104
1.18.2 Improving the acquisition / image quality
There are several use cases concerning the acquisition / image quality of the camera:
• Correcting image errors of a sensor (p. 104)
• Optimizing the color/luminance fidelity of the camera (p. 113)
• Working With Gain And Black-Level Values Per Color Channel (p. 122)
1.18.2.1 Correcting image errors of a sensor
1.18.2.1.1 Introduction Due to random process deviations, technical limitations of the sensors, etc. there are
different reasons that image sensors have image errors. MATRIX VISION provides several procedures to correct
these errors, by default these are host-based calculations, however some camera families support camera-based
corrections, which saves dozens of % CPU load and lowers latency.
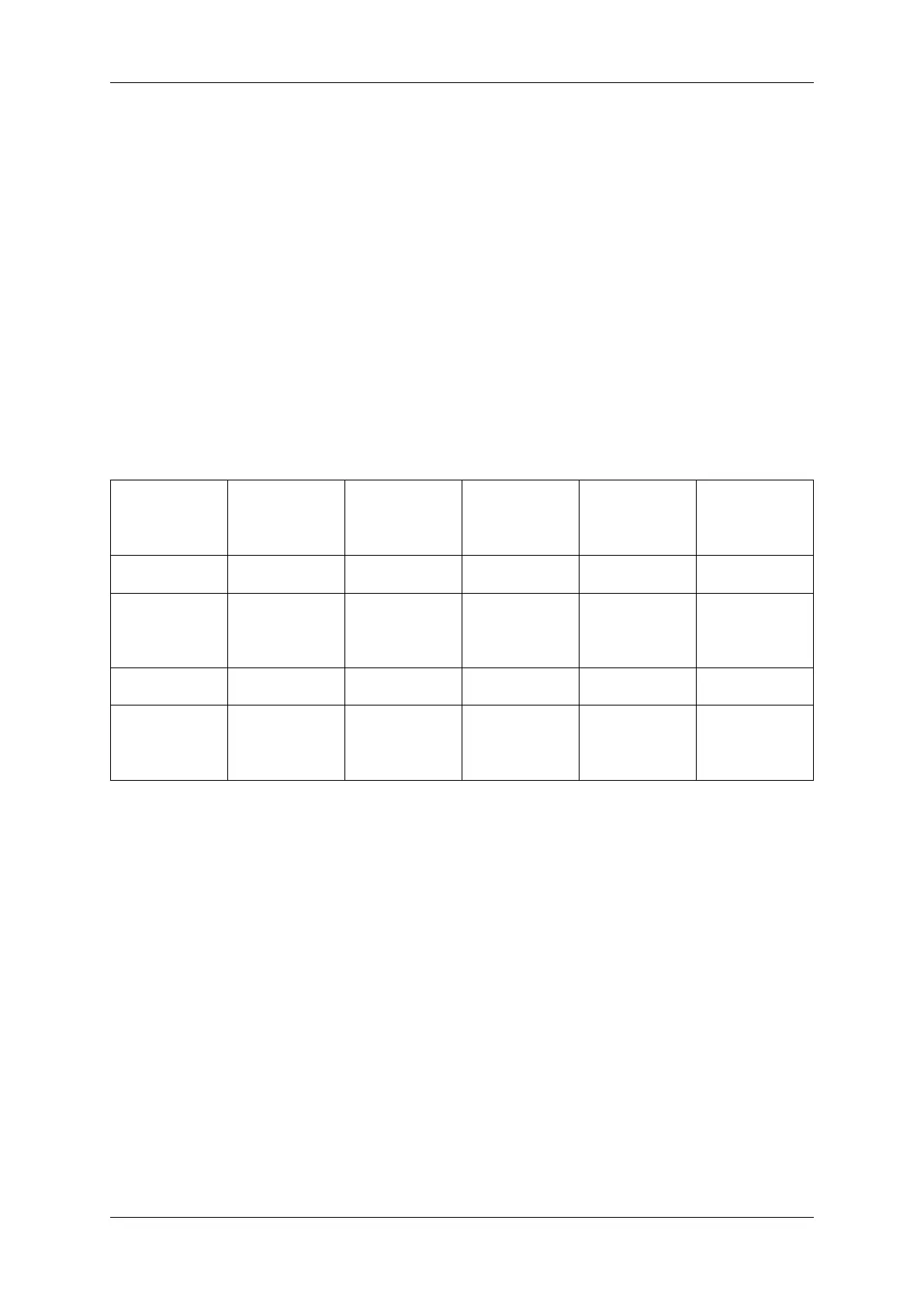
Camera Family Algorithm-←-
Based de-
tection and
correction
List-Based cor-
rection
Storing facility
for defective-
pixel list
Flat-Field Cor-
rection (Host)
Flat-Field
Correction
(Camera)
mvBlue←-
COUGAR-X
- - X X X
mvBlue←-
COUGAR-XD
If bin-
ning/decimation
is on -> no list
is stored
X X X
mvBlue←-
COUGAR-XT
X - - X X
mvBlueFOX3 If bin-
ning/decimation
is on -> no list
is stored
X X X -
Generally, removing defect pixels requires two sub-tasks:
• Detection of defective pixels
• Correction of defective pixels
Both tasks can performed in different "locations":
• Detection and correction on the host using mvIMPACT Acquire
• Detection on the host using mvIMPACT Acquire, correction on the camera using the camera's mv←-
DefectivePixelCorrectionControl in the list-based mode
• Detection and correction on the camera using mvDefectivePixelCorrectionControl in the
algorithm-based mode.
If detection is not happening in real-time, meaning during the image acquisition itself, it is necessary to store the
detected defects somewhere. This can be either on the camera or the host or both.
MATRIX VISION GmbH

 Loading...
Loading...