4: Polymerization completed
SYBR
®
Green I dye binds to the
double-stranded product,
resulting in a net increase in
fluorescence detected by the
instrument.

 Loading...
Loading...