13.2 IP Addressing
The CPUE05 must have a unique IP address that identifies it on the Ethernet network.
The IP Address is assigned using the configuration software, as described in chapter 6.
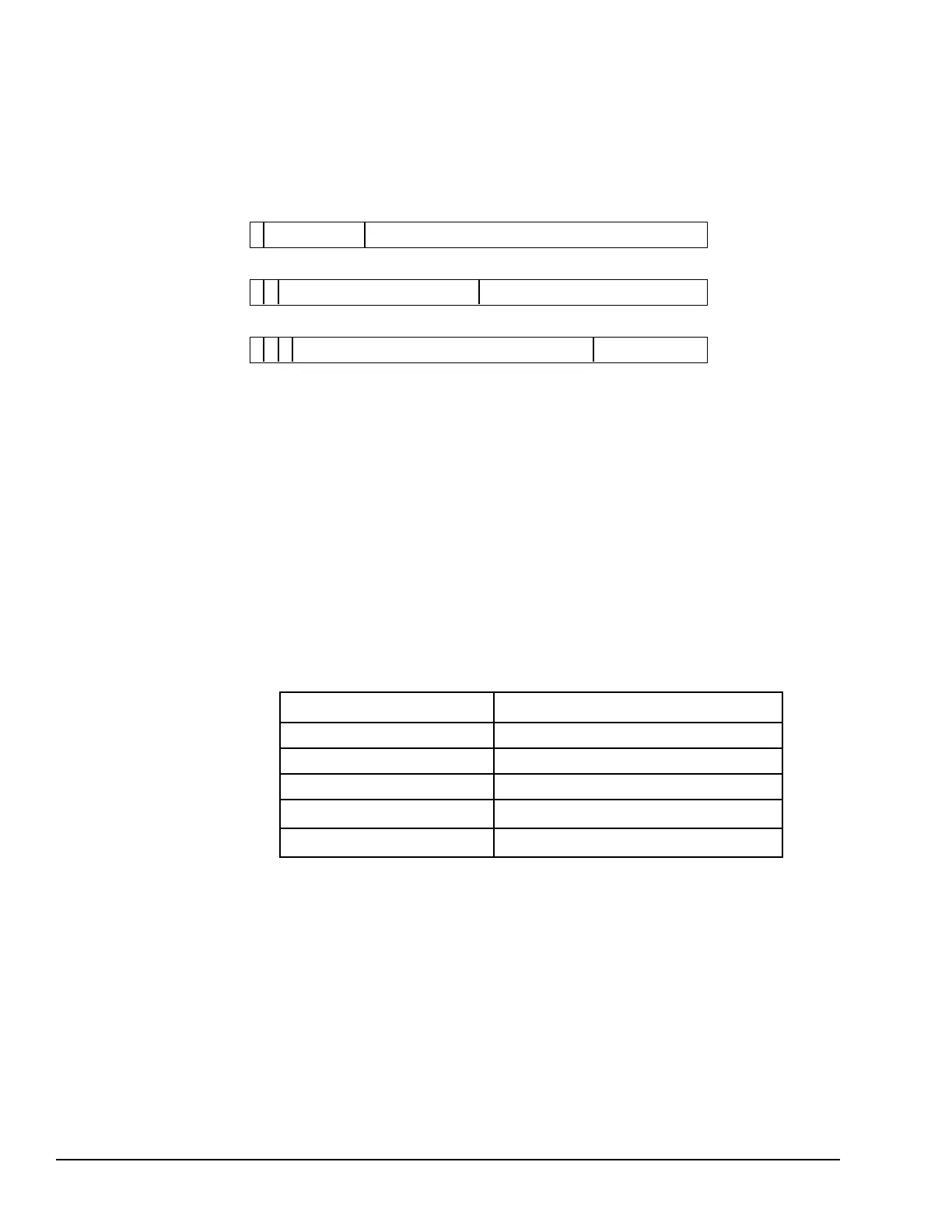
The IP address is 32 bits long and has a netid part and a hostid part. The format of the IP
address depends on the network class:
Each IP address on a network has:
• The same class. Each network is a Class A, Class B or Class C network. A Class A
network can support 16,777,214 hosts, Class B: 65,534 hosts, and Class C: 254 hosts.
• The same netid, which is generally assigned by the Internet authorities.
• A different hostid, giving it a unique IP address. The hostid is generally assigned by
your local network administrator.
IP addresses are written in “dotted-decimal” format as four decimal integers (0-255)
separated by periods. Each integer represents one byte of the IP address. For example, the
32-bit IP address
00001010 00000000 00000000 00000001
is written as
10.0.0.1
The class of an IP address is indicated by the first decimal integer:
Range of first integer
Class
0 - 127 A
128 - 191 B
192 - 223 C
224-239
D (Reserved for Multicast Use)
240 - 255
E (Reserved for Experimental Use)
RFC 1918 reserves IP addresses in the following ranges for private networks.
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 (Class A)
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 (Class B)
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 (Class C)
x.y.z.1 is reserved for gateways.
x.y.z.255 is reserved for subnet broadcast
252 GFK-1503E VersaMax PLC User Manual
For public disclosure

 Loading...
Loading...











