13 VoIP Subscriber Gateways
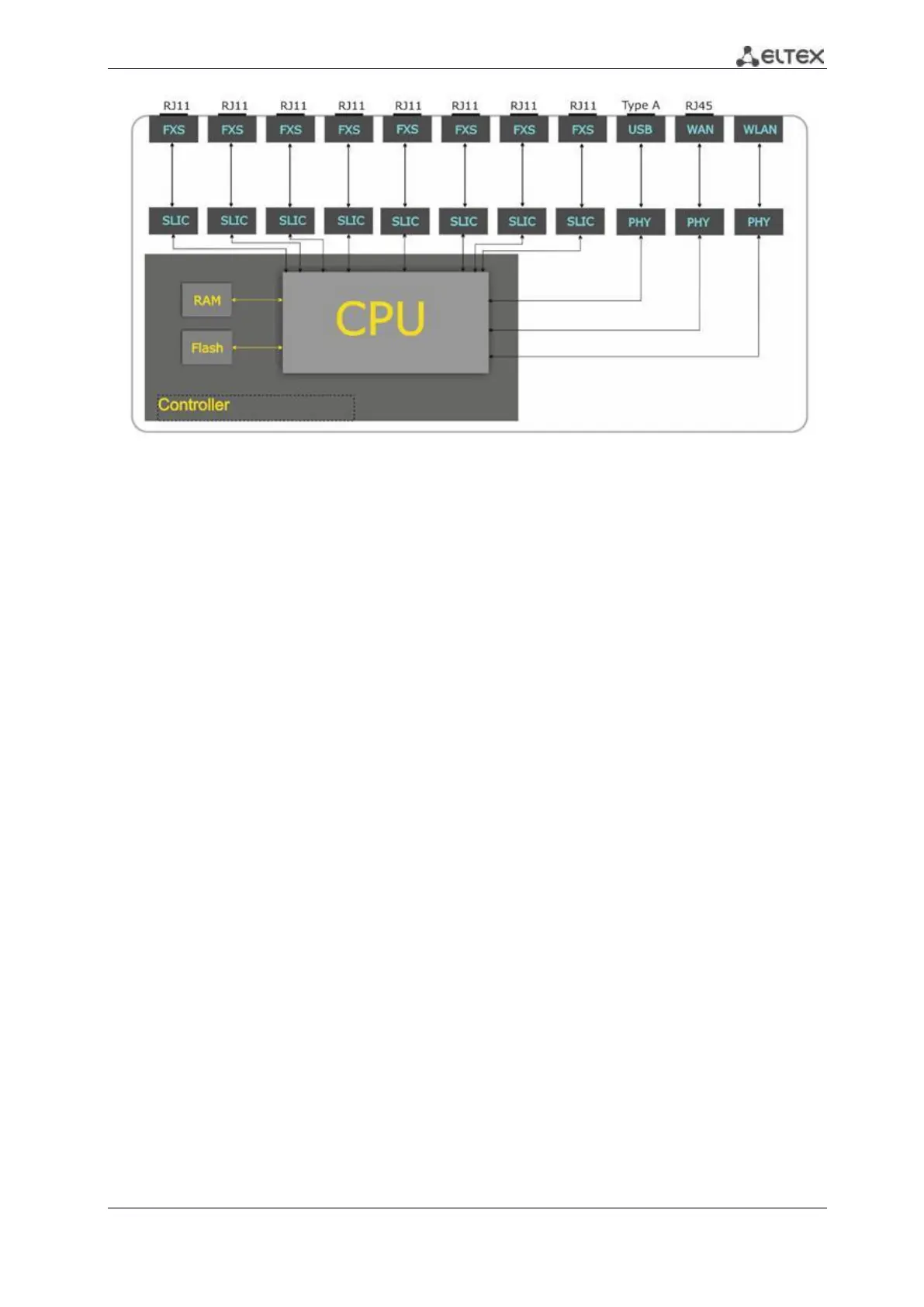
Figure 2 – TAU-8.IP structure diagram
The device may be functionally divided into four blocks:
- Device network features block;
- VoIP block;
- Multicast traffic processing block;
- Control block (Linux operating system).
Device network features block enables IP packet passing and switching according to the device
routing table. Depending on the network interface, this block can process both tagged and untagged
packets. Supports DHCP, PPPoE, PPTP.
VoIP block enables SIP operation for transmission of voice signals through the network that
features packet switching. The subscriber’s voice signal is transferred to the SLIC subscriber unit
module, where it is converted into digital form. The digitized signal is transferred to VoIP block to be
encoded using one of the selected standards and is transferred further in the form of digital packets to
the controller via the intrasystem backbone. In addition to voice signals, digital packets contain control
and interaction signals.
Multicast traffic processing block is designed to process multicast traffic with the aim of VoIP
function support.
Control block based on Linux operating system monitors operation of all the other blocks and
subsystems and manages their interaction.
 Loading...
Loading...