Asiga MAX User Guide
Copyright ASIGA © 2017 VERSION 1.04
Principle of Operation
The MAX is a 3D printer which builds objects from CAD data. The objects are built from
photopolymer resins which are liquid chemicals that can be solidified by exposure to light. A
physical model is built by solidifying successive layers of photopolymer against each other.
This process is called “stereolithography”.
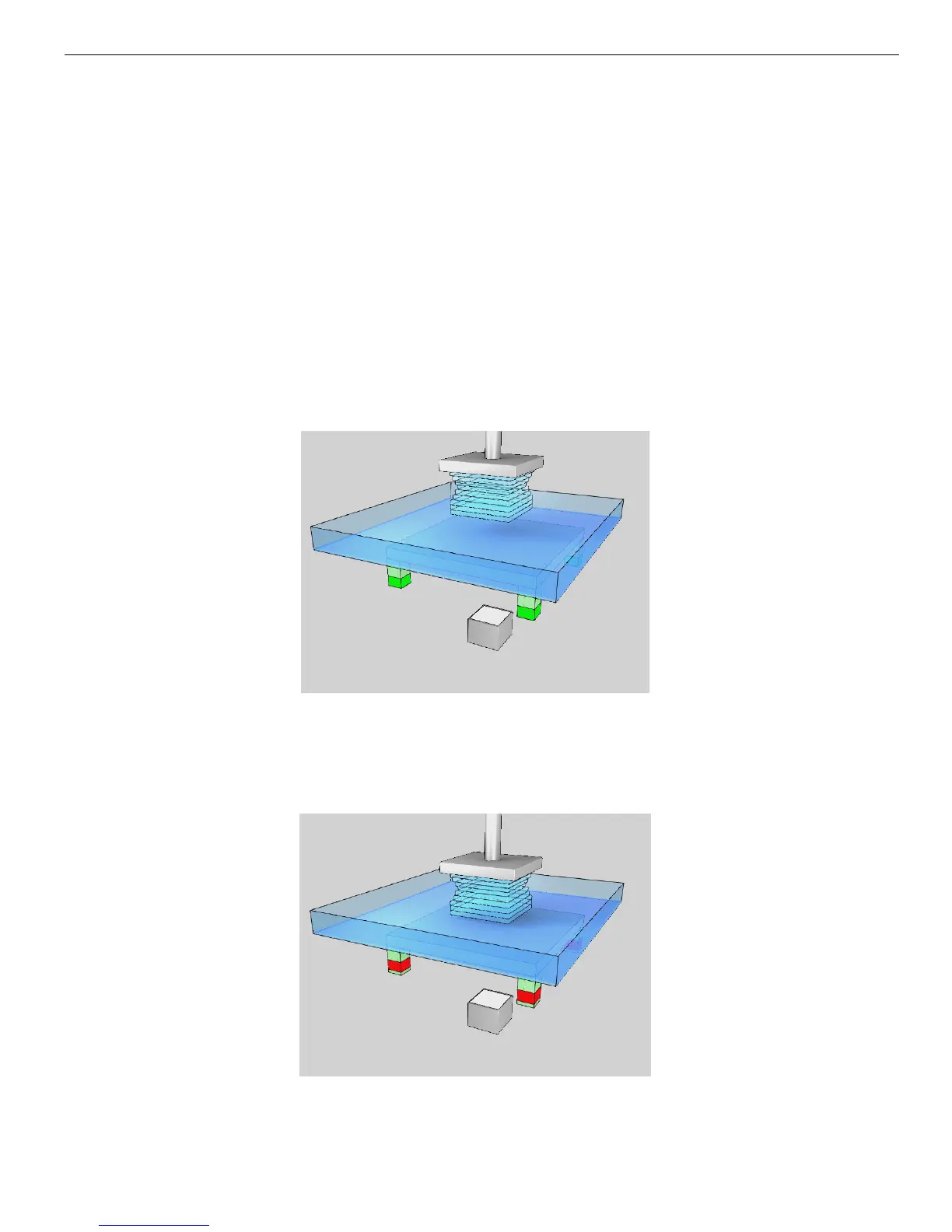
The MAX build process employs a unique feature which is referred to as the Smart
Positioning System (SPS). The SPS utilizes an array of position encoders which detect
when a layer of correct thickness is formed. The process works as follows:
1. The model under construction is positioned above the vat of photopolymer. The vat
bottom is made from a flexible transparent Teflon film which is supported by a glass
plate.
2. The model is moved downwards to one layer-thickness above the bottom of the vat.
The movement squeezes photopolymer resin out from the gap between the model
and the Teflon film. Viscous forces oppose the motion, resulting in mechanical
deflection of the apparatus.
3. Four position encoders at each corner of the glass plate precisely monitor the
mechanical deflection between the glass plate and the model under construction.
The process monitors the deflection until it is relieved.
 Loading...
Loading...