5 Categories and Use of Basic Application Instructions
DVP-PM Operation Instruction
5-36
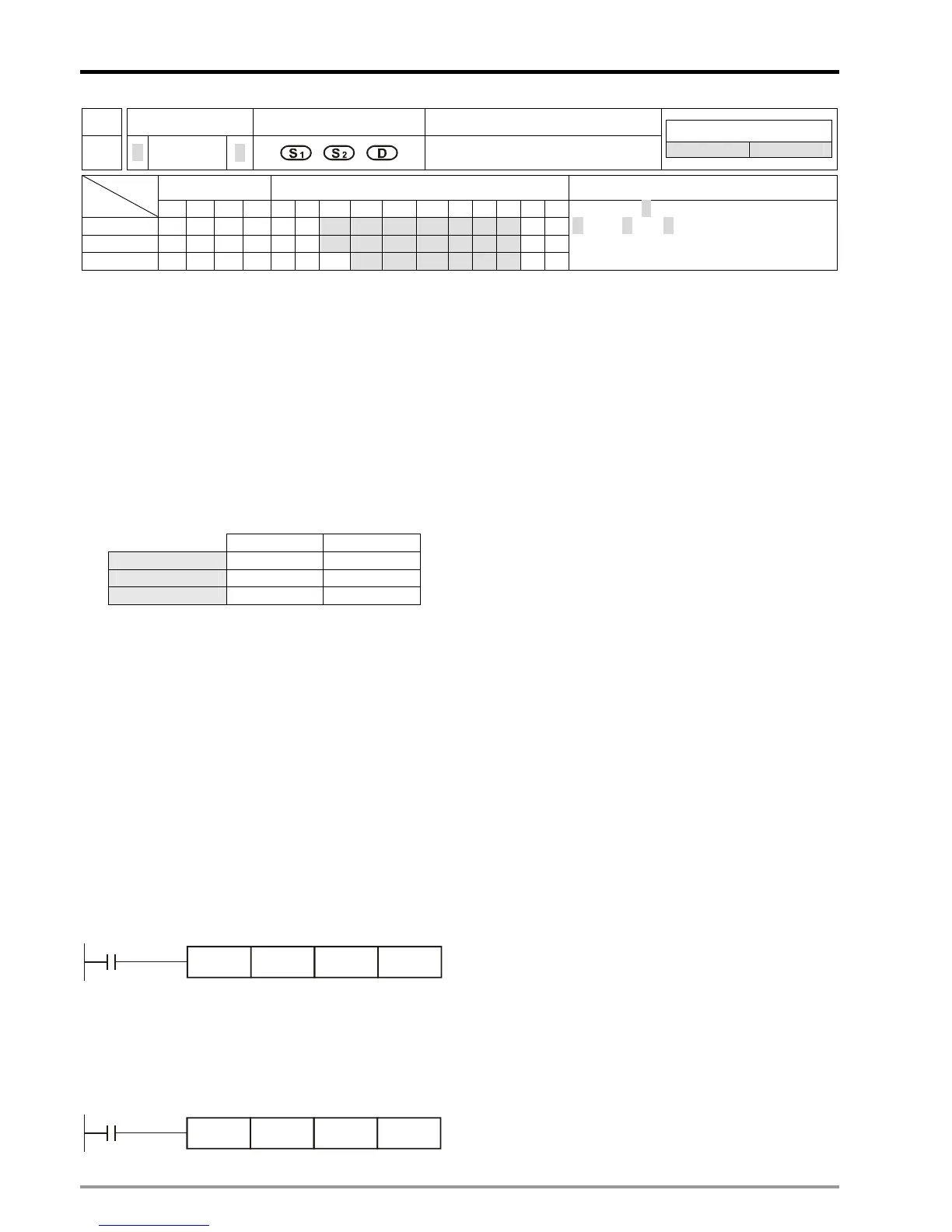
API Mnemonic Operands Function
20
D ADD
P
Addition
Controllers
20PM 10PM
Bit Devices Word Devices Program Steps
Type
OP
X Y M S K H KnX KnY KnM KnS T C D V Z
S
1
* * * * * * * * ***
S
2
* * * * * * * * ***
D
* * * * * ***
ADD, ADDP: 7 steps
DADD, DADDP: 9 steps
Operands:
S
1
: Summand S
2
: Addend D: Sum
Explanations:
1. This instruction adds S
1
and S
2
in BIN format and store the result in D
2. When ADD is used as 16-bit instruction, Z device cannot be adopted; when ADD is used as 32-bit instruction, V
device cannot be adopted.
3. The most significant bit (MSB) is the sign bit of the data. 0 indicates positive and 1 indicates negative. All
calculations is algebraically processed, e.g. 3 + (-9) = -6.
4. Flags:
OX O100
Zero flag M1808 M1968
Borrow flag M1809 M1969
Carry flag M1810 M1970
Flag changes in binary addition
In 16-bit BIN addition,
a) If the operational result = 0, zero flag will be ON.
b) If the operational result < -32,768, borrow flag will be ON.
c) If the operational result > 32,767, carry flag will be ON.
In 32-bit BIN addition,
a) If the operational result = 0, zero flag will be ON.
b) If the operational result < -2,147,483,648, borrow flag will be ON.
c) If the operational result > 2,147,483,647, carry flag will be ON.
Program Example 1:
In 16-bit BIN addition:
When X0 = ON, the content in D0 will plus the content in D10, and the sum will be stored in D20.
X0
DD D0 D10 D20
Program Example 2:
In 32-bit BIN addition:
When X1 = ON, the content in (D31, D30) will plus the content in (D41, D40), and the sum will be stored in (D51,
D50). D30, D40 and D50 are low words; D31, D41 and D51 are high words. .
X

 Loading...
Loading...