74 Section E
Water In The Refrigeration System
Even in very small quantities, water in any refrigeration system can cause the
following problems:
• Ice plugs in capillary tubes.
• Copper plating in compressor.
• Reactions with organic materials in systems.
• Corrosion of metals.
R-134a and Ester oil will aggravate the problem of water in the refrigeration
system. Ester oil may react with water vapor and is hydroscopic (it will absorb
water if it comes in contact with humid air). Water is also more soluble in R-134a
than R-12.
To minimize the water content whenever service work is performed, the
refrigeration system should always be thoroughly evacuated through process tube
adaptors on both the high and low sides of the system. Evacuation must be for a
minimum of 30 minutes to at least a 29.9 inch (500 micron) vacuum.
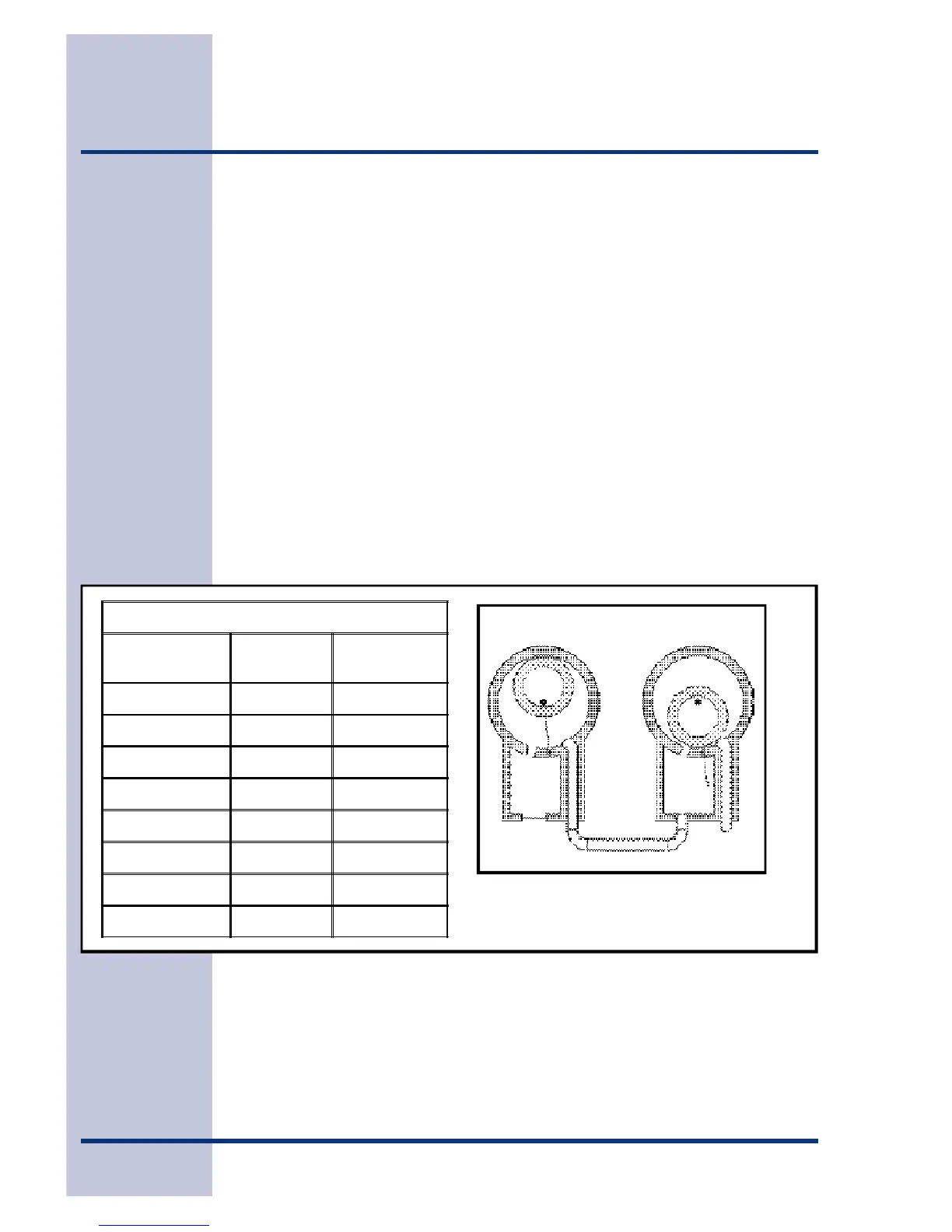
To achieve the required 29.9 inch (500 micron) vacuum, a properly maintained two-
stage vacuum pump in good condition is required. A two stage pump can reach a
deeper vacuum than a single stage because the exhaust from the first pumping
stage is discharged into the second pumping stage. This means the second stage
begins pumping at a lower pressure so a lower ultimate vacuum can be achieved
(See 2-Stage Vacuum Pump, Figure E3).
VACUUM CHART
Vacuum
Inches Hg.
Microns
Boiling Point
of Water °F
28.940 25000 77.9
29.530 10000 52.0
29.832 4600 32.0
29.882 1000 1.0
29.901 500 -11.2
29.915 150 -32.8
29.917 100 -38.2
29.919 50 -49.0
2-Stage Vacuum Pump
Figure E3
 Loading...
Loading...











