2.18
STEP 5: DETERMINE FEED RATE SETTING, FR (in/min) (mm/min).
# MATERIALS OPTIMUM BLADE SPEED
(ft/min) (m/min)
1 5” (125mm) Diameter Solid Carbon Steel 225 70
2 12” (300mm) I-Beam 290 90
3 4” x 4” (100mm x 100mm) Rect. Tube 1/4” (6mm) Wall 350 110
4 4” (100mm) 400 Stainless Steel 140 45
5 2” x 2” (50mm x 50mm) Rect. Tube 1/4” (6mm) Wall
Bundle 5” x 5” pcs. 10” x 10” (500mm x 500mm) 325 100
6 3” x 3” (75mm x 75mm) Inconel 60 20
The following table gives examples of the optimum blade speeds for dierent materials.
Materials and Blade Speed
FEED RATE is the vertical speed at which the blade descends through the work-piece.
The FEED RATE Knob controls FEED RATE of the blade descent. The FEED RATE should be adjusted only in one
direction (from “O” to required value). If you go too far, go back to “O” and come back up. To set FEED RATE for
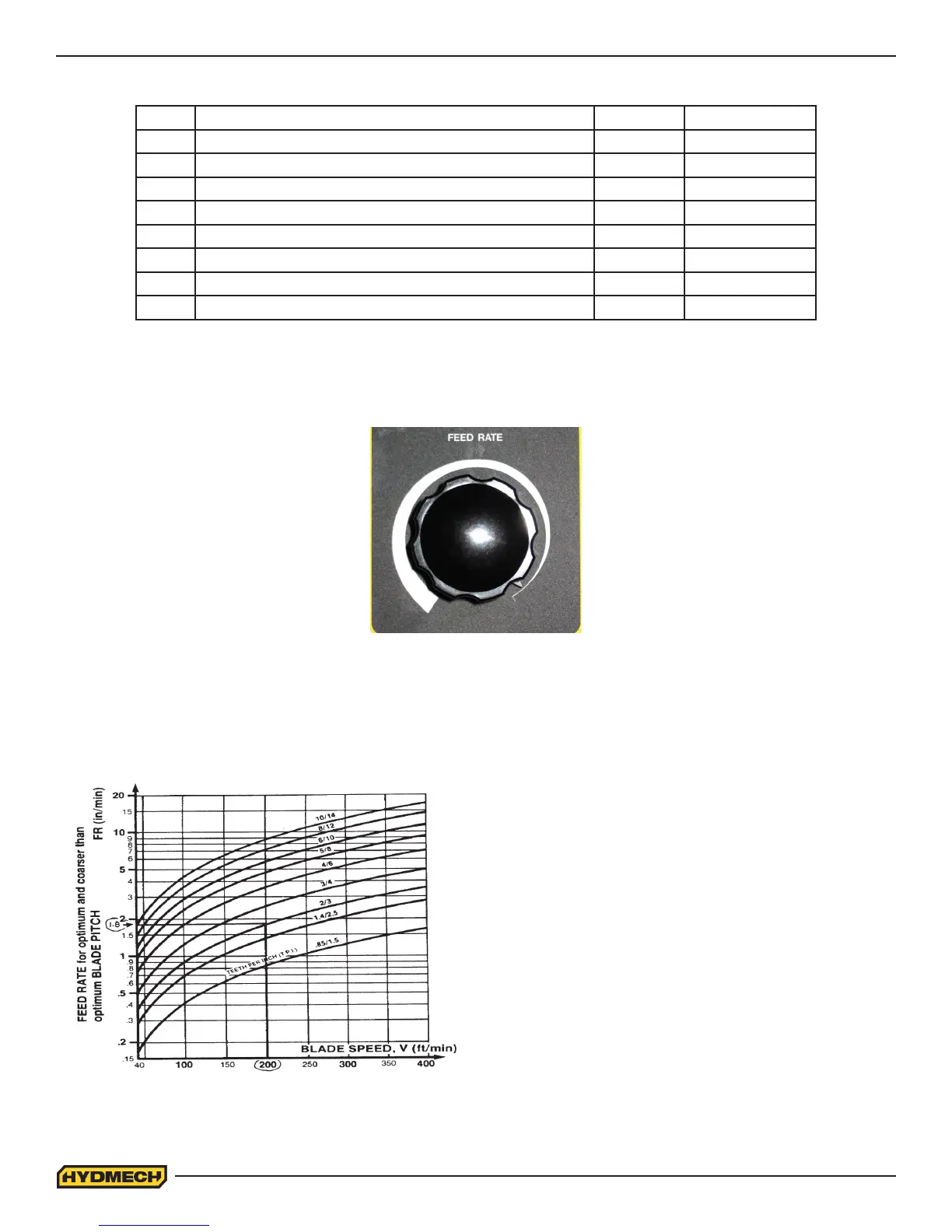
particular cutting situations use the graph below, which represents the relationship
between FEED RATE, blade speed and blade pitch.
Example #1: It is known from Step 3 that optimum blade
pitch is 2/3, and from Step 4 that blade speed is 200 ft/min
(60mm/min). From the Graph on the left, the FEED RATE is
determined in the following way:
1. On the horizontal axis (blade speed axis), nd
200 ft/min (60mm/min).
2. Find the point where a ver tical line from 200 ft/min
(60mm/min) would intersect the 2/3 blade pitch curve
3. From this intersection point run horizontally left to the
ver tical (FEED RATE) axis, to ar rive at 1.8 in/min
(45mm/min) FEED RATE. Thus 1.8 in/min (45mm/min)
is the FEED RATE for cutting 8” (200mm) diameter 1045
Carbon Steel when the optimum 2/3 pitch blade is used.
Feed Rate Calculation

 Loading...
Loading...