Theory
of
Operation
2-9
Processor
Stack
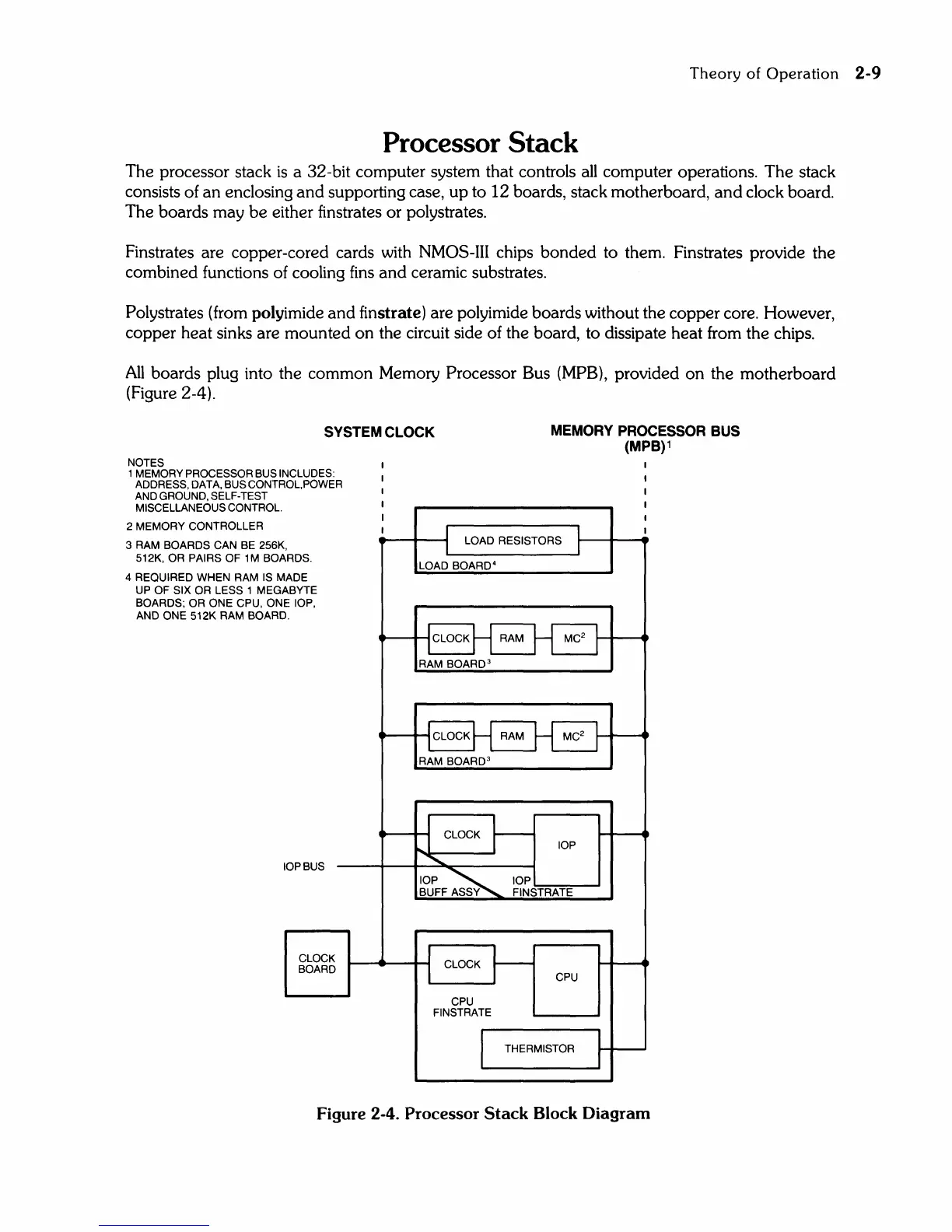
The processor stack
is
a 32-bit computer system that controls
all
computer operations. The stack
consists of an enclosing
and
supporting case, up to 12 boards, stack motherboard,
and
clock board.
The boards may
be
either finstrates or polystrates.
Finstrates are copper-cored cards with
NMOS-III chips bonded to them. Finstrates provide the
combined functions of cooling
fins
and
ceramic substrates.
Polystrates (from polyimide and finstrate) are polyimide boards without the copper core. However,
copper heat sinks are mounted on the circuit side of the board, to dissipate heat from the chips.
All
boards plug into the common Memory Processor Bus
(MPB),
provided on the motherboard
(Figure 2-4).
SYSTEM
CLOCK
MEMORY PROCESSOR BUS
(MPB)1
NOTES
1 MEMORY PROCESSOR BUS INCLUDES:
ADDRESS,
DATA, BUS CONTROL,POWER
AND GROUND, SELF-TEST
MISCELLANEOUS CONTROL
2 MEMORY CONTROLLER
3 RAM BOARDS CAN BE 256K
512K,
OR PAIRS OF 1M BOA RDS.
ADE
4
REQUIRED WHEN RAM IS M
UP
OF SIX OR LESS 1 MEG
BOARDS; OR ONE CPU, ON
AND ONE 512K RAM BOARD
ABYTE
E
lOP,
lOP BUS
CLOCK
BOARD
I
I
I
J I
I
I
LOAD RESISTORS
I
LOAD BOARD
4
lCLOCK
RAM
MC
2
RAM BOARD
3
~.CLOCK
RAM
MC
2
RAM BOARD
3
I
CLOCK
~
I
lOP
"'-
lOP
~
lOP
BUFF ASSY FINSTRATE
: CLOCK
~
CPU
CPU
FINSTRATE
I
THERMISTOR
Figure 2-4. Processor
Stack
Block
Diagram
 Loading...
Loading...