Goodrive18 series two-in-one VFD Communication
-114-
In a character frame, only the data bits carry information. The start bit, check bit, and stop bit
are used to facilitate the transmission of the data bits to the destination device. In practical
applications, you must set the data bits, parity check bits, and stop bits consistently.
In RTU mode, a new frame always must be preceded by a time gap with a minimum length of
3.5 bytes. On a network where the transmission rate is calculated based on the baud rate, the
transmission time of 3.5 bytes can be easily obtained. After the idle time ends, the data
domains are sent in the following sequence: slave address, operation command code, data,
and CRC check character. Each byte sent in each domain includes 2 hexadecimal characters
(0–9, A–F). The network devices always monitor the communication bus. After receiving the
first domain (address information), each network device identifies the byte. After the last byte
is sent, a similar transmission interval (with a minimum length of 3.5 bytes) is used to indicate
that the frame transmission ends. Then, the transmission of a new frame starts.
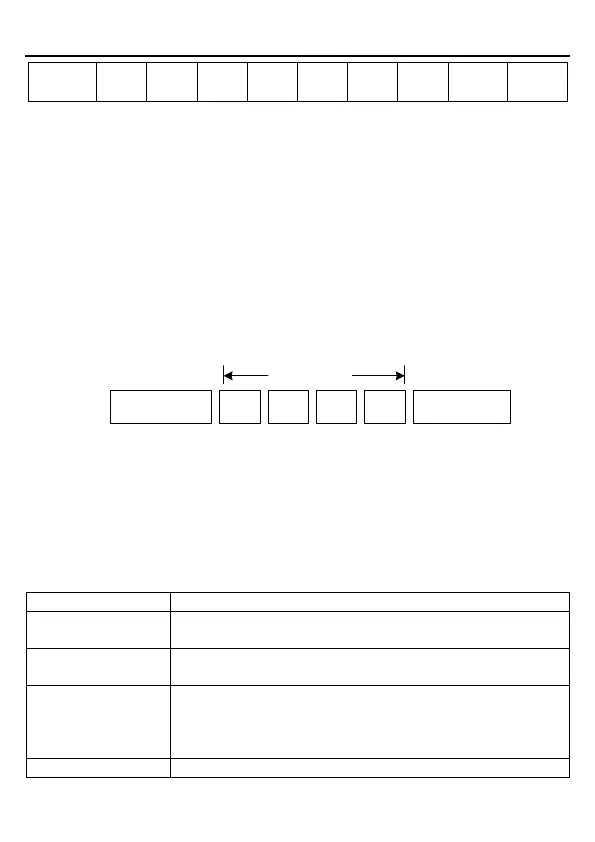
RTU data frame format
Modbus packet
Start with a time gap
(with a min. length of 3.5
bytes)
Slave
address
Function
code
Data Check
End with a time gap
(with a min. length of
3.5 bytes)
The information of a frame must be sent in a continuous data flow. If there is an interval
greater than the transmission time of 1.5 bytes before the transmission of the entire frame is
complete, the receiving device deletes the incomplete information, and mistakes the
subsequent byte for the address domain of a new frame. Similarly, if the transmission interval
between two frames is shorter than the transmission time of 3.5 bytes, the receiving device
mistakes it for the data of the last frame. The CRC check value is incorrect due to the disorder
of the frames, and thus a communication fault occurs.
The following table describes the standard structure of an RTU frame.
T1-T2-T3-T4 (time gap with a min. length of 3.5 bytes)
ADDR (slave address
domain)
Communication address: 0–247 (decimal system) (0 is the broadcast
address)
03H: read slave parameters
06H: write slave parameters
DATA (N-1)
...
DATA (0)
(data domain)
Data of 2×N bytes, main content of the communication as well as the
core of data exchanging
Detection value: CRC (16 bits)

 Loading...
Loading...