© 1999-2017 Citrix Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. p.197https://docs.citrix.com
Consolidation With Sharing of a Physical Port by More
Than One Instance
Apr 12, 20 13
You can enable and disable VLAN filtering on an interface as required. For example, if you need to configure more than 100
VLANs on an instance, assign a dedicated physical interface to that instance and disable VLAN filtering on that interface.
Enable VLAN filtering on instances that share a physical interface, so that traffic for one instance is not seen by the other
instance.
Note: VLAN filtering is not a global setting on the appliance. You enable or disable VLAN filtering on an interface, and the
setting applies to all instances associated with that interface. If VLAN filtering is disabled, you can configure up to 4096
VLANs. If VLAN filtering is enabled, you can configure up to 63 tagged VLANs on a 10G interface and up to 32 tagged
VLANs on a 1G interface.
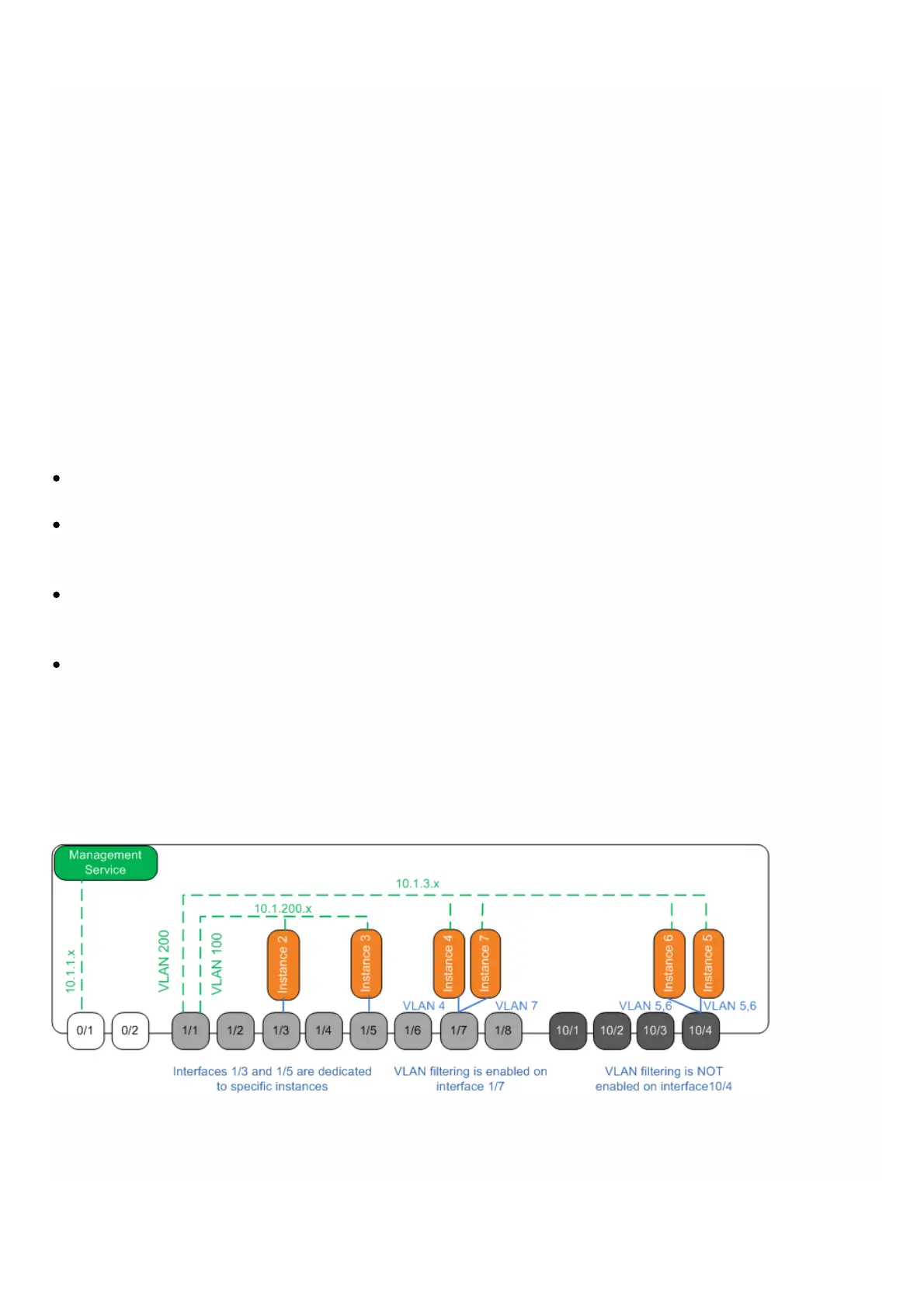
In the following example, the instances are part of multiple networks.
Interface 1/1 is assigned as a management interface to all the instances. Interface 0/1 is assigned to the Management
Service, which is part of the internal 10.1.1.x network.
NetScaler instances 2 and 3 are in the 10.1.200.x network, and instances 4, 5, 6, and 7 are in the 10.1.3.x network.
Instances 2 and 3 each have a dedicated physical interface. Instances 4 and 7 share physical interface 1/7, and instances
5 and 6 share physical interface 10/4.
VLAN filtering is enabled on interface 1/7. Traffic for Instance 4 is tagged for VLAN 4, and traffic for Instance 7 is
tagged for VLAN 7. As a result, traffic for Instance 4 is not visible to Instance 7, and vice versa. A maximum of 32 VLANs
can be configured on interface 1/7.
VLAN filtering is disabled on interface 10/4, so you can configure up to 4096 VLANs on that interface. Configure VLANs
500-599 on Instance 5 and VLANs 600-699 on Instance 6. Instance 5 can see the broadcast and multicast traffic from
VLAN 600-699, but the packets are dropped at the software level. Similarly, Instance 6 can see the broadcast and
multicast traffic from VLAN 500-599, but the packets are dropped at the software level.
The following figure illustrates the above use case.
Figure 1. Network topology of an SDX appliance with Management Service and NetScaler instances distributed across
networks
The following table lists the names and values of the parameters used for provisioning NetScaler instances 7 and 4 in this
example.
 Loading...
Loading...