Gaseous Fuel Systems
24 Installation Guidelines for Spark-Ignited Stationary Emergency Generators
5.5.2— Sizing LP Tanks for Vapor Withdrawal
The manufacturer recommends that the installer consult with a reputable LP supplier when sizing LP storage tanks and
their associated pressure regulators and piping systems. Many factors come into play when working with LP in either
its vapor or liquid form.
The operation of an LP-Vapor system depends on the vaporization of the liquid stored in the tanks. As the vapor above
the liquid level is withdrawn the pressure in the tank decreases. This change in pressure causes the liquid to “boil” in
order to restore the pressure equilibrium. The liquid in the tank uses the temperature difference between its boiling
point (-44º F for Propane) and the outside temperature to extract enough heat to enable vaporization (boiling). Only the
liquid in contact with the tank wall absorbs heat from the outside. The area of the tank where the liquid is in contact with
the tank wall is referred to as the “wetted surface area”. Cold weather results in a reduced tank vaporization capacity
because there is less heat energy available to boil off the liquid into vapor. The wetted surface area of the tank must be
large enough to sustain the vaporization rate required by the generator. Depending on the relative humidity and the
ambient temperature, frosting can occur on the outside of the tank when it is in use. This condition further inhibits the
heat transfer required to sustain vaporization.
Several factors affect the rate of vaporization for LP tanks:
• The size of the tank (wetted surface area). As the wetted surface area decreases the rate of vaporization
decreases.
• The lowest liquid level the tank will be allowed to reach (relates directly to the wetted surface area). The typical
maximum fill level for LP tanks is 80%, and the lowest recommended operating level is 20%. This provides a vol-
ume equivalent to 60% of the tank capacity to be used to calculate run time. Most tank sizing tables provide the
vaporization rate of the tank at the lowest allowable level (20%); any tank level above this point will have a higher
vaporization rate.
• The lowest normal temperature expected. Typical tank tables provide vaporization rates at 40º F, 20º F, and 0º F.
For temperatures below 0º F consult a reputable LP dealer for options.
• The mean relative humidity.
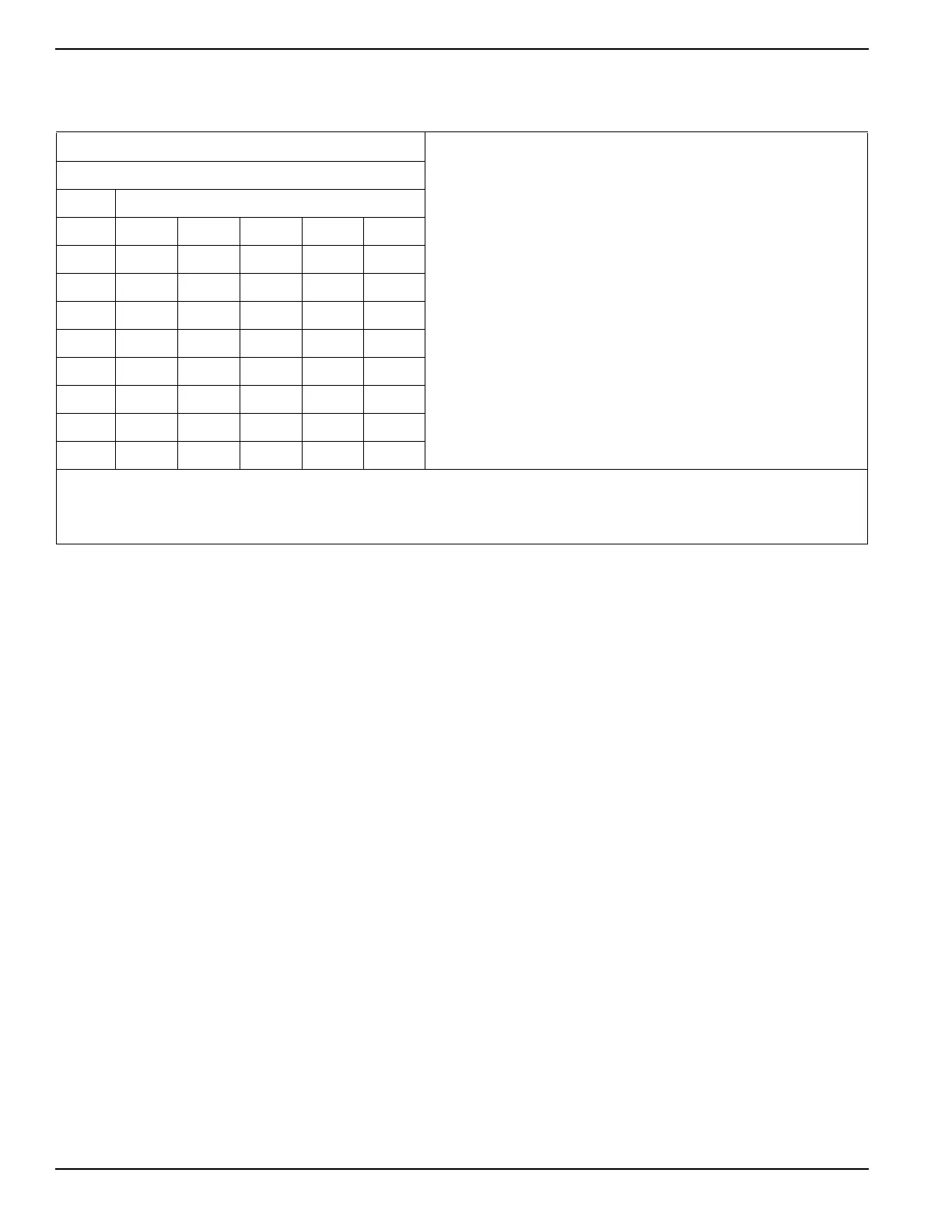
Table 5-3. Fuel Pipe Sizing for Natural Gas (NG)
LP Vapor (LPV) 11" to 14" of Water Column
LP
LPG: 8.55 ft 3/lb., 4.24 lbs./gal., 2500 btu/ft
3
LPG: 36.3 ft3 = 1 gal.
Pressure
1 inch mercury = 13.61 inches water column
1 inch Water Column = 0.036 psi
11–14 inches water column = 0.396 psi to 0.50 psi
Note:
• Pipe sizing is based on 0.5" H
2
O pressure drop.
• Sizing includes a nominal number of elbows and tees.
• Please verify adequate service and meter sizing.
• Tables based on black pipe.
Table values are maximum pipe run in feet.
Pipe Size (inches)
kW 1 in 1.25 in 1.5 in 2 in 2.5 in
22 85 365 — — —
25 60 275 605 — —
27 55 260 575 — —
30 40 195 435 — —
35-36 20 125 290 1030 —
45 — 82 195 725 —
48 — 70 165 620 —
60 — 45 115 445 1095
Note: Size the fuel pipe to the sizing charts or to local codes. When installing other than Sch. 40 black pipe, please refer to the manufactures
sizing charts.
The liquid-cooled generator is not a constant flow appliance, the fuel pipe was sized large enough to supply at least 125% of the generator BTU/hr
rating.
 Loading...
Loading...